What Does EMT Stand For in Electrical? A Complete Guide to Electrical Metallic Tubing
1 المقدمة
When working with electrical systems, choosing the right type of conduit is essential for safety, durability, and compliance with building codes. One of the most common options used by electricians today is EMT, which stands for Electrical Metallic Tubing.
EMT conduit is known for being lightweight, strong, and easy to work with. It’s widely used in residential, commercial, and light industrial wiring projects and supports a clean, organized electrical installation.
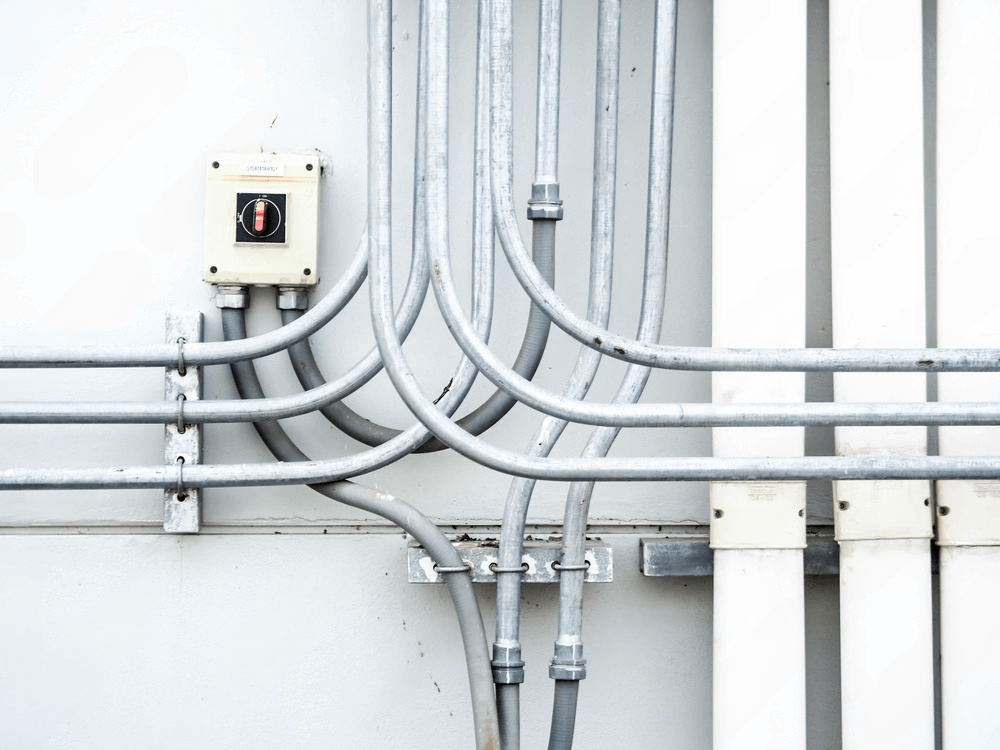
In this post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about EMT — from what it is, where and when it’s used, how to install it, to its advantages and limitations. We’ll also answer some of the most frequently asked questions.
By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of why EMT is one of the go-to solutions for modern electrical conduit systems.
2. What is EMT Conduit?
2.1 Definition and Meaning of EMT Pipe
EMT stands for Electrical Metallic Tubing, often referred to as thin-wall conduit because of its thinner wall thickness compared to other metal conduits like IMC (Intermediate Metal Conduit) and RMC (Rigid Metal Conduit).
EMT is a type of rigid conduit with non-threaded and designed to be joined using special fittings such as couplings and connectors.

Despite being rigid, EMT is more flexible than other metal conduits and can be bent with the proper tools, making it easy to install in tight or complex spaces.
As a result of its thinner walls and flexiblility, it is sometimes not classified as a ‘rigid metal conduit’ under certain codes.
2.2 Material and Construction of Conduit EMT
Most EMT conduit is made from aluminum and stainless steel, which helps protect against corrosion and physical damage.
The tubing has a smooth interior surface, which makes pulling wires easier and reduces wear on insulation.
