أنبوب PVC مقابل قناة PVC، الدليل الشامل للمقارنة (2025)
1 المقدمة
كثيراً ما يُخلط بين أنابيب PVC وقنوات PVC نظرًا لتشابه مظهرها، إلا أنهما يخدمان أغراضًا مختلفة تمامًا في البناء. تُستخدم أنابيب PVC بشكل أساسي في أنظمة نقل مياه الشرب والصرف الصحي والصرف الصحي والتهوية (DWV)، بالإضافة إلى الري.
على النقيض من ذلك، تم تصميم قنوات PVC لحماية الأسلاك الكهربائية في البيئات السكنية والتجارية والصناعية.

Their differences go beyond just application—factors such as material composition, structural design, color coding, fittings, adhesives, and regulatory standards set them apart.
In this post, we’ll break down these key differences one by one, explain why distinguish these pipe types important.
2. تركيب المواد والتصنيع بين أنابيب PVC وقنوات PVC
2.1 What Is PVC Pipe and Conduit Made Of?
In the world of PVC pipes and electrical conduits, everything starts with the same basic ingredient: PVC resin (Polyvinyl chloride resin).
Think of it as the “building block” of the plastic family. With different recipes and processing methods, this material can be shaped into products for a wide range of uses.
⚠️But even though they’re all called PVC pipe or conduit, they’re not made the same way.
The PVC used for water pipes and the PVC used for electrical conduits differ a lot in terms of resin grade and molecular structure.
🍞🥟It’s a bit like baking—bread and dumpling wrappers both use flour, but the recipe and purpose are totally different.
To keep everything consistent and safe, there’s an official guideline called ASTM D1784.

🔬 This standard tells manufacturers what kind of PVC or CPVC (that’s Chlorinated PVC, which can handle higher heat) they should use for different applications—like water pipes, fittings, or electrical conduits.
These materials are chosen for their chemical resistance, heat tolerance, and durability. That’s why you’ll find them in everything from home plumbing systems to industrial equipment.
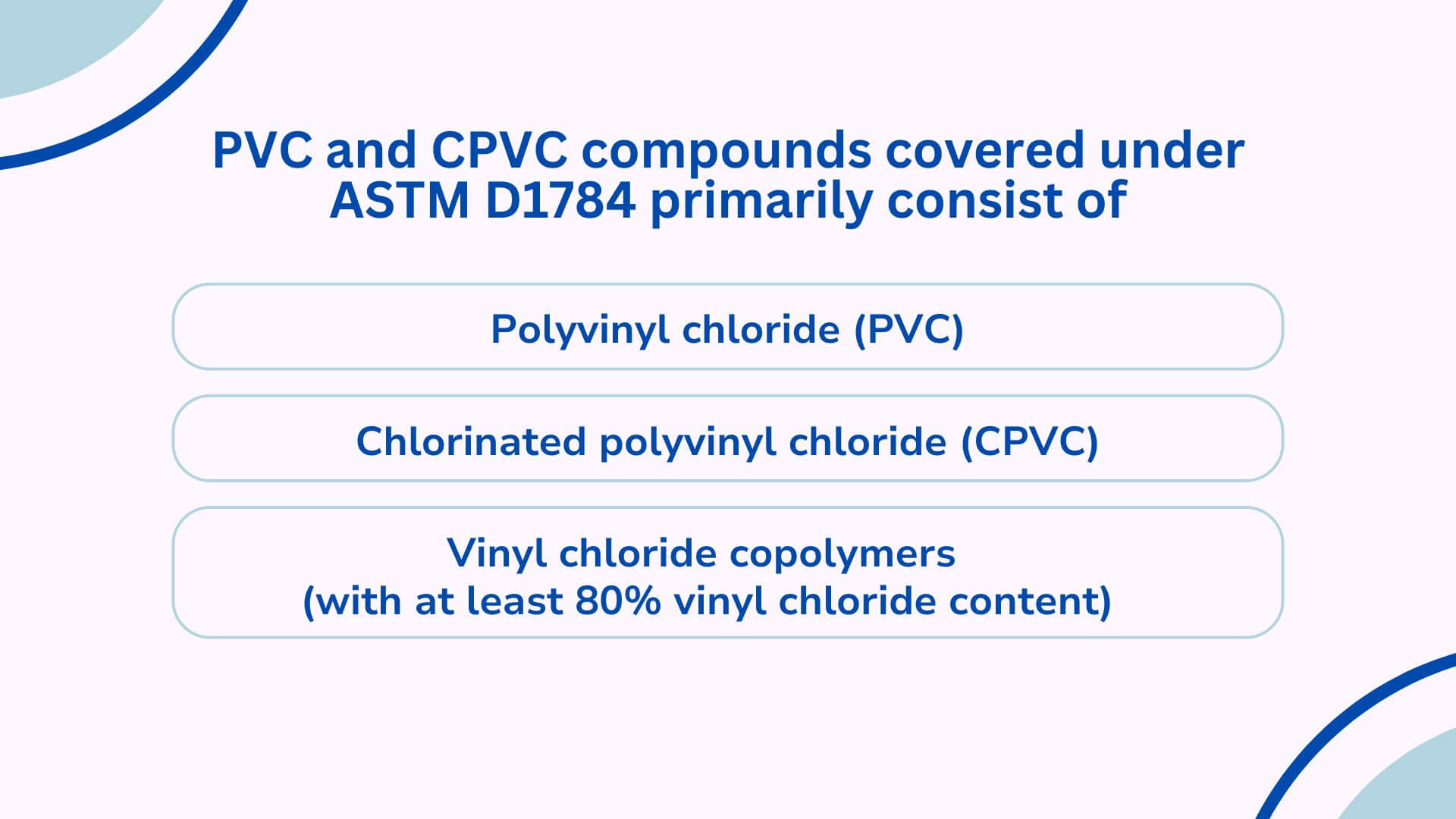
🧪 What’s Inside the PVC Recipe?
PVC and CPVC compounds listed in ASTM D1784 usually include:
- بولي فينيل كلوريد (PVC)
- كلوريد البولي فينيل المكلور (CPVC)
- كوبوليمرات كلوريد الفينيل (مع محتوى كلوريد الفينيل 80% على الأقل)
🧵 What Material About PVC Pipes?
PVC pipes are made from high-quality plastic that meets safety standards. Before they go out into the field, they must pass two big strength tests:
- Short-term strength – Can it handle sudden pressure?
- Long-term strength – Will it last for years without cracking or leaking?
And therefore, some common pipe compounds include:
- بولي كلوريد الفينيل 12454 - يوفر قوة عالية ومقاومة للصدمات.
- بولي كلوريد الفينيل 14333 - يوفر متانة وأداءً معززين.
And if pipes are used for drinking water, they also need to meet NSF/ANSI 14 standards and be marked with a label that shows they passed testing. If they’re used for reclaimed water, they also need special markings to show that clearly.
⚡ What Material About Conduits?
PVC electrical conduits have their own rules. They’re made from virgin (pure) PVC compounds, also under ASTM D1784. Some common grades include:
- 12254 أو 121643 - يتطلب قوة شد لا تقل عن 4000 رطل لكل بوصة مربعة (28 ميجا باسكال).
- 12264 – Stiffer, Requires a minimum tensile modulus of 500,000 psi, providing enhanced rigidity.
- Fittings (like elbows or junctions) are also made with tested materials such as: 12234 or 13343
🔍Some of the classification numbers like 12254 might seem a bit confusing at first, so we’ll give a simple explanation here.
😊 If you’r curious, feel free to read on.
➡️If not, no worries — you can skip ahead to the next section, where we talk about the different additives used in PVC pipes and conduits.
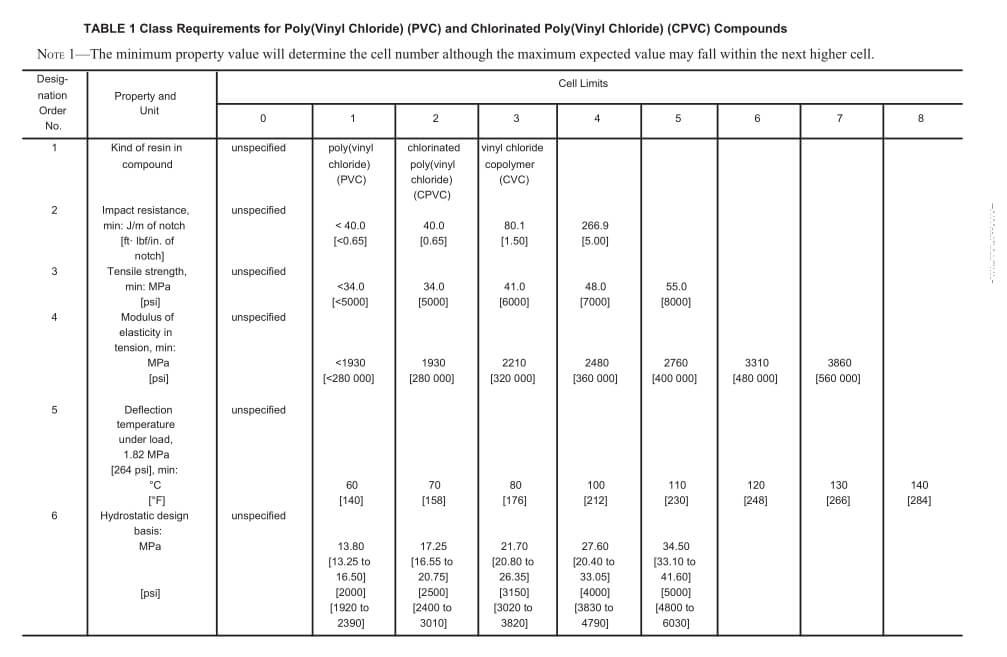
📝What Do Those Numbers Mean?
Those codes—like 12454 or 12264—might seem random, but they’re actually a smart classification system. Each number tells you something about the material’s performance. Think of it like a scorecard that rates things like:
- مقاومة التأثير (القدرة على تحمل القوة دون الكسر)
- قوة الشد (مقاومة قوى السحب)
- معامل المرونة (الصلابة والمرونة)
- درجة حرارة الانحراف تحت الحمل (مقاومة الحرارة)
- أساس التصميم الهيدروستاتيكي (تحمل الضغط بمرور الوقت)
على سبيل المثال، مركب PVC مع التصنيف 12454 can be broken down as follows, according to the table above:
- 1:نوع الراتنج الأساسي – بولي فينيل كلوريد (PVC)
- 2: مقاومة الصدمات - مستوى متوسط (40 قدمًا-رطل/بوصة أو 0.65 جول/متر)
- 4:قوة الشد - الحد الأدنى 7000 رطل لكل بوصة مربعة (48 ميجا باسكال)
- 5:معامل المرونة - الحد الأدنى 400000 رطل لكل بوصة مربعة (2760 ميجا باسكال)
- 4: درجة حرارة الانحراف - 100 درجة مئوية (212 درجة فهرنهايت)
So, once you understand the code, you can quickly compare different PVC materials to find the best one for your project.
💡Even though ASTM D1784 gives us a solid guide, choosing the right material still depends on your specific needs—like whether the pipe is underground, exposed to sunlight, carrying drinking water, or shielding electric wires. Always check with your supplier to make sure the material matches the job.
2.2 Key Additives: What Makes PVC Pipes and Conduits Different
According to ASTM D 1784, in addition to the PVC raw materials we have mentioned above, there will be some compounding ingredients consist of lubricants, stabilizers, non-poly(vinylchloride) resin modifiers, pigments, and inorganic fillers to produce the PVC pipe and PVC conduit.
And in this part, we call additives.
👨🍳Think of baking a cake. The main ingredient (PVC resin) is like the flour.
But to get the texture, color, and flavor you want, you need to add things like sugar, eggs, butter—these are like additives in PVC.

