Electrical Rigid Conduit Comparison: PVC Conduit vs Metal Conduit (EMT, RMC, IMC)
1. Introduction: Why Electrical Rigid Conduit Matters
If you wants to understand the key differences between rigid conduit made of PVC or metal like EMT, RMC, and IMC, this guide maybe helpful. For anyone—from electricians and project managers to homeowners and curious DIYers.
1.1 Understanding the Confusion: PVC Conduit vs EMT Electrical Conduit
This post is written because we found that many people compare PVC conduit and EMT conduit when planning an electrical installation. This is a very common and practical starting point — both are widely used, both offer protection for electrical wiring, and both are available in most hardware stores.
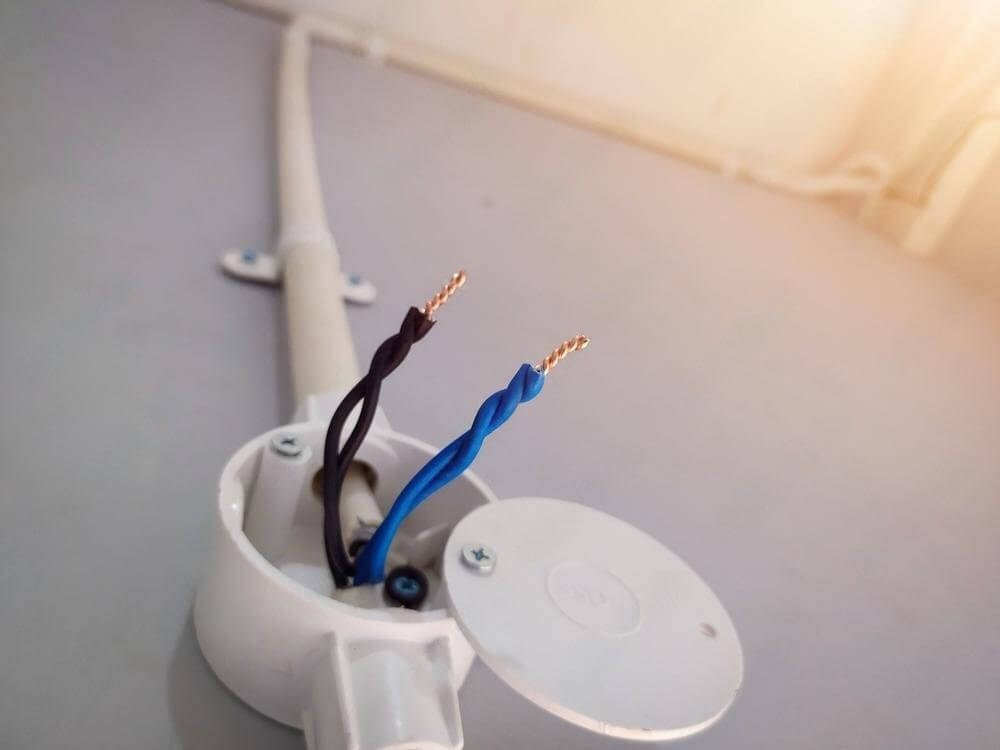
However, the term PVC conduit often refers specifically to PVC rigid conduit, even though PVC conduit actually includes both rigid and flexible types. EMT, on the other hand, is a specific type of metal conduit—a thin-walled, rigid steel or aluminum tube.
Comparing PVC conduit to EMT pipe is a bit like comparing “plastic pipes” to “a type of steel pipe.” It’s possible, but we first need to clarify the broader categories involved.
1.2 What You’ll Learn in This Guide
So this guide aims to help clarify these differences. We’ll compare different types of PVC rigid conduit and metal conduit in terms of strengths, costs, and best-fit applications so you can make smart, code-compliant decisions for your next electrical project.
2. Overview of Electrical Conduit Categorization and Materials
When choosing the right conduit for an electrical project, understanding how conduit types are categorized is the first important step.
In general, electrical conduits are classified based on material, structure, and sometimes application environment.