Importantly, EMT conduit is typically not threaded. Unlike rigid metal conduit RMC or IMC, which requires threads and special connectors, EMT is connected using set-screw or compression fittings. This makes installation faster and easier, especially in tight spaces.
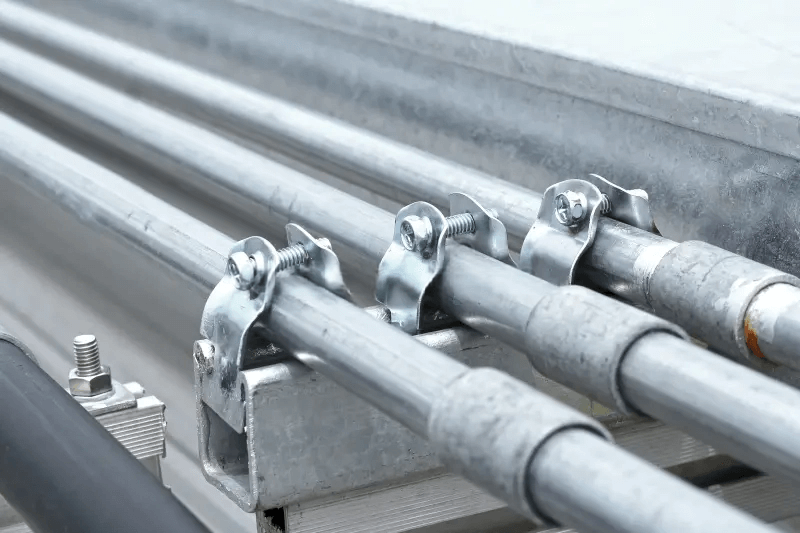
2.3 Common EMT Conduit Sizes: Dimensions and Weight
EMT conduit is available in a variety of standard sizes to suit different electrical installations. The size refers to the trade size of the tubing, not its actual outer diameter. Here are the size requirements, such as length, dimensions and weight according to the UL 797.
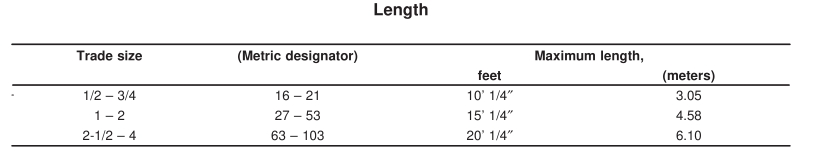
The length of electrical metallic tubing shall not be greater than given in Table above.
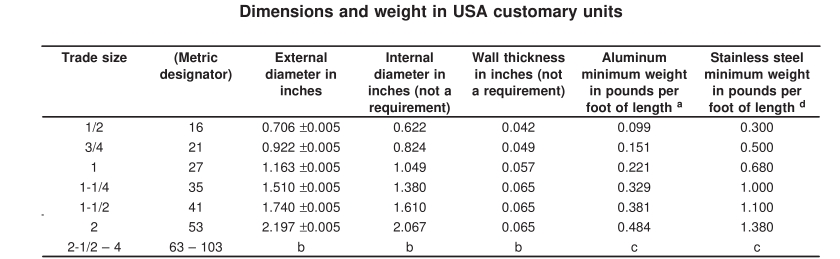
The external diameter and weight of finished tubing shall be within the limits indicated in Table given above.

EMT is available in sizes ranging from 1/2 inch to 4 inches or more, depending on the project requirements.
| EMT Size | Typical Uses |
| 1/2 بوصة | Light-duty residential wiring, lighting circuits |
| 3/4 inch | Small commercial applications, branch circuits |
| 1 بوصة | Larger circuits, feeder cables |
| 1-1/4 inch | Heavy commercial or light industrial wiring |
| 1-1/2 بوصة | Feeder lines, service entrance conductors |
| 2 بوصة | Industrial or high-capacity electrical systems |
| 2-1/2 to 4 inch | Large-scale wiring, main services, and data centers |
2.4 Electrical Metallic Tubing Colors
Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) is most commonly available in a natural metallic finish, but it can also be found in a range of colors for specific applications.
The color of EMT conduit can serve various purposes such as enhancing durability, aesthetic appeal, or providing identification for different electrical systems.