These additives determine strength, flexibility, UV resistance, and fire-retardant capabilities of PVC pipe and conduit.
So, the different additives make differences between PVC pipe and PVC conduit.
🧪Additives at a Glance
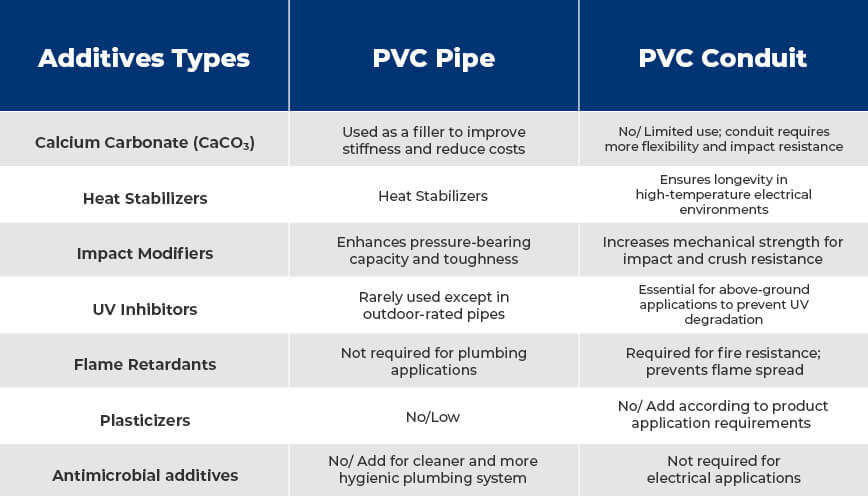

☀️ Role of UV Inhibitors
يعد ثاني أكسيد التيتانيوم (TiO₂) المثبت الأساسي للأشعة فوق البنفسجية، ويعمل كحاجز وقائي لمنع التحلل الضوئي.
أنبوب PVC, especially potable water and DWV (Drain, Waste, Vent) applications, is usually buried or installed indoors, reducing the need for UV inhibitors.
قد تحتوي بعض أنابيب PVC المقدرة للضغط والمستخدمة في الري الخارجي أو شبكات المياه الرئيسية على مستويات منخفضة من مثبتات الأشعة فوق البنفسجية، ولكنها ليست واسعة النطاق مثل تلك الموجودة في الأنابيب الكهربائية.
قناة بي في سي requires enhanced UV resistance especiallyinstalled above ground, where prolonged sun exposure can cause embrittlement and surface degradation.
🧯 Role of Flame Retardancy
يتم عادةً إضافة ثلاثي أكسيد الأنتيمون (Sb₂O₃) والمركبات الهالوجينية كمثبطات للحريق لمنع انتشار اللهب في الأنابيب الكهربائية.
PVC Pipe is not required to have flame retardants because it is designed only for fluid transmission.
قناة بي في سي is required by the National Electrical Code and UL or other national electrical safety requirements to be flame-resistant and self-extinguishing.
من المتطلبات الشهيرة تصنيف UL 94 V-0 الذي يضمن أن أنابيب PVC تنطفئ ذاتيًا في غضون 10 ثوانٍ بعد التعرض للهب.