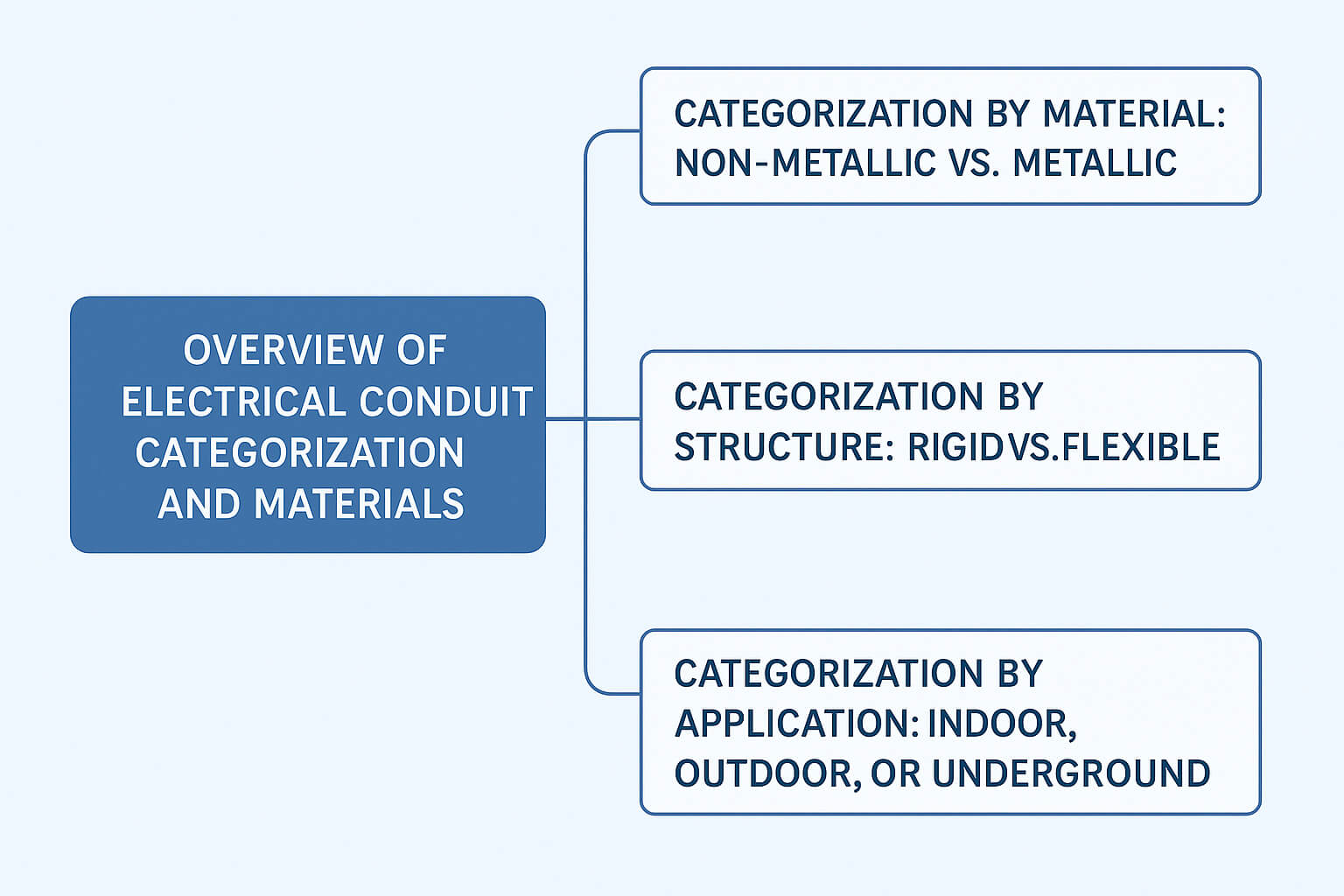
These categories help professionals select the best conduit for safety, durability, and code compliance.
2.1 Categorization By Material: Non-metallic vs. Metallic
Non-metallic conduits are made from plastic-based materials like PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), or RTRC (Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Conduit).
Metallic conduits, on the other hand, are typically made from steel, aluminum, or stainless steel.
2.2 Categorization By Structure: Rigid vs. Flexible
Another major classification is based on flexibility.
Rigid conduits hold their shape and provide strong protection for wiring. Most metal conduits (like EMT, RMC, IMC) and rigid PVC fall into this category.
Flexible conduits can bend easily, making them ideal for tight or irregular spaces. Examples include PVC flexible conduit, ENT (Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing), and FMC (Flexible Metal Conduit).
2.3 Categorization By Application: Indoor, Outdoor, or Underground
Electrical conduits are also selected based on their installation environment.
Indoor use may prioritize aesthetics, ease of access, or cost.
Outdoor or exposed environments require UV and weather resistance.
Underground installations must meet burial ratings and moisture resistance
With a clear understanding of how electrical conduits are categorized, we’re now ready to focus on one of the most common and practical comparisons in the field.
We’re narrowing the scope to specific comparison: PVC rigid conduit vs. EMT and other types of metal rigid conduits.
3. What is PVC Conduit?
PVC conduit is made from polyvinyl chloride, a type of plastic known for being lightweight, moisture-resistant, and non-conductive.
Because it’s not made of metal, it won’t rust, and it doesn’t carry electricity.
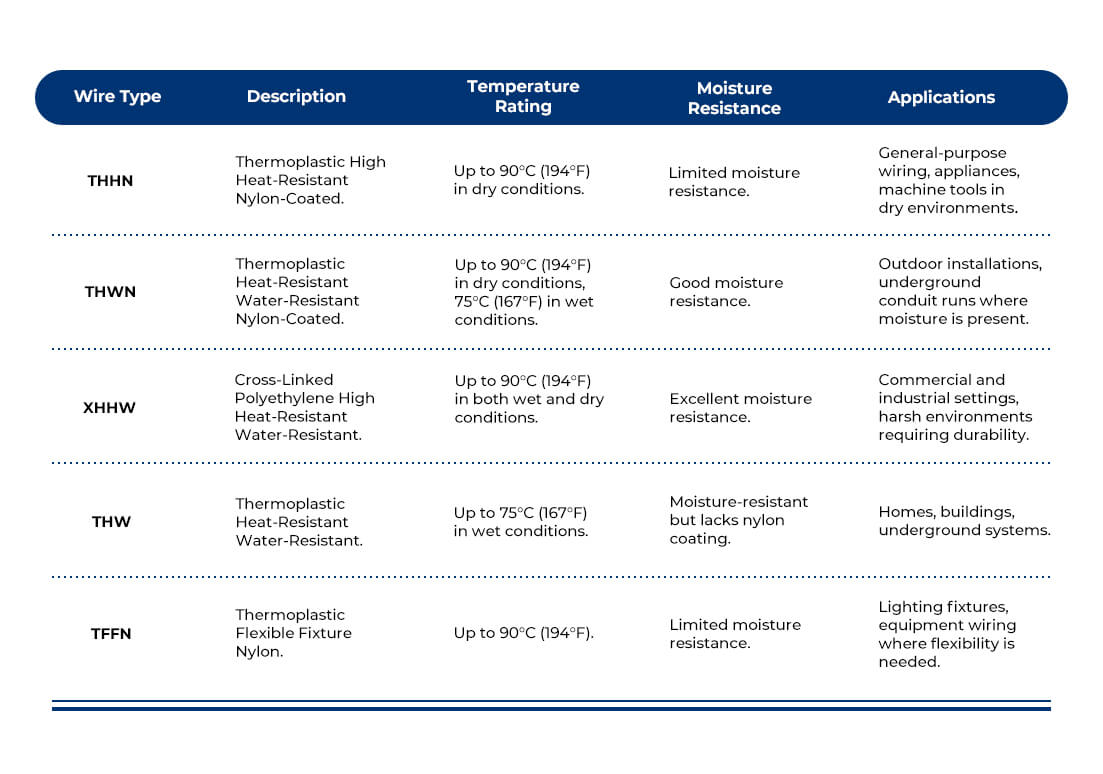
3.1 Types of PVC Conduit
When people say “PVC conduit,” they usually mean rigid PVC conduit — the straight, gray plastic pipe that looks similar to water pipes. But in reality, “PVC conduit” is a category of conduit products, which includes different forms based on structure and flexibility.