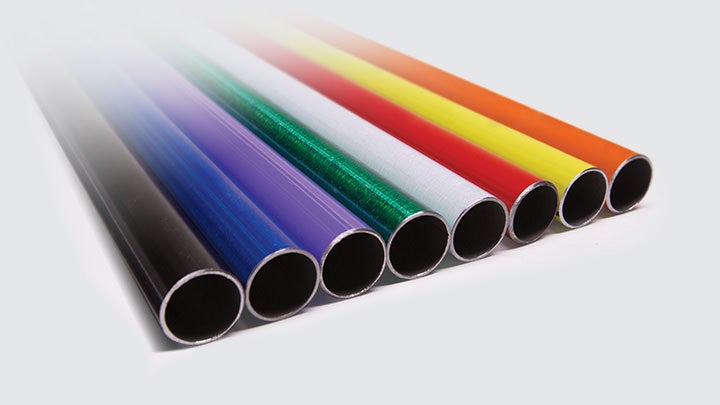

Metallic/Silver Finish (Natural): Galvanized steel and aluminum EMT typically come in this natural metallic color. Most commonly used in both residential and commercial installations.
Gray: Gray EMT is typically aluminum or coated steel, offering both corrosion resistance and a neutral appearance.
Black: Black EMT is often used in outdoor applications. This color also provides UV protection, making it suitable for areas with significant sunlight exposure.
In some cases, EMT may be available in custom colors like red, blue, or white.
Here are the table for EMT Conduit Colors and Their Applications:
| لون | Typical Application |
| أحمر | Fire alarm circuits or emergency circuits |
| أزرق | Low-voltage or Data and communication wiring |
| أخضر | Healthcare or medical systems |
| أصفر | High voltage lines |
| البرتقالي | Fiber optic cables |
| أسود | Design-focused use like UV resistance outdoor |
| أبيض | Neutral circuits or aesthetic choice |
✅ Note: These color codes are widely used in North America, but regional codes and project requirements may vary. Always check with your local electrical authority before specifying colored EMT for system identification.
2.5 Advantages and Disadvantages of EMT Conduit
Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) is a popular choice in commercial and light industrial applications due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. However, like any material, it comes with both strengths and limitations.
2.5.1 Advantages of EMT Conduit
مقاوم للحرائق
Made of metal, EMT conduit is non-combustible and does not emit toxic fumes when exposed to fire. This makes it a preferred choice in buildings where fire safety is a critical requirement.
خفيفة الوزن وسهلة التركيب
One of the main advantages of EMT is that it’s lightweight compared to rigid metal conduit (RMC), making it easier to cut and bend on site. This simplifies the installation process and helps reduce labor time and costs.
Relatively Cost-Effective
Though some may ask, “why is EMT conduit so expensive?”, EMT is actually more affordable than heavier alternatives like IMC or RMC. Its lower material and shipping costs make it a budget-friendly option within the metal conduit family.
2.5.2 Disadvantages of EMT Conduit
Limited Mechanical Protection
Compared to thicker options like IMC or RMC, EMT provides less impact resistance. It is not ideal for areas with heavy machinery or where the conduit might be subject to physical damage. It’s best used where extensive mechanical protection isn’t needed.
Unsuitable for Harsh or Underground Environments
EMT is not designed for underground applications unless it is encased in concrete or otherwise protected. Similarly, using EMT outdoors (especially in exposed conditions) is not recommended without appropriate corrosion-resistant treatment.
3. EMT Conduit Uses: Where and When to Use Electrical Metallic Tubing
Now that we’ve explored the basic characteristics, benefits, and limitations of Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT), you might be wondering – what is EMT conduit used for in real-world projects? And where is EMT conduit used most often?
Let’s explore the practical applications and ideal scenarios for EMT.
3.1 When to Use EMT Conduit
You need basic physical protection for wires without requiring heavy-duty armor
The conduit will be run in dry, indoor locations or mild environments
You want to reduce installation time—EMT is easy to cut and bend
You’re working in commercial or light-duty industrial projects
3.2 Where is EMT conduit used? Specific Application
🏠 Residential Uses
In home wiring systems, EMT conduit is used for protecting wires in exposed indoor areas, such as basements, garages, and utility rooms. It’s particularly useful in places where there’s a need for neat, organized wiring with some degree of mechanical protection.