- الاتحاد الأوروبي:يحظر استخدام بعض الفثالات في تطبيقات ملامسة الطعام والماء بموجب REACH (اللائحة EC 1907/2006).
- الولايات المتحدة (وكالة حماية البيئة وإدارة الغذاء والدواء):ينظم الملدنات في أنابيب مياه الشرب، ويتطلب الامتثال لمعايير NSF/ANSI 61.
- الصين:يحظر استخدام الفثالات المحددة في تطبيقات الأغذية ومياه الشرب.
- اليابان:يحظر استخدام DEHP والمواد الملينة المماثلة في أنظمة مياه الشرب.
🧼 Role of Antimicrobial Additives
Antimicrobial additives are chemical compounds incorporated into PVC materials to inhibit the growth of bacteria, mold, fungi, and algae.
These additives help maintain hygienic conditions and prevent biofilm formation.

Common types such as Silver ions (Ag⁺), Zinc-based compounds, Triclosan alternatives.
أنبوب PVC: Prevents microbial-induced degradation in sewage and drainage pipes to extend pipe lifespan. And ensures potable water remains safe for human consumption.
PVC Conduit: Doesn’t need these—there’s no water, and its job is to protect wires, not stop germs.
3. الاختلافات في التصميم الهيكلي بين أنابيب PVC وقنوات PVC
بعد أن استكشفنا الاختلافات في المواد الخام والمواد المضافة المستخدمة في أنابيب وموصلات PVC، من المهم بنفس القدر دراسة اختلافاتها الهيكلية والتصميمية. قد يبدو المنتجان متشابهين للوهلة الأولى، إلا أن سمك جدارهما ومتانتهما وتصنيفات ضغطهما وترميز ألوانهما مصممة خصيصًا لتطبيقاتهما المقصودة.
في الأقسام التالية، سنقوم بتقسيم هذه التمييزات البنيوية الرئيسية لمساعدتك على فهم وظائفها واستخدامها الصحيح بشكل أفضل.
3.1 سمك الجدار وقوته
One of the most fundamental differences between PVC pipes and PVC conduits lies in their wall thickness and structural strength.
These variations are driven by their intended applications.
PVC pipes must withstand internal water pressure, while PVC conduits are designed to protect electrical wiring without carrying fluids.
So tests they should pass are different, and we will make the details in the following.
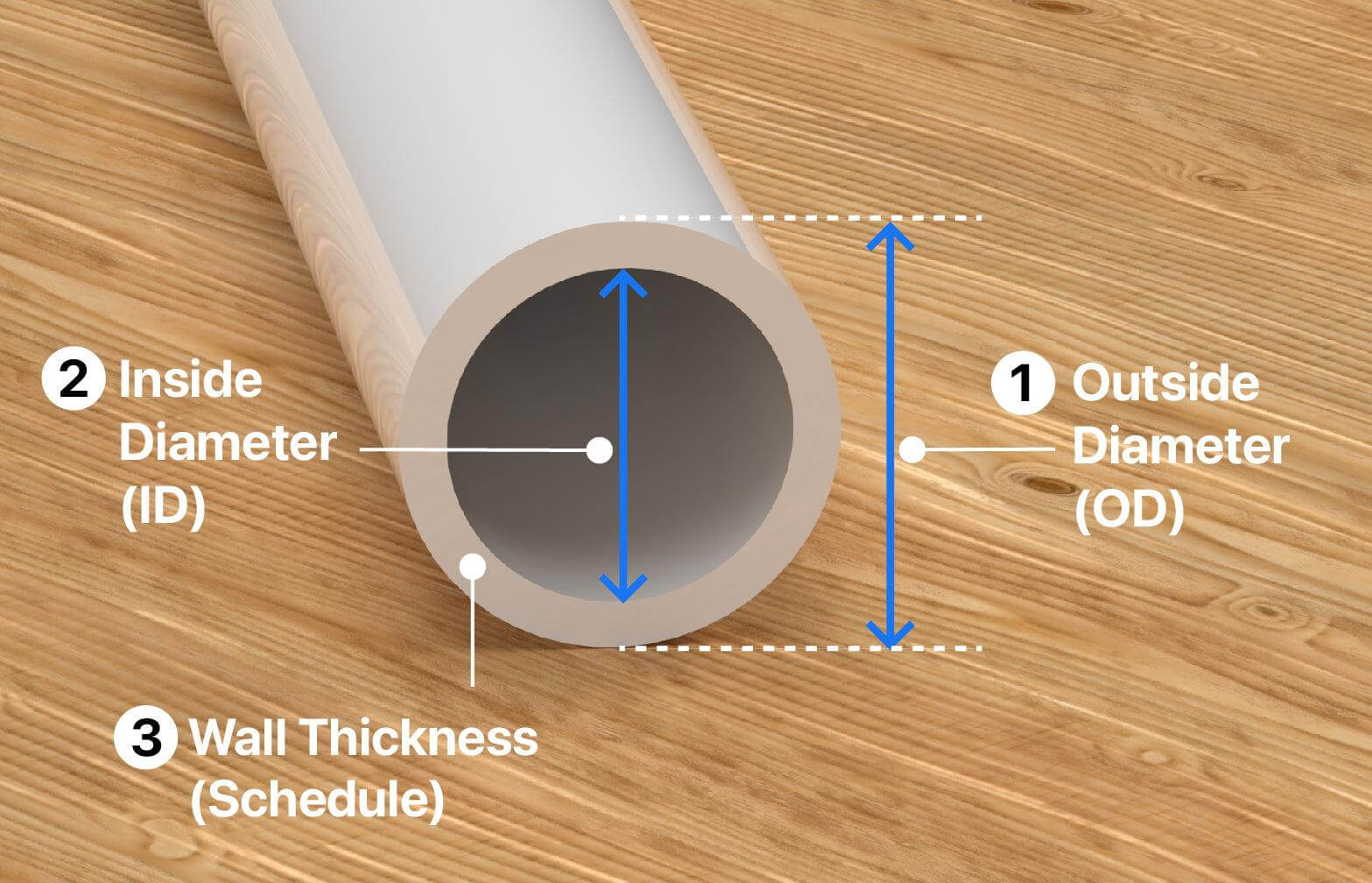

- S (إجهاد التصميم الهيدروستاتيكي): يتم قياسها بوحدة psi (أو MPa).
- P (تصنيف الضغط):يتم قياسها أيضًا بالرطل/بوصة مربعة (أو ميجا باسكال).
- D₀ (متوسط القطر الخارجي):يتم قياسه بالبوصات أو المليمترات، وهو القطر الخارجي للأنبوب، والذي يؤثر بشكل مباشر على قدرته على الضغط.
- t (الحد الأدنى لسمك الجدار):يتم قياسه بالبوصات أو المليمترات، وهو يمثل أرق قسم مسموح به من جدار الأنبوب، مما يضمن سلامة الهيكل تحت الضغط.