There are two main types, include rigid PVC conduit and flexible PVC conduit.
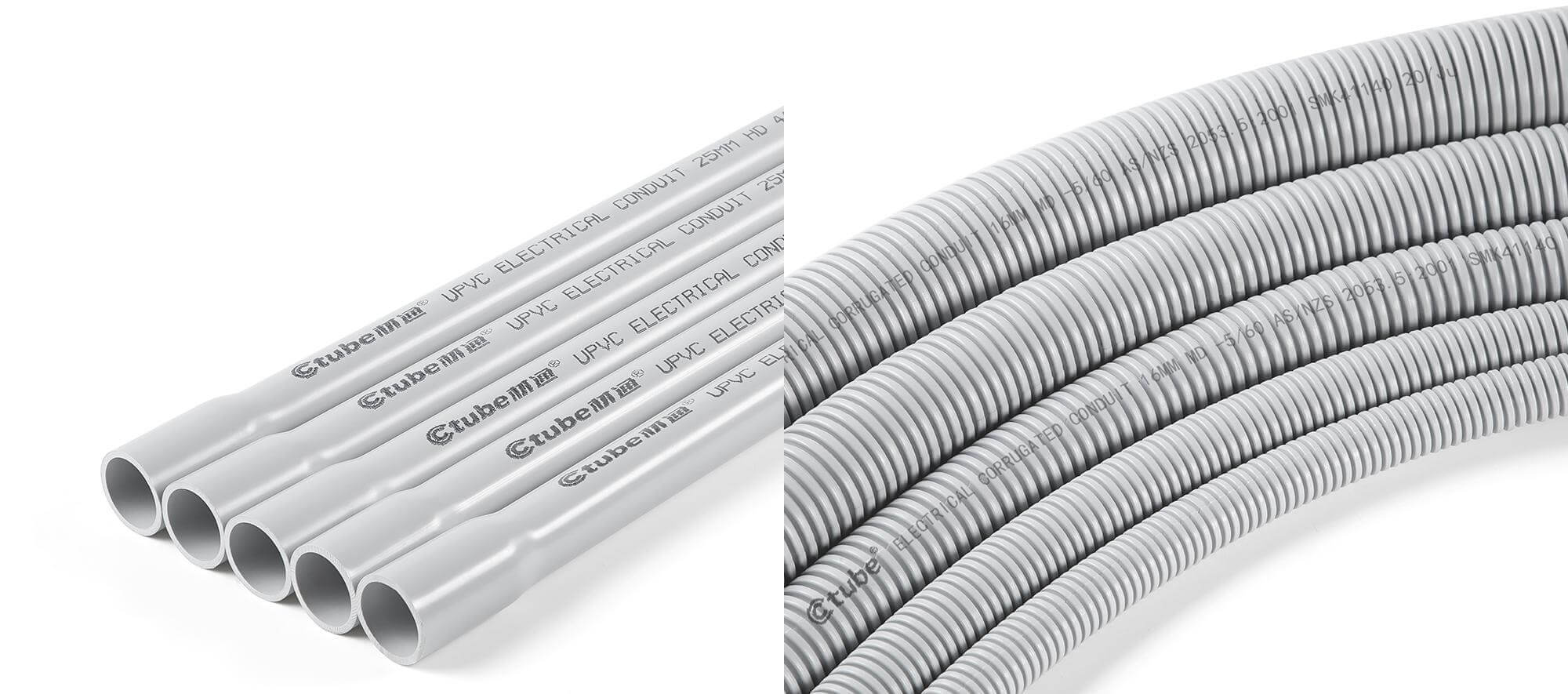

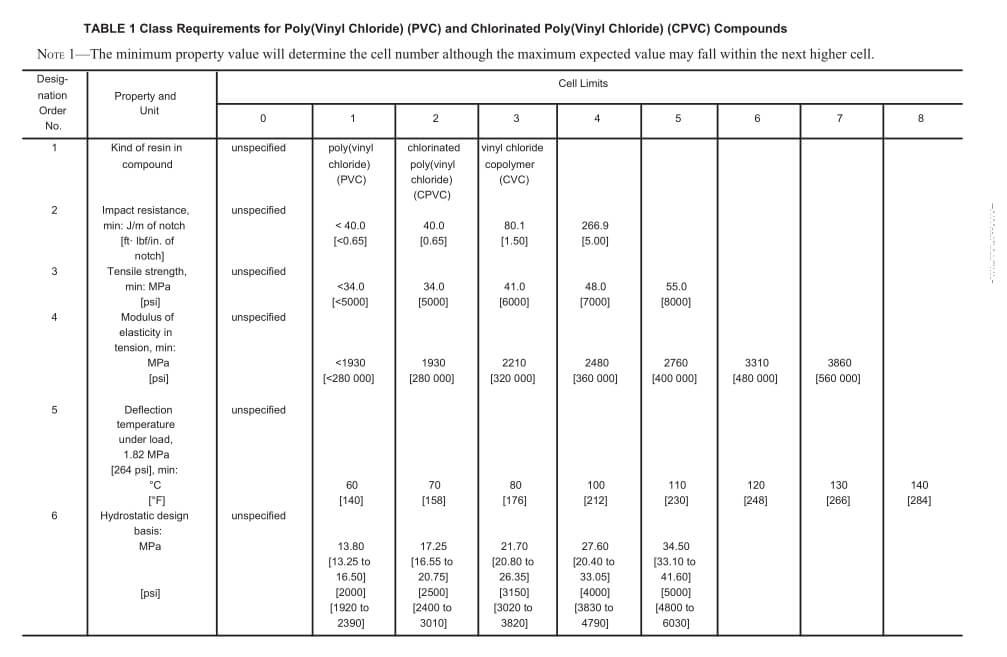
Within rigid PVC conduit, you’ll find various types used for different environments (typically in North America), such as Type A, Type EB, Type DB, SCH 40 & 80 series. And in Australia and New Zealand, rigid conduit can be divided into medium duty and heavy duty/ This means not all PVC rigid conduits are the same—some are thicker, and some are specially designed for underground use.