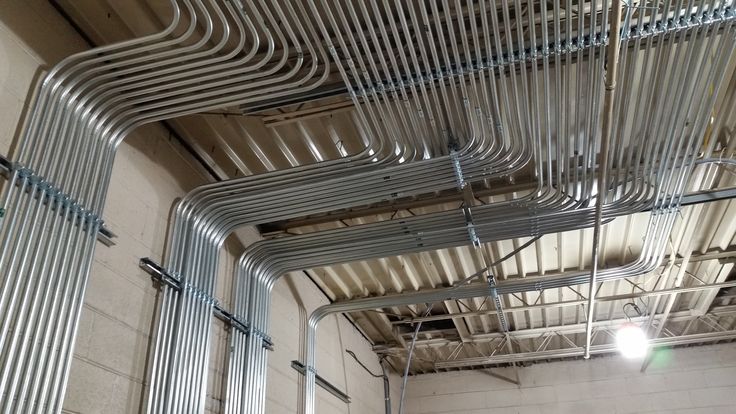

🏢 Commercial and Office Buildings
EMT is widely used in commercial spaces like offices, schools, and retail shops. These environments typically don’t require heavy-duty conduit, but they benefit from EMT’s clean appearance, ease of installation, and code compliance.
🏭 Light Industrial Settings
In some light industrial or warehouse environments, EMT conduit helps organize and protect wiring along walls and ceilings. However, it is not recommended in areas with high impact risks or chemical exposure, where stronger alternatives like RMC or PVC-coated conduit would be more suitable.
3.3 Types of Electrical Conduit Comparison: EMT vs IMC vs RMC
EMT is the thinnest wall among the three. It is much lighter and easier to handle on-site.
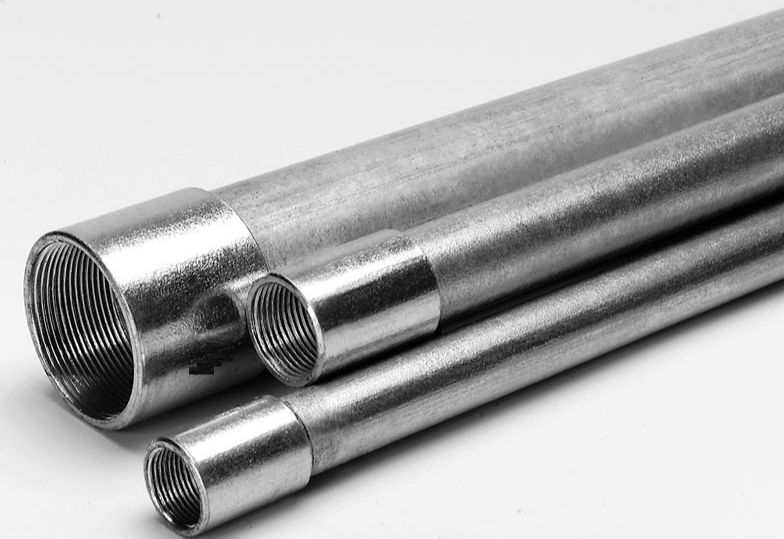

IMC has a thicker wall than EMT, offering greater mechanical protection while still being lighter than RMC.
RMC is the heaviest and thickest, providing maximum protection in harsh environments.
4. Electrical Metallic Tubing Installation Tips
Installing EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) conduit requires proper techniques to ensure both safety and code compliance. Below are practical tips for cutting, bending, connecting, and splicing EMT conduit during installation.
4.1 How to Cut and Bend EMT
To cut EMT conduit, you can use a pipe cutter for a clean, smooth edge or a hacksaw for quicker jobs. After cutting, always deburr the edges to prevent damage to wire insulation. Here we provide the cutting guide.