🔧 How Pipes Are Tested
Like crash-testing a car before it’s sold, PVC pipes go through several tough tests to make sure they’ll last:
- اختبار الضغط المستمر:Checks if the pipe can hold high water pressure for long periods.
- اختبار الانحدار المتسارع:يتنبأ هذا الاختبار بمقاومة ضغط الماء على المدى الطويل وعمر الخدمة لأنبوب PVC.
- اختبار ضغط الانفجار:يحدد أقصى ضغط داخلي يمكن أن يتحمله الأنبوب قبل الانفجار.
- اختبار التسطيح: Evaluates the mechanical strength and flexibility of the PVC pipe under external compression.
This test ensures the pipe can withstand soil pressure, heavy loads, and physical impacts during installation and service.
⚡PVC Conduit: Built to Protect Wires
Now, imagine a plastic straw wrapped around spaghetti wires—that’s similar to how PVC conduit works.
It doesn’t need to hold pressure inside, but it does need to protect what’s inside from bumps, weight, or accidents on the outside.
When selecting PVC electrical conduit, there are some several key factors that the buyer maybe focus on.
Critical aspects include wall thickness, outer and inner diameter, wall thickness as well as wire fill capacity.
- القطر الخارجي (OD):يحدد العرض الإجمالي للقناة، مما يؤثر على توافق التثبيت مع التركيبات والدعامات.
- القطر الداخلي (ID):يُحدد عدد الأسلاك الكهربائية التي يُمكن تمريرها بأمان داخل الأنبوب. يجب أن تتوافق المساحة المتوفرة داخل الأنبوب مع لوائح ملء الأسلاك.
- سمك الجدار: يؤثر على القوة الميكانيكية، ومقاومة الصدمات، والمتانة البيئية. كما أنه أساسي لحسابات المساحة الداخلية.
- سعة تعبئة الأسلاك:يشير إلى الحد الأقصى لعدد وحجم الموصلات الكهربائية التي يمكن تركيبها بأمان داخل قناة دون التسبب في ارتفاع درجة الحرارة أو المقاومة المفرطة.

📏 إرشادات NEC لملء الأنابيب
توفر NEC إرشادات محددة لنسبة ملء الأسلاك القصوى استنادًا إلى عدد الموصلات داخل القناة:
- سلك واحد:يمكن ملء ما يصل إلى 53% من المساحة الداخلية للقناة.
- سلكين:حتى 31% من المساحة الداخلية.
- 3 أسلاك أو أكثر:يجب ألا يتجاوز إجمالي الملء 40% من المساحة الداخلية.
تساعد جداول ملء الأنابيب الكهربائيين على اختيار حجم الأنابيب المناسب لعدد معين من الموصلات.
🛠️ Strength Tests for Conduit
Just like a helmet needs to pass safety tests before hitting the market, conduits are tested to ensure they protect wiring properly:

- مقاومة التأثير:يجب أن يتحمل مجرى PVC التأثير الميكانيكي وفقًا لـ UL 651، مما يضمن عدم تشققه أو كسره في ظل ظروف التركيب العادية.
- قوة الشد:يقيس هذا مقدار قوة السحب التي يمكن أن يتحملها الأنبوب قبل الانكسار.
- مقاومة السحق: يشير إلى مقدار الضغط الخارجي (على سبيل المثال، من التربة أو الخرسانة أو الأحمال الثقيلة) الذي يمكن أن يتحمله الأنبوب دون تشوه.
- اختبار الانحراف:يقوم هذا بتقييم مدى قدرة الأنبوب على الانحناء تحت الضغط قبل حدوث تشوه دائم.
3.2 فهم الجدول الزمني وتصنيفات الضغط في أنابيب PVC وقنوات PVC
In our earlier discussion on PVC water pipes, we introduced the concept of pressure rating, which is crucial for determining a pipe’s ability to withstand internal water pressure.
Think of it like a balloon — if you blow too much air into it, it will burst. Similarly, a water pipe needs to handle a certain amount of internal pressure.
If the pressure inside exceeds the pipe’s strength, just like an overinflated balloon, the pipe can fail.
This pressure rating is an essential factor for water pipes, but it’s less relevant for PVC conduits, since they’re not designed to carry fluids under pressure.
🟢 What Does “Schedule” Mean in PVC Pipe and PVC Conduit?
When looking for both water pipes and electrical conduits, you’ll often come across the term “Schedule” or “SCH.”