While flexible PVC conduit sometimes referred to as PVC corrugated conduit, or ENT (Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing). This conduit is bendable and easy to route around corners. It’s usually used indoors, in tight spaces, or behind walls.
3.2 Different Types of Rigid PVC conduit
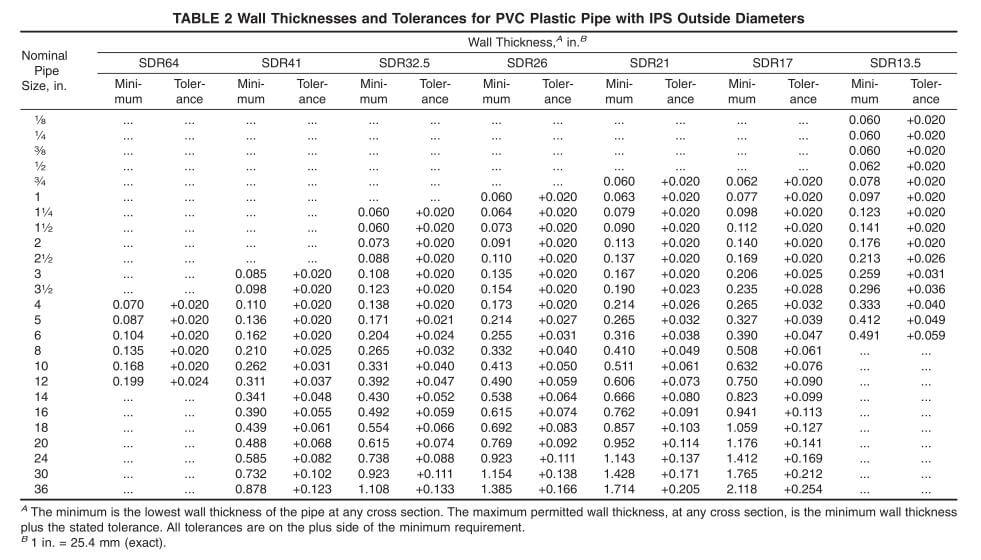
3.2.1 Schedule 40 PVC Conduit
Wall Thickness & Design: Schedule 40 offers a balanced wall thickness, making it suitable for both above-ground and underground applications. It’s often chosen for standard electrical wiring in residential or commercial buildings where moderate protection is sufficient.
Common Applications: Used in both above-ground and underground systems. Suitable for residential, commercial, and light industrial settings. Performs well in environments not exposed to high external forces.
Strengths:
●Easy to cut, glue, and install.
●Compatible with solvent cement bonding.
●Good UV resistance (when UV-rated).
●Flame-retardant versions available.