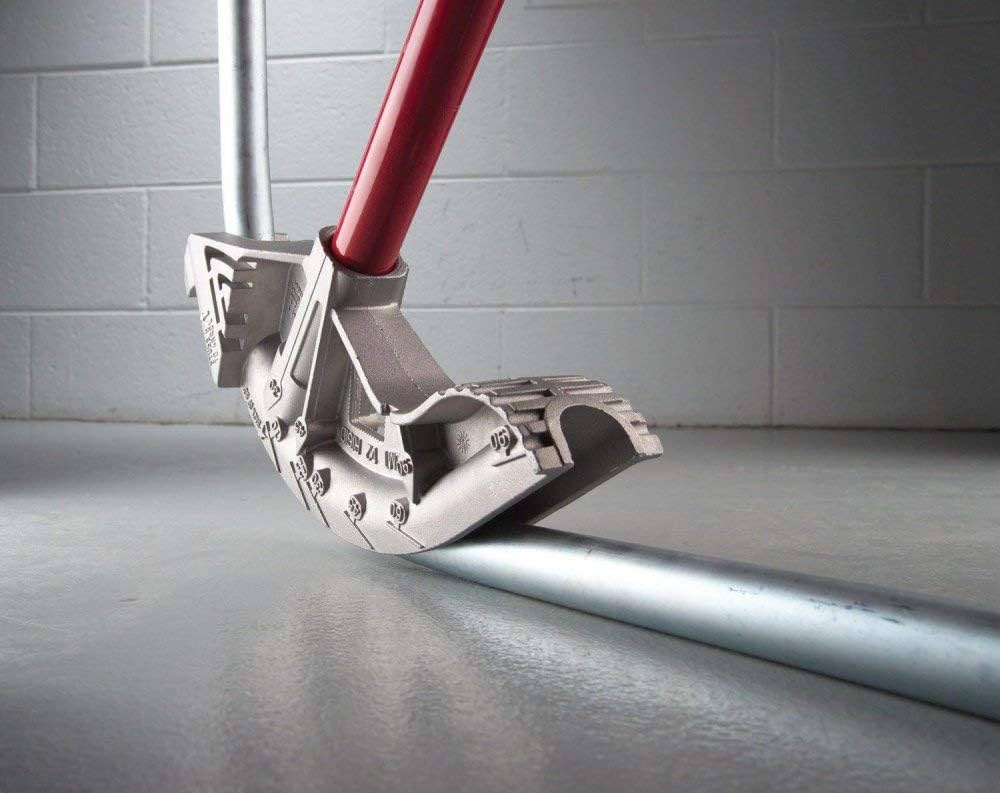

When it comes to bending EMT conduit, the easiest and most accurate method is to use a conduit bender.
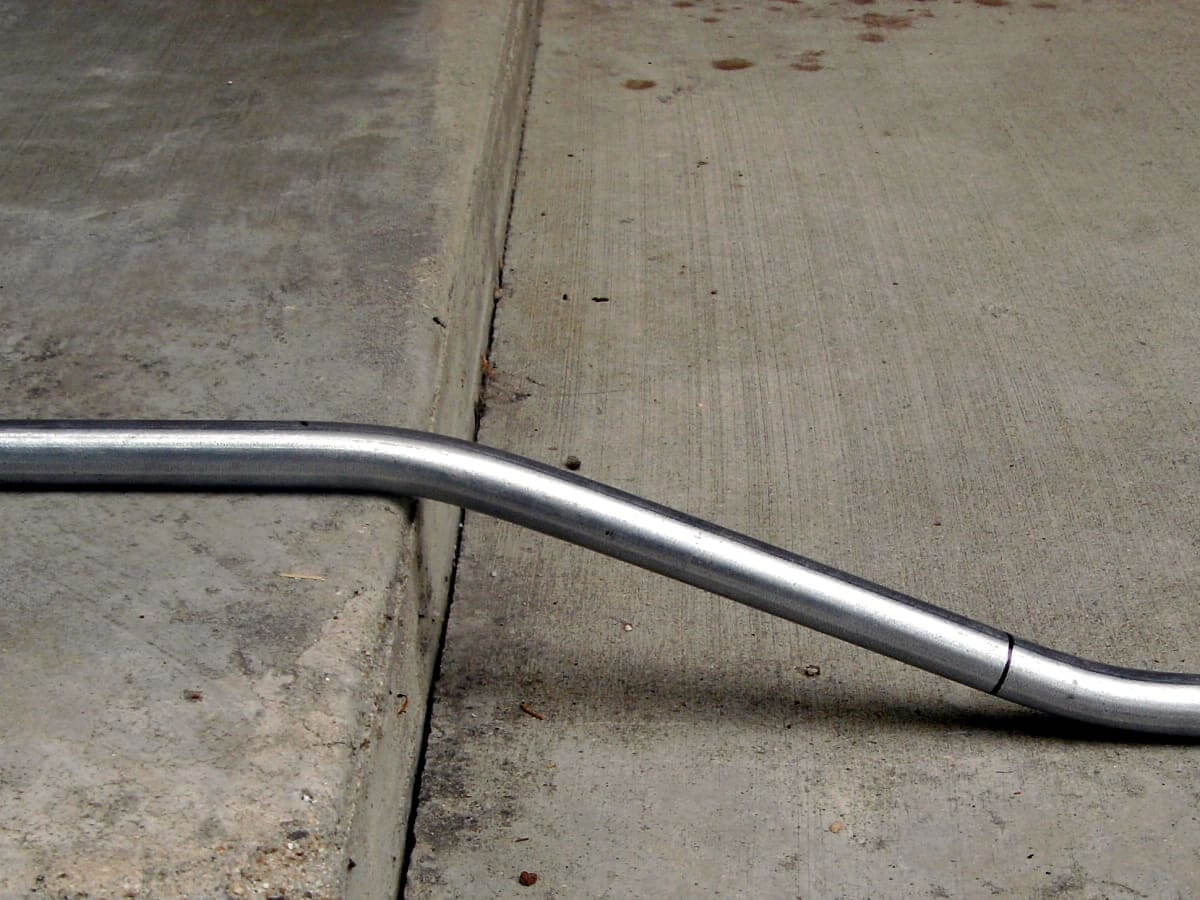

However, if you don’t have a bender, EMT can be bent without a bender using manual methods:
- Secure one end of the conduit.
- Apply steady pressure to bend the tubing gradually over a round object (like a pipe or sturdy cylinder).
- Be cautious to avoid kinks or flattening the conduit.
Bending Requirements (According to NEC 358.24 & 358.26)
- Bends must be made without damaging the tubing or reducing its internal diameter.
- No more than 360 degrees of total bends (e.g., four 90° bends) are allowed between pull points.