The Schedule (Sch) classification refers to the wall thickness of a PVC pipe or conduit relative to its nominal size.
It is a standardized system primarily used in North America, with common classifications including الجدول الزمني 40 (الجدول 40) و الجدول 80 (الجدول 80).
The higher the Schedule number, the thicker the pipe wall.
For example, Sch 80 pipes have thicker walls than Sch 40 pipes of the same nominal size, making them stronger and more resistant to pressure.
🔵 SDR في أنابيب PVC
While Schedule is one way to describe pipe strength, there’s another system used mostly for water pipes: SDR, or Standard Dimension Ratio.
💡 Note: SDR is used for PVC pipes, not for conduits.
SDR (Standard Dimension Ratio) is a key parameter used to define the relationship between a PVC pipe’s outer diameter (OD) and wall thickness.
It is an essential factor in determining the pressure rating of the pipe.
SDR pipes maintain a consistent OD-to-wall thickness ratio, meaning that wall thickness increases proportionally with pipe size while maintaining the same pressure rating.
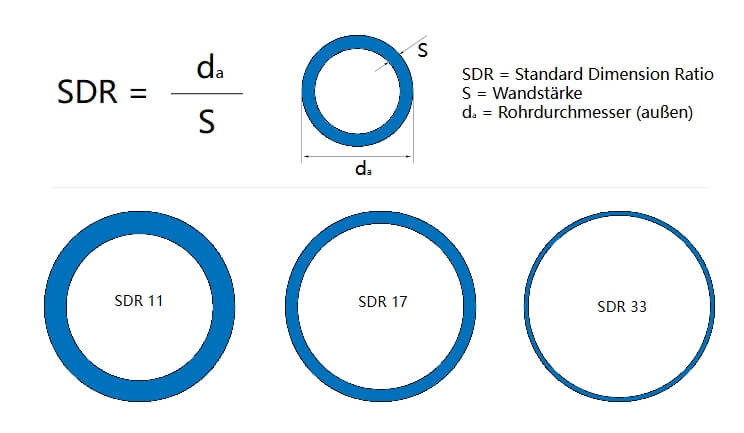
صيغة SDR هي: SDR = القطر الخارجي (OD) / سمك الجدار
- Lower SDR = Stronger pipe = thicker walls and higher pressure resistance.
- Higher SDR = Lighter but weaker pipe = thinner walls and lower pressure resistance.
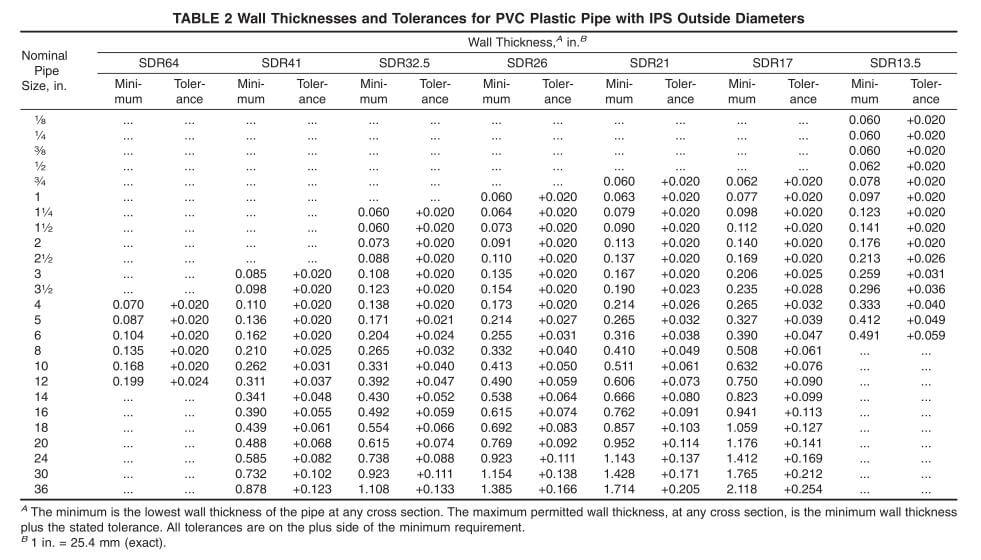
كما هو موضح في الجدول 2.
3.3 ترميز الألوان والتعريف في أنابيب وقنوات PVC
Color coding is like a universal language for PVC pipes and conduits. It helps anyone who’s working with them quickly figure out what each one is used for, even if they’re not familiar with the specific installation.
Color coding is like a traffic light system 🚦 — each color tells you what to do next. Just as a red light means stop, and a green light means go, each color of PVC pipe or conduit signals its specific function. Understanding these color codes is crucial for safety and getting the job done efficiently.
While regional standards might slightly vary, there are common color conventions that help differentiate PVC pipes and conduits at a glance. Let’s break it down:
🚰 ترميز الألوان القياسي لأنابيب PVC
غالبًا ما تتبع أنابيب PVC المستخدمة في السباكة والري والتطبيقات الصناعية اتفاقيات الألوان العامة التالية:
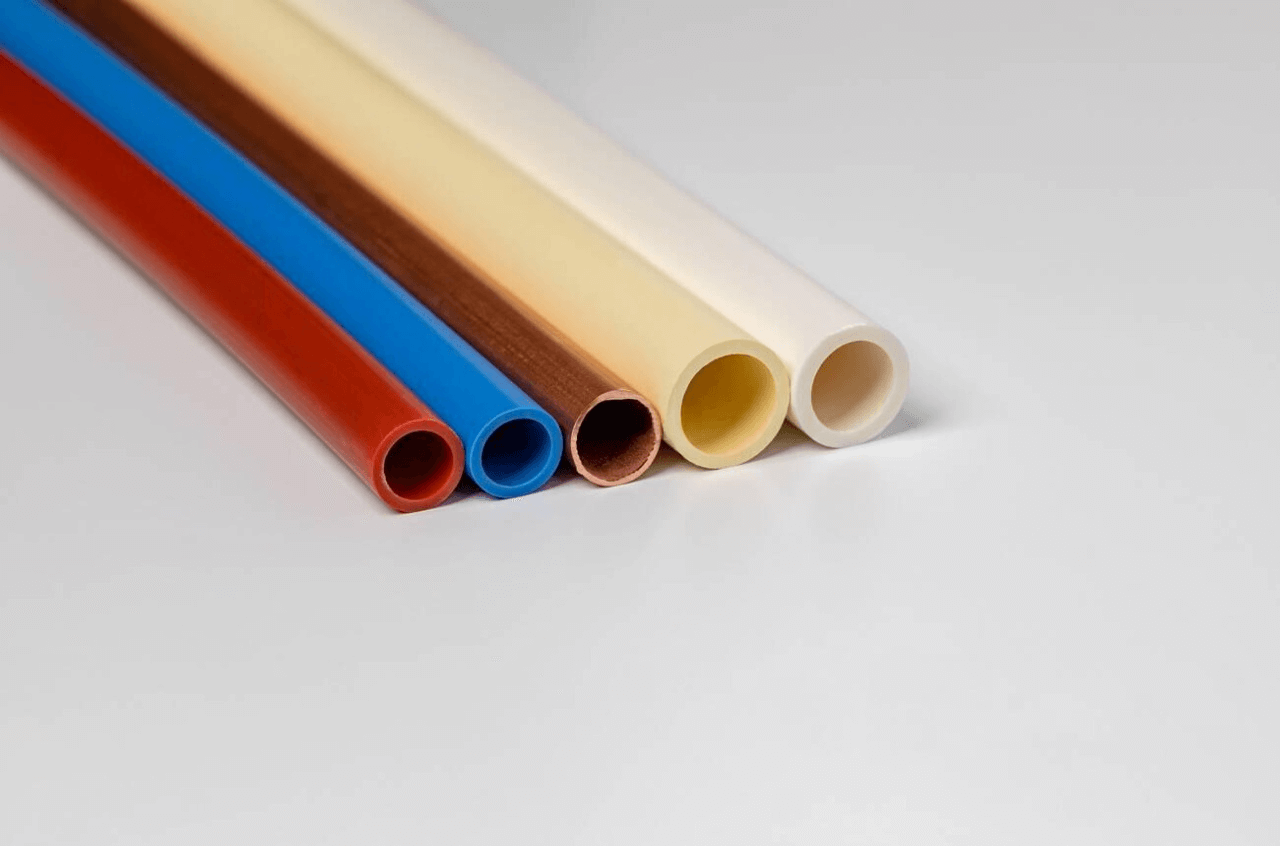
- أبيض أو رمادي - تستخدم عادة لتوفير مياه الشرب ومياه الصرف الصحي ومياه الصرف الصحي والمياه غير الصالحة للشرب للري وإعادة الاستخدام الصناعي.
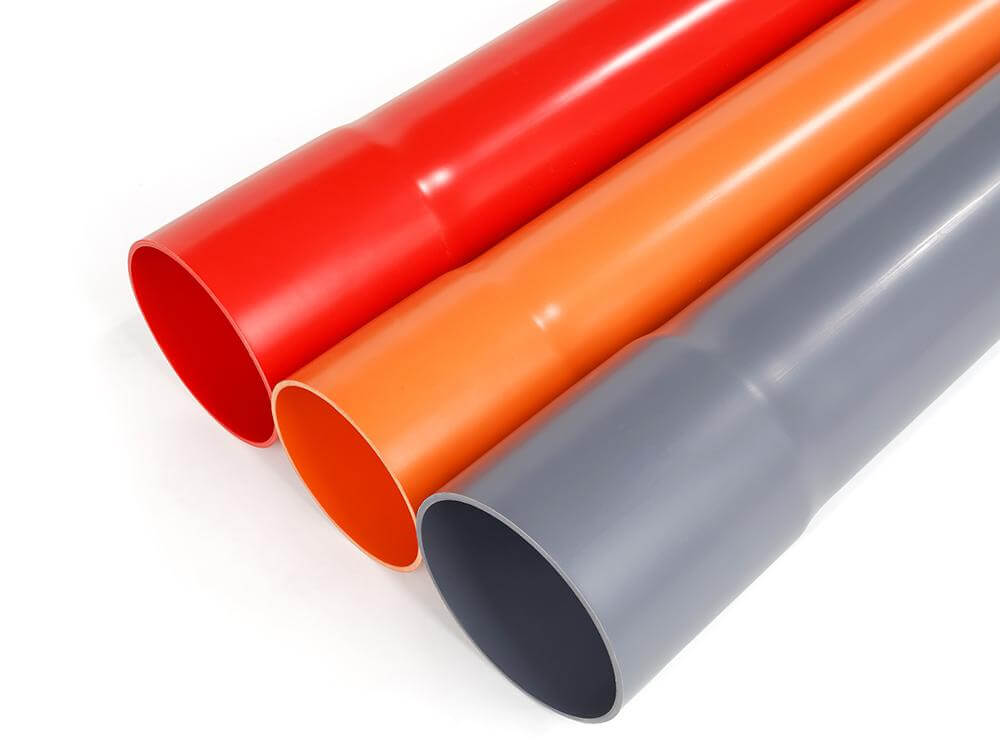
- برتقالي أو أحمر - يستخدم في أنظمة إخماد الحرائق (على سبيل المثال، شبكات الحريق تحت الأرض).
🔥 ترميز الألوان القياسي لأنابيب PVC
تتبع الأنابيب الكهربائية المصنوعة من مادة PVC مجموعة مختلفة من اتفاقيات الألوان، والتي تم تحديدها بشكل أساسي من خلال معايير الصناعة والرموز الكهربائية:

- رمادي - اللون الأكثر شيوعًا للأنابيب الكهربائية القياسية، بما في ذلك أنابيب PVC من الجدول 40 والجدول 80 المستخدمة في الأسلاك السكنية والتجارية والصناعية.
- برتقالي أو أحمر - يتم استخدامها غالبًا في الخطوط الكهربائية ذات الجهد العالي أو الموجودة تحت الأرض للإشارة إلى الحذر أثناء الحفر.
- أزرق أو أبيض - يتم استخدامها بشكل متكرر لكابلات الاتصالات وخطوط الألياف الضوئية وتطبيقات الجهد المنخفض.
⚠️ However, the color of PVC conduit might change based on the manufacturer or the specific job.
So while these color codes are general rules, always make sure to check your local codes and regulations to stay on the safe side!
🔖 Markings and Identification Labels
If you’re ever unsure, the markings on PVC pipes and conduits will tell you exactly what you need to know.
These markings are like the labels on a product in a store — they give you key information about what you’re dealing with.
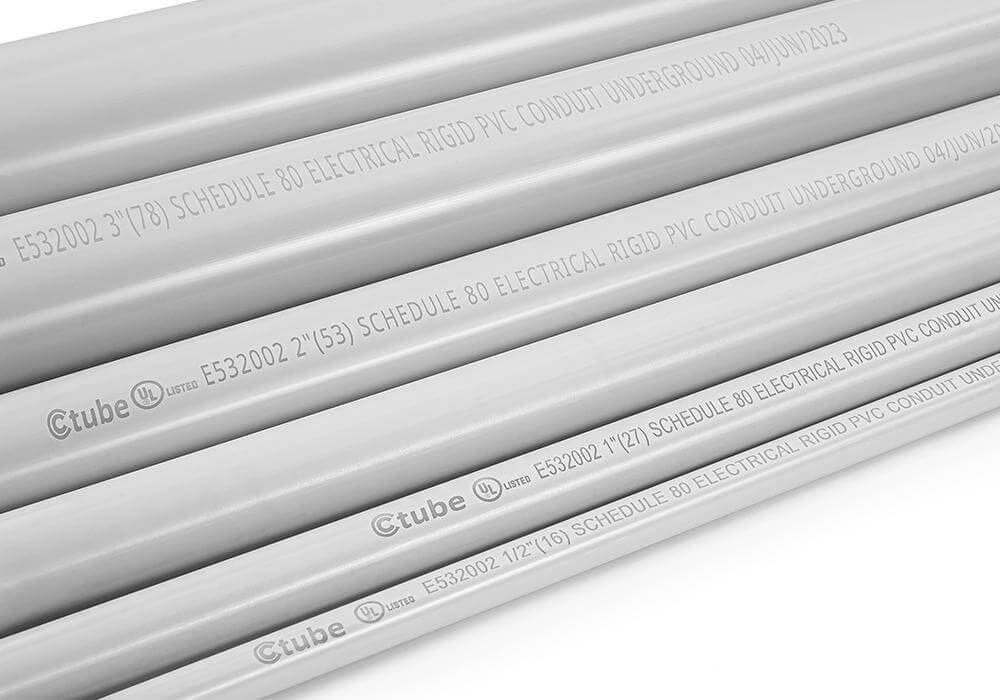

Common elements found on PVC pipe and conduit markings:
- اسم الشركة المصنعة أو رمزها:يحدد منتج الأنبوب أو القناة.
- تاريخ الإنتاج ورمز الدفعة:تستخدم لمراقبة الجودة وإمكانية التتبع في حالة وجود عيوب أو استدعاءات.
- حجم الأنبوب وأبعاده:يشير بوضوح إلى حجم الأنبوب الاسمي (NPS) أو القطر الخارجي (OD) لضمان الاختيار الصحيح والتوافق.
- تسمية المواد:مُصنف بـ "PVC" متبوعًا بدرجة المادة (على سبيل المثال، "PVC 1120" أو "PVC 1220").
- الجدول الزمني (SCH): شائع لكل من السباكة والقنوات، يشير إلى تصنيفات سمك الجدار مثل "SCH 40" أو "SCH 80".
4. مقارنة طرق التوصيل في أنابيب وموصلات PVC
بالإضافة إلى الاختلافات في المواد والمفاهيم والبنية واللون التي ناقشناها، فإن أنابيب المياه البلاستيكية والقنوات الكهربائية تختلف أيضًا بشكل كبير في تجهيزاتها وطرق توصيلها.
For example, water pipes need to prevent water from leaking out, while electrical conduits need to keep water from flowing in.
Let’s explore how these differences play out in the connection methods.
4.1 Same وظائف وأدوار التركيبات في أنابيب وممرات PVC
Fittings are essential components in both PVC piping and conduit systems.
- أقسام التوصيل:الربط - ربط قطعتين أو أكثر من الأنابيب أو القنوات معًا لتوسيع النظام.
- تغيير الاتجاه:المرفق - يسمح بالانتقالات السلسة في زوايا مختلفة للتنقل بين العوائق أو التوافق مع متطلبات التصميم.
- تفرع النظام:تي- إنشاء مسارات متعددة لتدفق السوائل (في السباكة) أو توجيه الأسلاك (في التطبيقات الكهربائية).
- الختم والحماية:ضمان توزيع المياه بشكل خالٍ من التسربات للسباكة والتوصيلات المعزولة الآمنة للأنابيب الكهربائية.
4.2 Different Fittings Requirements in PVC Pipe and Conduit
أحد الفروقات الرئيسية بين النظامين هو الحاجة إلى صناديق الوصلات والصناديق القابلة للتكيف في أنظمة التوصيلات الكهربائية، والتي لا توجد في أنابيب المياه.
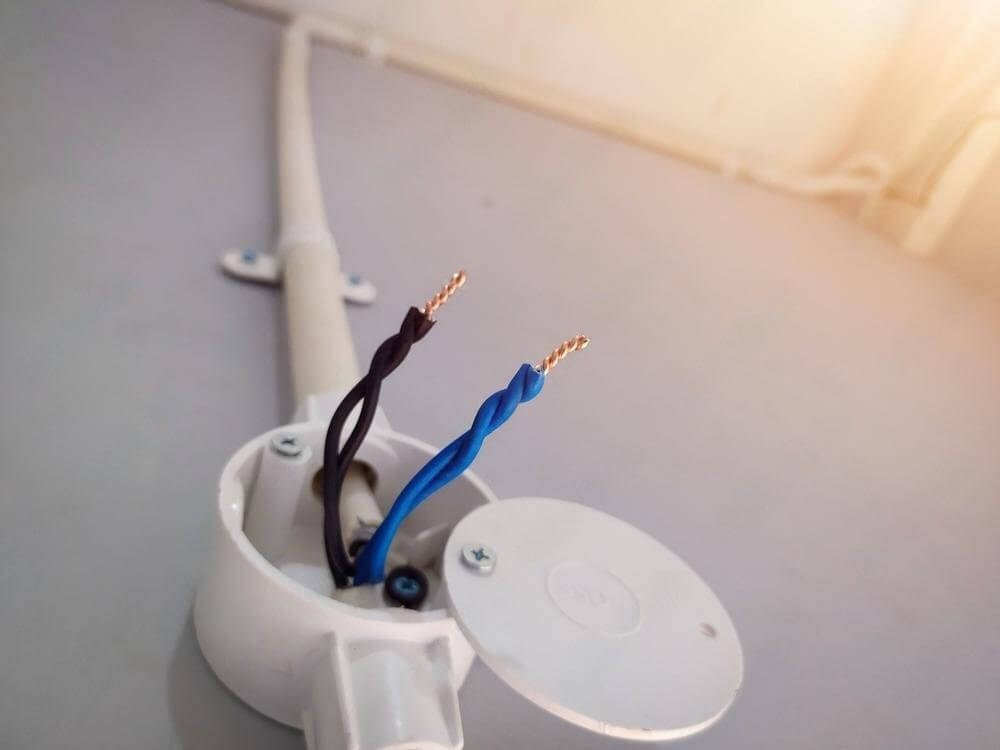