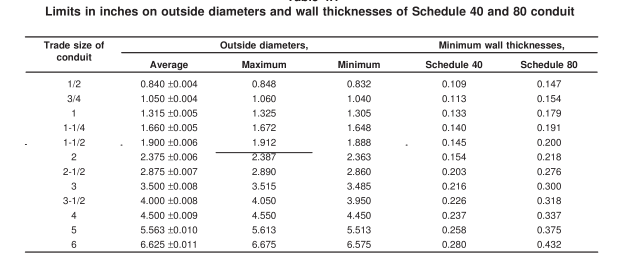
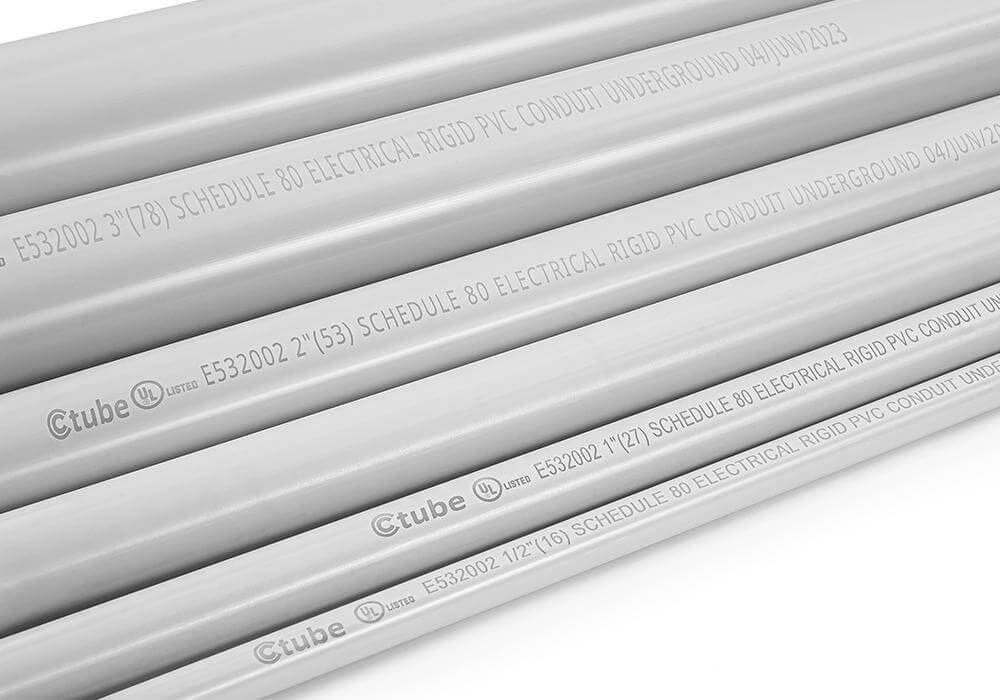
3.2.2 Schedule 80 PVC Conduit
Wall Thickness & Strength: Schedule 80 increases wall thickness significantly compared to Schedule 40, boosting mechanical strength. This makes it ideal for harsh environments where conduits are exposed to high traffic, potential impact, or need to support long spans without sagging.
التطبيقات: Recommended for locations exposed to high mechanical stress, such as commercial parking structures, utility service entrances, or exposed industrial zones. Often used where conduit must run vertically along exterior walls.
المزايا:
●Withstands greater mechanical abuse.
●Approved for direct burial and concrete encasement.
●Maintains structural integrity in demanding environments.
3.2.3 Type EB (Encased Burial) Conduit
Design Purpose: Type EB (Encased Burial) has thinner walls than both SCH 40 and 80 because it is designed to be encased in concrete, which provides the necessary external protection. Its structural role is secondary, relying on the concrete for durability.
Wall Design: Thinner than SCH 40 but designed to withstand the surrounding structural support of concrete.
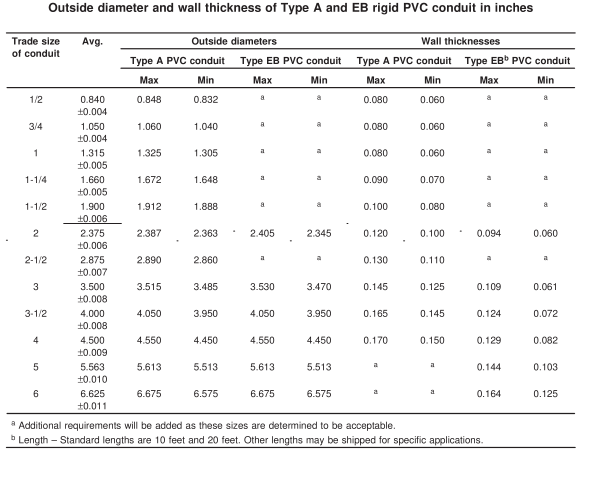
3.2.5 Type A PVC Conduit
Design & Application: Type A PVC conduit has wall thickness similar to SCH 40 but with lower tolerance limits, which results in lower mechanical strength. This type is often used in light-duty or communication projects where minimal physical stress is expected.
3.2.4 Type DB (Direct Burial) Conduit — DB60 / DB100 / DB120
Rigid PVC conduits under the “DB” classification are built for direct burial, meaning they can be installed directly into soil without the need for concrete encasement.
Type DB products can also be used for concrete encased applications where specified.
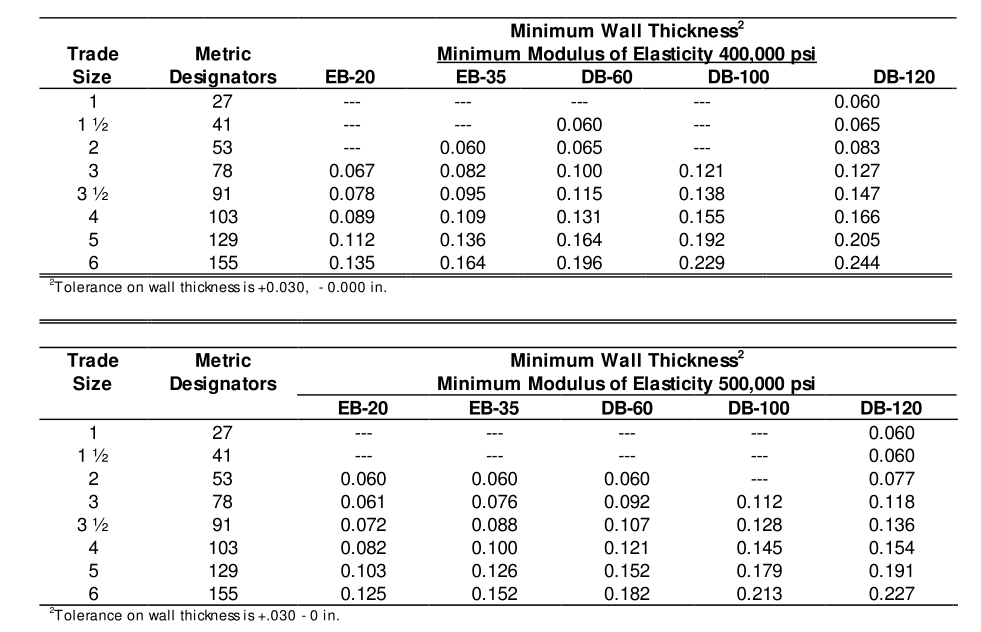
They come in three grades—DB60, DB100, and DB120—indicating increasing strength. The higher the DB number, the thicker the wall and the better the conduit can withstand soil pressure, thermal expansion, and mechanical loads.