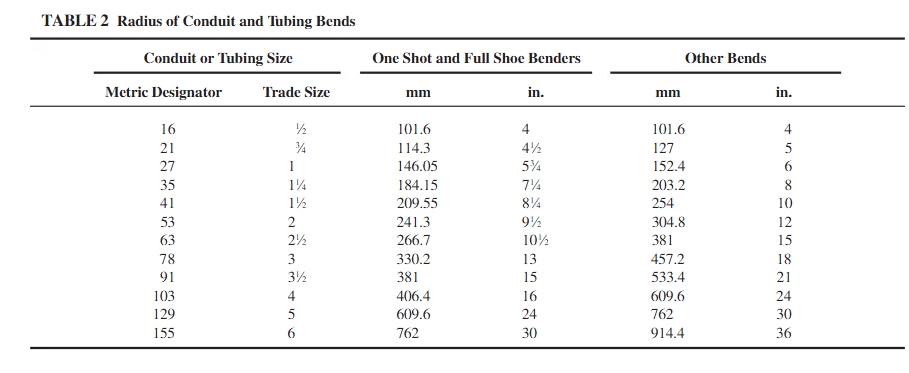
- Minimum bending radius must conform to NEC tables (e.g., Chapter 9, Table 2).
4.2 Fittings and Connectors: Connecting, Securing and Supporting
To join lengths of conduit or connect EMT to electrical boxes, you’ll need fittings such as:
EMT couplings – used to connect two straight sections of EMT conduit.
EMT securing clamp – used to hold EMT conduit securely in place, preventing movement, shifting.
- EMT must be securely fastened within 3 feet (900 mm) of each outlet box, junction box, device box, cabinet, or similar point.
- EMT must also be supported every 10 feet (3 meters) or less.