- صناديق التقاطع act as interconnection points for electrical wires, providing space for splicing and ensuring safety.
- صناديق قابلة للتكيف allow flexibility in conduit design, making it easier to modify or expand electrical systems.
⚡توفر هذه العبوات أيضًا حماية ميكانيكية للوصلات الكهربائية، مما يمنع التعرض للرطوبة والغبار والأضرار الخارجية.
🔄Another biggest difference is the requirement about the bending and turning.
لا توجد قواعد صارمة بشأن زوايا الانحناء الكلية في نظام أنابيب المياه المصنوعة من مادة PVC، طالما تم الحفاظ على كفاءة التدفق.
But in electrical conduit installation, NEC (National Electrical Code) limits the total bends between pull points to 360° to prevent excessive wire friction.
If more bends are needed, a junction box or pull box must be installed. The requirement ensure wires can be pulled through the conduit without excessive friction or damage.
4.3 لحام الأسمنت المذيب (الغراء) في أنابيب PVC وقنوات PVC
مادة الأسمنت المذيبة هي نوع من المواد اللاصقة المصممة خصيصًا لربط أنابيب وتجهيزات PVC عن طريق تليين المادة كيميائيًا لإنشاء اتصال قوي ودائم.
لا يقتصر لاصق المذيب على لصق الأسطح معًا فحسب، بل يدمجها في قطعة واحدة متصلة. تضمن طريقة الترابط هذه وصلة متينة ومقاومة للتسرب، مما يجعلها مستخدمة على نطاق واسع في تركيبات أنابيب السباكة والكهرباء.
However, there’s a difference in cement for water pipes and electrical conduits:
- 💧Water Pipe Cement: This type of cement needs to meet strict standards to ensure it’s safe for drinking water. Think of it as making sure your cup is clean and safe to drink from.
- ⚡Electrical Conduit Cement: This cement is formulated for durability and water resistance, designed to keep electrical connections safe even in damp or harsh environments.
📋 Always check with your supplier to make sure the solvent cement is made for either water pipes or electrical conduits.
While some cements can be used for both, others are specially formulated for one or the other.

🔍 If you’re curious about the technical side, solvent cements are actually governed by a detailed standard: (Reapproved 2024).
✅محتوى الراتنج:يجب أن يكون محتوى راتينج PVC 10% على الأقل.
✅القدرة على الذوبان:يجب أن يكون الأسمنت قادرًا على إذابة 3% إضافي بالوزن من مركب PVC 12454-B (سواء كان مسحوقًا أو حبيبيًا) أو راتينج PVC مكافئ عند 73.4 ± 3.6 درجة فهرنهايت (23 ± 2 درجة مئوية) دون علامات التجلط.
✅iscosity and Strength Over Time:
Cements are classified based on how strong they get over time:
- ≥ 250 psi (1.7 MPa) after 2 hours of curing
- ≥ 500 psi (3.4 MPa) after 16 hours of curing
- ≥ 900 psi (6.2 MPa) after 72 hours of curing
✅Hydrostatic Burst Strength: The minimum hydrostatic burst strength must be ≥ 400 psi (2.8 MPa) after 2 hours of curing.
Generally speaking, plumbing-grade solvent cement must meet potable water safety standards, ensuring no harmful chemicals leach into drinking water.
Electrical conduit solvent cement is formulated for durability and water resistance, as it is often used in environments where electrical safety is a concern.
🛒 Pro Tip Before You Buy
1️⃣ Check the label or spec sheet to understand the product’s specifications. Look for keywords like “potable water safe” or “electrical use only.”
2️⃣ Confirm its intended use—is it made for water pipes or electrical conduits? Each has different bonding needs.
3️⃣ Ask your supplier if you’re unsure. It’s better to double-check than to risk using the wrong cement. They can guide you to the right choice.
5. الامتثال للمعايير واللوائح: الفرق بين أنابيب المياه والوصلات الكهربائية
يجب أن تتوافق أنابيب المياه البلاستيكية (PVC) والأنابيب الكهربائية البلاستيكية (PVC) مع اللوائح والمعايير الصناعية المحددة لضمان السلامة والأداء والمتانة. ومع ذلك، تختلف المعايير التي تحكم هذين النوعين من الأنابيب اختلافًا كبيرًا باختلاف استخداماتهما. فيما يلي بعض الأمثلة في الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية وكندا، ولكن تذكر أنه يجب عليك اتباع اللوائح المحلية.
5.1 لوائح أنابيب المياه البلاستيكية
يتم تنظيم أنابيب المياه البلاستيكية في المقام الأول من خلال معايير السباكة وجودة المياه لضمان قدرتها على التعامل مع المياه المضغوطة بأمان دون تسرب المواد الضارة.
- NSF/ANSI 61 - التأكد من أن الأنبوب آمن لمياه الشرب.
- ASTM الدولية (ASTM D1785، D2241، إلخ.) - تحدد معايير المواد والأداء.
- جمعية أعمال المياه الأمريكية (AWWA C900، C905) - تحكم أنابيب المياه ذات القطر الكبير.
- ISO 1452 – المعيار الدولي لأنابيب الضغط المصنوعة من مادة PVC-U.
5.2 لوائح التوصيلات الكهربائية
يجب أن تتوافق الأنابيب الكهربائية المصنوعة من مادة PVC مع قواعد السلامة الكهربائية لضمان توفير الحماية الكافية للأسلاك ومقاومة العوامل البيئية والقوة الميكانيكية.