3.3 Choosing Between Different Rigid PVC Conduit
As what we mentioned above, here we make some tips for you.
Each PVC conduit type reflects a balance between structural integrity, application suitability, and installation efficiency.
For above-ground exposed installations, especially where UV exposure is a concern, Schedule 40 or Schedule 80 with UV-resistant ratings is ideal. SCH 80 is particularly well-suited to outdoor vertical runs and installations on external walls due to its rigidity and strength.
In underground systems, selection depends on burial method:

If concrete encasement is planned (e.g., under roadways), Type EB is most appropriate.
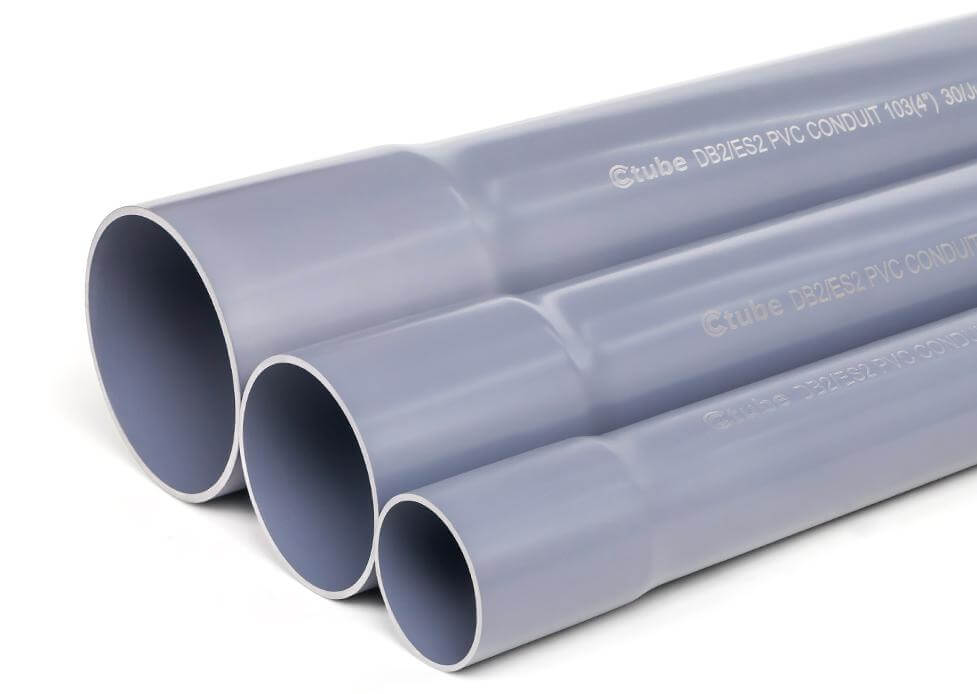

If the conduit is to be directly buried in soil, choose Type DB, with DB100 or DB120 offering more protection in areas with heavy soil pressure, such as driveways or industrial zones.
Type A is mostly used for indoor or controlled environments where the conduit is protected from mechanical stress, UV, or moisture. It is commonly seen in utility buildings, commercial interiors, or pre-fab structures.
Budget is also an important factor to consider. While Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduits offer enhanced strength and performance, they typically come at a higher cost compared to lighter-duty options like Type A or DB-rated conduits.
If you’re unsure which conduit suits your project best—or want to get detailed product information and pricing—feel free to contact us!
Our team is here to help you choose the most cost-effective and efficient solution for your specific needs.
3.4 Common Standards For PVC Conduit
UL 651 – Schedule 40 and 80, Type A, EB Rigid PVC Conduit and Fittings
UL 1653 – Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT)
AS/NZS 2053.2 – Rigid plain conduits and fittings of insulating material
AS/NZS 2053.5 – Corrugated conduits and fittings of insulating material
CSA C22.2 No. 211.2 – Canadian standard for rigid PVC conduits
NEMA TC 6 & 8-2013 – Polyvinyl Chloride(PVC) Plastic Utilities Duct for Underground Installers
IEC 61386-21 – Rigid Conduit Systems
IEC 61386-23 – Flexible Conduit Systems
4. What is Metal Conduit?
Metal conduit, on the other hand, is typically made from steel, or aluminum.