- Exception: Secure fastening at up to 5 feet (1.5 m) is allowed where structural members don’t permit fastening within 3 feet.
EMT connectors – used to connect conduit to enclosures, like electrical boxes.
4.3 Splicing and Tapping of EMT Pipe Usage
According to the NEC, when using EMT type conduit, splices and taps shall be made only in accessible boxes or enclosures. This means that any time you’re joining or branching off conductors inside EMT, you must use an approved electrical box such as a junction box or device box. Open-air splices are not allowed.
In addition, splicing methods must comply with applicable standards for secure electrical connections — this often includes the use of twist-on wire connectors, push-in connectors, or mechanical lugs depending on the wire size and application.
Always check local code and NEC Article ensure compliance during splicing and tapping operations.
5. الخاتمة
In this post, we have explored the definition, advantages, disadvantages, and common applications of Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT). And hope these information helpful.
EMT is widely used in electrical installations due to its lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation.
The correct choice of conduit should be based on a comprehensive assessment of the specific needs of the project, including budget, environmental conditions, and future maintenance requirements.
While EMT is an excellent choice for many applications, it does have limitations. For example, EMT may not provide the required strength in certain high-stress environments, nor can it effectively resist chemical corrosion in harsh conditions.
This is where PVC conduit comes into play. PVC conduit offers superior protection against chemical corrosion. In addition, unlike EMT, PVC conduit pipes are resistant to moisture and UV degradation, making them an ideal option for both indoor and outdoor electrical systems.

في كتوب, we provide a range of high-quality PVC conduit products designed to meet various electrical needs. Whether you are working with قناة جامدة, قناة مرنة, or specialized conduits like solar UPVC conduit or قناة LSZH, or special rigid conduit types such as SCH 40, SCH 80, or DB, EB series, we can satisfy your requirements.
Our products are rigorously tested to ensure they meet the highest standards, offering reliability and peace of mind for your electrical installations.
If you have a project need, contact us!
We also address some common questions related to the article in the following.
الأسئلة الشائعة
1. What does EMT conduit mean?
Electrical Metallie Tubing (EMT). An unthreaded thinwal!raceway of circular cross section designed for the physicalprotection and routing of conductors and cables and for use as an equipment grounding conductor when installed utilizing appropriate fittings.
2. Will EMT Conduit Rust?
Yes, EMT can rust if not properly protected. It’s typically galvanized to resist corrosion, but in wet, humid, or chemical-heavy environments, the coating may eventually break down. This is why EMT is not recommended for extended outdoor use without additional protection.
3. Can EMT conduit be used underground?
Not directly. EMT is not designed for underground applications unless it is encased in concrete or otherwise protected.
According to UL 797, Aluminum and stainless steel electrical metallic tubing does not require a protective coating.
But aluminum electrical metallic tubing intended for use in concrete, for direct burial, or for use inseverely corrosive environments, shall be provided with a protective coating.
4. Can EMT Conduit Be Used Outdoors?
Yes—but with conditions. EMT conduit can be used outdoors if it is properly installed and coated to resist corrosion.
However, it should be kept above ground and out of direct exposure to moisture whenever possible.
For outdoor or exposed locations, check local electrical codes or use EMT with corrosion-resistant finishes.
5. Where EMT is Allowed and Not Allowed?
EMT can be used for both exposed and concealed work. In damp and wet locations.
EMT must not be used in the conditions where subject to severe physical damage.
6. Why Use Colored EMT Conduit?
Easy Circuit Identification: Reduces confusion in large systems with multiple circuits.
Time-Saving: Facilitates faster maintenance, troubleshooting, and inspections.
Safety: Helps avoid accidental disconnection or contact with critical systems (e.g., fire alarms or high-voltage lines).
Aesthetics and Compliance: Offers a clean, professional appearance and may align with architectural or safety code standards.
7. How is EMT conduit different from other types like IMC or RMC?
EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) conduit is lighter and more flexible, and the least expensive compared to IMC (Intermediate Metal Conduit) and RMC (Rigid Metal Conduit).
What Does EMT Stand For in Electrical? A Complete Guide to Electrical Metallic Tubing اقرأ أكثر "