- UL (مختبرات التأمين، UL 651، 1653) - إصدار شهادات سلامة لموصلات الكهرباء ومقاومة الحرائق.
- الكود الكهربائي الوطني (NEC، NFPA 70) – يحدد متطلبات التثبيت.
- الرابطة الوطنية لمصنعي الأجهزة الكهربائية (NEMA TC-2، TC-3) - يحدد خصائص القناة.
- CSA (الجمعية الكندية للمعايير، C22.2 رقم 211.1) - تحكم معايير الأنابيب الكهربائية في كندا.
6. الخاتمة
تُصنع أنابيب وقنوات PVC من PVC، ولكنها تختلف في تصميمها الهيكلي وتركيبها المادي وطريقة استخدامها. صُممت الأنابيب أساسًا لنقل السوائل والغازات، بينما صُممت القنوات لحماية الأسلاك الكهربائية.
بالنسبة للمحترفين وهواة الأعمال اليدوية، من الضروري اختيار أنابيب أو مواسير PVC بناءً على الغرض منها. ينبغي على الكهربائيين إعطاء الأولوية للمواسير في تركيبات الأسلاك الكهربائية، مع ضمان الامتثال لمعايير السلامة وطول العمر. أما السباكون، فينبغي عليهم استخدام أنابيب PVC المصممة لأنظمة السوائل. اتبع دائمًا إرشادات الشركة المصنعة، وتأكد من اختيار التركيبات والمواد اللاصقة المناسبة لضمان جودة ومتانة التركيب.
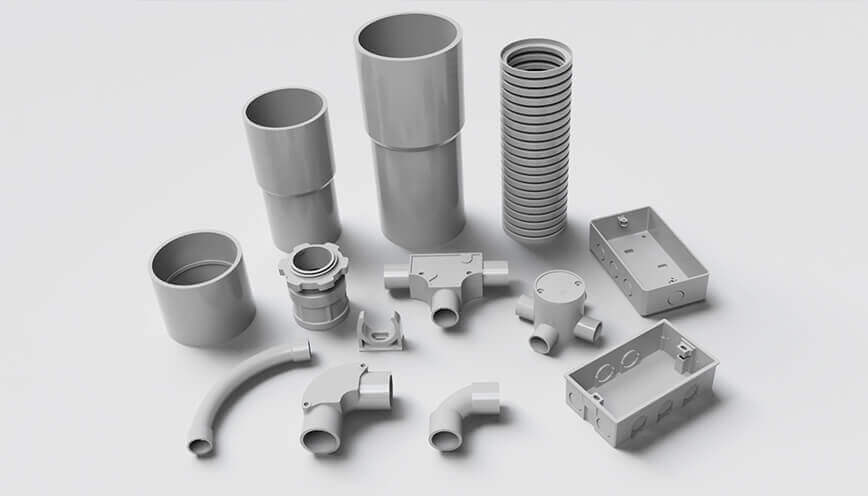

كتوب هو مورد موثوق به للأنابيب الكهربائية، ويقدم مجموعة واسعة من الأنابيب عالية الجودة بولي كلوريد الفينيل, UPVC، و LSZH أنابيب التوصيل. صُممت منتجاتنا لتلبية متطلبات مختلف التطبيقات الكهربائية، موفرةً متانة وسلامة وأداءً استثنائيًا. سواءً كنت تعمل في مشروع سكني أو تجاري أو صناعي، تقدم Ctube حلول الأنابيب المناسبة لضمان تركيبات آمنة وطويلة الأمد.
شكرا لقراءتك، ونتمنى لك حظا سعيدا في مشروعك.
مرجع
- ASTM D 4396 المواصفة القياسية لمركبات بولي (فينيل كلوريد) (PVC) الصلبة وبولي (فينيل كلوريد) (CPVC) المكلورة للأنابيب البلاستيكية والتجهيزات المستخدمة في التطبيقات غير المضغوطة
- ASTM D 3915 المواصفة القياسية لمركبات بولي (كلوريد الفينيل) الصلب (PVC) وبولي (كلوريد الفينيل) المكلور (CPVC) المستخدمة في الأنابيب البلاستيكية والتجهيزات المستخدمة في تطبيقات الضغط1
- ASTM D 2241 المواصفة القياسية لأنابيب البولي (فينيل كلوريد) (PVC) المقاومة للضغط (سلسلة SDR)
- ASTM D 1784 المواصفة القياسية لمركبات بولي (كلوريد الفينيل) (PVC) الصلبة ومركبات بولي (كلوريد الفينيل) (CPVC) المكلورة
- ASTM D 2665 المواصفة القياسية لأنابيب الصرف الصحي والنفايات والتهوية البلاستيكية والتجهيزات المصنوعة من بولي (كلوريد الفينيل) (PVC)
- ASTM F512-12 المواصفة القياسية لأنابيب البولي فينيل كلوريد (PVC) ذات الجدران الملساء والتجهيزات للتركيب تحت الأرض
- ASTM D1785-21a المواصفة القياسية لأنابيب البلاستيك المصنوعة من بولي (كلوريد الفينيل) (PVC)، الجداول 40 و80 و120
- ASTM D4216 المواصفة القياسية لمركبات البولي فينيل كلوريد الصلب (PVC) ومركبات البولي فينيل كلوريد ذات الصلة ومركبات البولي فينيل كلوريد المكلورة (CPVC) لمنتجات البناء
- ASTM D2122 طريقة الاختبار القياسية لتحديد أبعاد الأنابيب والتجهيزات البلاستيكية الحرارية
- ASTM D1785 المواصفة القياسية لأنابيب البلاستيك المصنوعة من بولي (كلوريد الفينيل) (PVC)، الجداول 40 و80 و1201
- ASTM D2564-20 المواصفة القياسية للأسمنت المذيب لأنظمة الأنابيب البلاستيكية المصنوعة من بولي (كلوريد الفينيل) (PVC)
- ASTM F493-20 المواصفة القياسية للأسمنت المذيب لأنابيب ووصلات البلاستيك المصنوعة من بولي (كلوريد الفينيل) المكلور (CPVC)
- ASTM D3138-21 المواصفة القياسية للأسمنت المذيب للمفاصل الانتقالية بين مكونات الأنابيب غير المضغوطة المصنوعة من أكريلونيتريل بوتادين ستايرين (ABS) وبولي (كلوريد الفينيل) (PVC)
- ASTM D2855-20 الممارسة القياسية لطريقة الخطوتين (طبقة أساس ومادة لاصقة مذيبة) لربط أنابيب بولي (كلوريد الفينيل) (PVC) أو أنابيب بولي (كلوريد الفينيل) (CPVC) المكلورة ومكوناتها ذات المقابس المخروطية
- ASTM F656-21 المواصفة القياسية للبرايمرات المستخدمة في وصلات الأسمنت المذيب لأنابيب ووصلات البلاستيك المصنوعة من بولي (كلوريد الفينيل) (PVC)
أنبوب PVC مقابل قناة PVC، الدليل الشامل للمقارنة (2025) اقرأ أكثر "