4.1 Types of Metal Conduit
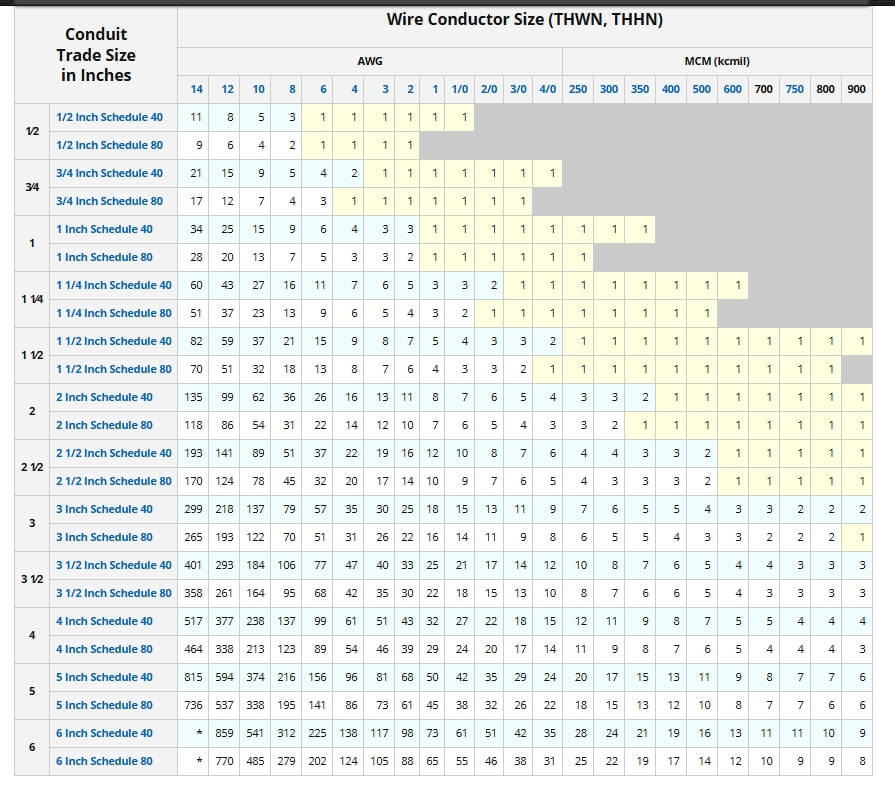
Common rigid types include EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing), RMC (Rigid Metal Conduit), and IMC (Intermediate Metal Conduit).
However, when people say “rigid metal conduit” (RMC) specifically, they are usually referring to the thick-walled, threaded steel conduit that offers the highest level of mechanical protection.
And also have flexible metal conduit (FMC).
These are known for their strength, durability, and ability to act as a grounding path.
4.2 Different Types of Rigid Metal conduit
There are also several distinct types of rigid metal conduit, each with its own material, wall thickness, connection method, and ideal application scenarios.
Some times people clarify different types of metal rigid conduit by their wall thickness, and they can be commonly divided into 3 types Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC), Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC), Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT).
4.2.1 Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC)
Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC) is also know as Galvanized Rigid Conduit (GRC) , Rigid Aluminum Conduit (RAC), Stainless Steel Conduit (SSC or RMC-SS). They are categorized according to the material and has different names.
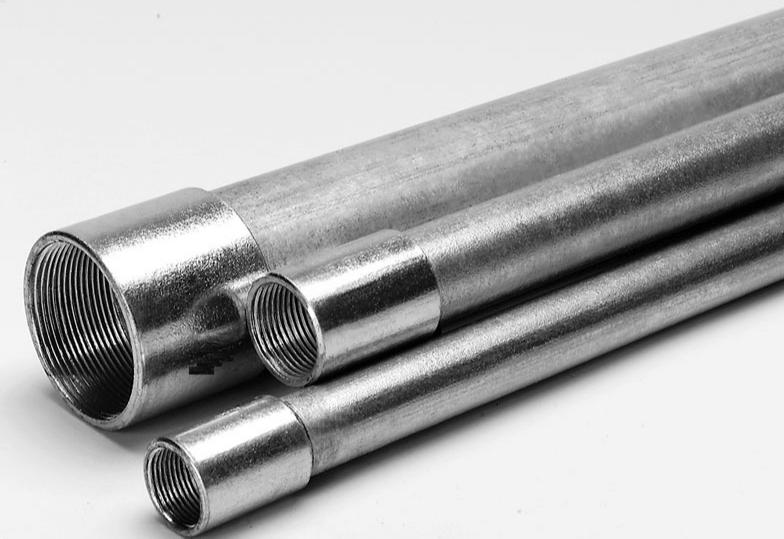

RMC have threaded at ends, allowing secure connections with threaded couplings and fittings.
RMC is the strongest and thickest. It provides superior protection in environments where heavy physical impact is possible.
Additionally, Galvanized RMC has a zinc coating that protects the steel from rust, making it ideal for outdoor and underground installations when paired with the proper fittings and seals.
RMC in aluminum (RAC) or stainless steel (SSC) offers even greater corrosion resistance, especially in marine, coastal, or chemical plant environments
4.2.2 Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC)
Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC) is a slightly lighter and more economical version of RMC. Also have threaded at ends like RMC.
IMC offers a good balance between protection and manageability. It is strong enough for most commercial and industrial applications.
4.2.3 Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT)
Conduit EMT has the thinnest walls, making it the lightest and easiest to bend by hand or with a simple tool. However, this also means it’s best suited for indoor environments where mechanical hazards are minimal.
EMT electrical conduit is not inherently rust-proof, but versions with zinc coating or protective enamel are available for moderately damp locations.
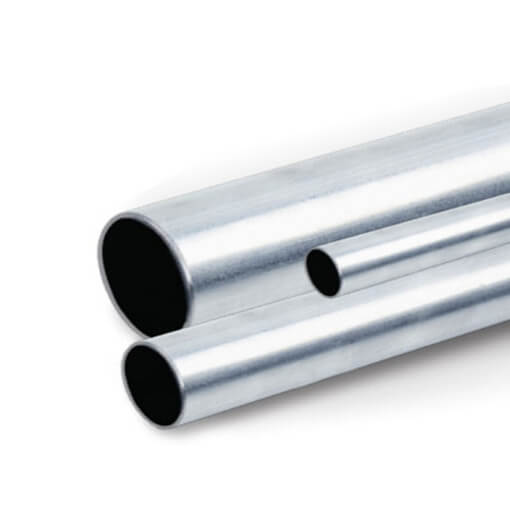

Compared to true rigid metal conduit (RMC), EMT has thinner walls, is non-threaded, and offers less mechanical protection.
So it’s technically not classified as a “rigid metal conduit” under some codes due to its thinner walls.
But EMT electrical conduit pipe comes in straight lengths and looks similar in shape to rigid conduits so here we introduce is this section.
4.3 Choosing Between Different Rigid Metal Conduit
As mentioned above, each type of metal conduit serves a specific purpose. We provide the tips for you as before.
For maximum strength and durability, especially in outdoor or high-impact areas like utility service entrances or exposed mechanical rooms, Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC) is the best choice. It offers the thickest wall and highest level of mechanical protection, often required by code in demanding commercial or industrial settings.
Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC) is a strong alternative when you still need solid mechanical protection but want to reduce material weight and cost. It performs well in most commercial environments and is also approved for outdoor and underground use.
Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) is ideal for indoor applications or places with low physical risk. It’s easier to install and bend, and often used in commercial office spaces, ceiling installations, and conduit runs inside walls. However, because it has thinner walls and is not threaded, EMT provides less protection and may not be suitable for exterior or underground use without additional safeguards.
Cost efficiency also matters. RMC is the most expensive due to its weight and material, followed by IMC.
4.4 Common Standards For Metal Conduit
UL 6 – Rigid Metal Conduit
UL 1242 – Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC)
UL 797 – Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT)
AS/NZS 2053.7- Rigid metal conduits and fittings
AS/NZS 2053.8 – Flexible conduits and fittings of metal or composite material
IEC – Same as PVC conduit
5. What Is the Difference Between PVC Conduit and Metal Conduit (EMT, IMC, RMC)?
After a overview of rigid conduit types between PVC and metal , let’s now make a comparison between these two common materials for rigid conduitl. And hope the information help you to make a better choice.
The main difference between PVC conduit and metal conduit (such as EMT, IMC, and RMC) lies in their material properties and how they perform in different environments.
PVC conduit is made from plastic, making it lightweight, easy to install, and resistant to corrosion. It’s especially ideal for damp or underground locations, where rust is a concern.
It’s also more cost-effective and simpler to work with, which helps reduce labor time and installation costs.
On the other hand, metal conduits like EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing), IMC (Intermediate Metal Conduit), and RMC (Rigid Metal Conduit) offer superior strength and mechanical protection.
They are preferred in commercial or industrial settings where durability and fire resistance are important. EMT is lighter and easier to bend, while IMC and RMC are thicker and provide more robust protection—particularly in high-impact or exposed areas.
In short, choosing between PVC and metal conduit often depends on the specific demands of your project.
6. How to Choose Between PVC Conduit and Metal Conduit?
When selecting between PVC and Metal electrical conduit, it’s crucial to evaluate project requirements, environmental factors, and budget constraints.
1. تقييم الظروف البيئية لموقع التركيب، بما في ذلك التعرض للرطوبة والمواد الكيميائية والمواد المسببة للتآكل.
2. ضع في اعتبارك درجات الحرارة القصوى والتعرض للأشعة فوق البنفسجية إذا كان سيتم تركيب القناة في الخارج أو في المناطق التي تتعرض لأشعة الشمس المباشرة.
3. تقييم تكلفة المواد والتركيب ومتطلبات الصيانة طويلة المدى لكل نوع من أنواع المواسير.
4. تأكد من أن نوع القناة المختار يلبي معايير الامتثال التنظيمية ومتطلبات التأمين للمشروع المحدد وموقع التثبيت.
5. يمكن أن توفر التشاور مع خبراء الصناعة ومراجعة دراسات الحالة السابقة رؤى قيمة حول الاختيار الناجح للقناة.
من خلال وزن هذه العوامل بعناية، يمكنك ضمان الاختيار الأمثل للقناة لمشروعك الكهربائي، مما يعزز الكفاءة والموثوقية والسلامة.
Certainly, as a PVC electrical conduit manufacturer,Ctube is committed to meeting the needs of our customers and continuously pursuing innovative research and development.

We’ve remained dedicated to improving the drawbacks of PVC electrical conduit and fittings by focusing on products that boast greater waterproofing, corrosion resistance, and pressure resistance, along with enhanced UV and fire resistance.
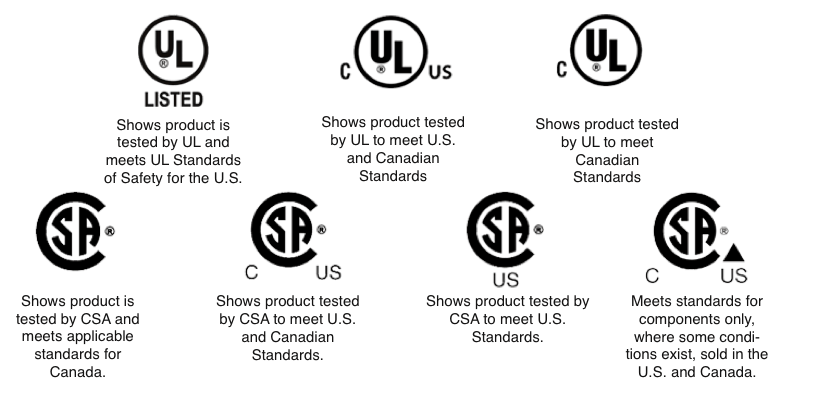
Our products are certified by UL 651, CSA, AS/NZS 2053, CE, ROHS, IEC, etc.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، قمنا بتطوير قنوات منخفضة الدخان وخالية من الهالوجين لتعزيز اعتبارات السلامة والبيئة.
If you’re interested in our products, feel free to contact us anytime.
Edited by Ctube Official
Electrical Rigid Conduit Comparison: PVC Conduit vs Metal Conduit (EMT, RMC, IMC) اقرأ أكثر "