Everything You Need to Know About Solar Conduit (2025 Updated)
1. Introduction to Solar Conduit
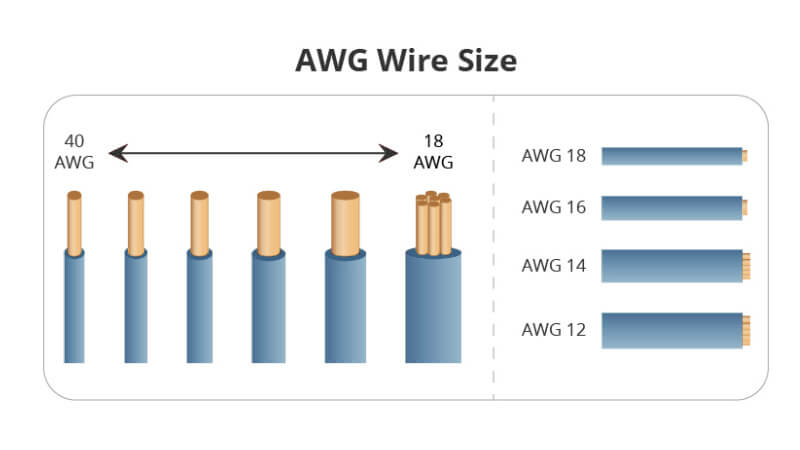
1.1 What Is Solar Conduit?
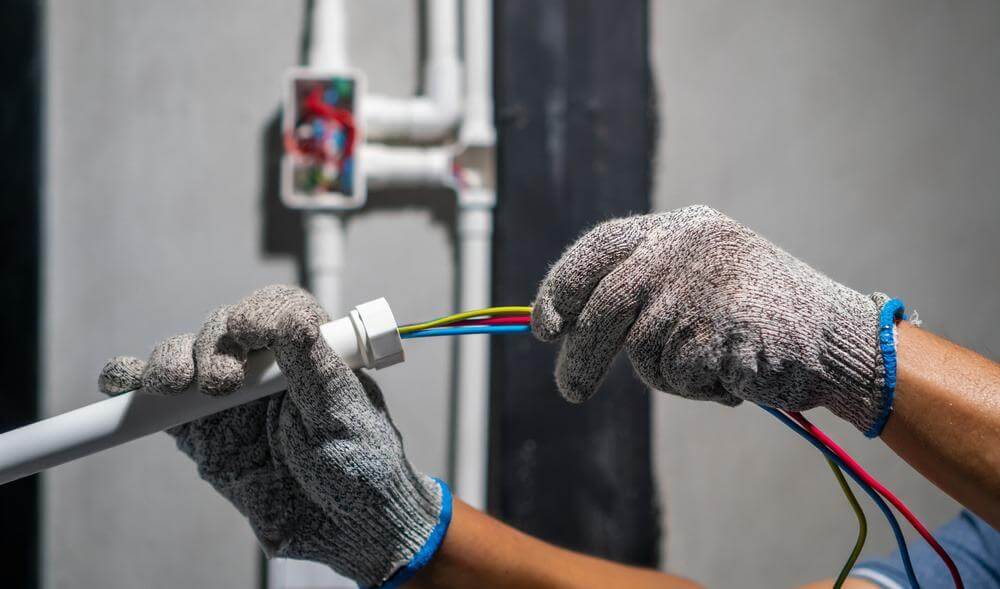
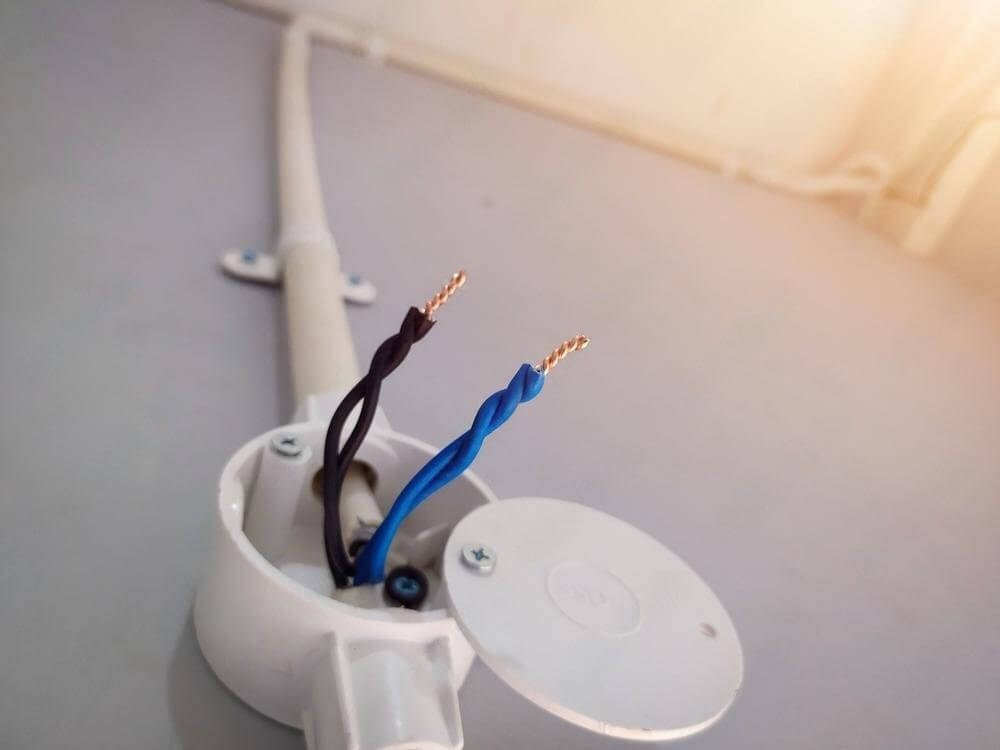
Solar conduit is a protective pipe for your solar system’s wiring. Whenever solar panels generate electricity, that power needs to travel—often across rooftops, down walls, or underground—before reaching your inverter or power box. And just like water needs a pipe to flow safely, solar wiring needs a safe pathway too. That’s the job of solar conduit.
Made from tough materials like PVC, metal, or fiberglass, solar conduit is specially built for outdoor use. It keeps your electrical cables organized, secured, and out of harm’s way—whether on a home rooftop or a solar farm. If you‘re a contractor, electrician, homeowner, or project planner, this article may be helpful for you. We’ll break down the key differences between different solar conduits, and help you choose the right materials that meet safety standards and last longer in real-world conditions.
1.2 Why Is Conduit Necessary in Solar Installations?
Solar conduit might sound like just another type of electrical conduit but actually it’’s the result of years of experience in the field.
At first, people used standard conduits for solar systems. But over time, they started to notice a problem: conduits exposed to strong sunlight would turn brittle, fade in color, crack, or even break apart.
Especially on rooftops or open fields where the sun beats down for hours, regular conduit just didn’t last. And solar conduit can avoid these situation we mentioned above and prolong the lifespan of conduit.
That’s when the need for a more durable, UV-resistant solution became clear — and solar conduit was developed. You could say it’s not just a product, but a lesson learned through trial and error.
In most installations, conduit is required by building codes and safety standards, especially when wires are run outdoor. It ensures your project is up to code, safe to use, and built to last.
1.3 What Exactly Does Solar Conduit Protect Against?
🟠 From the Sun (UV Damage)
Long-term exposure to sunlight can be brutal. UV rays slowly break down insulation, causing wires to become brittle and crack.
→ Solar conduit acts like sunscreen and a shade cloth rolled into one—blocking those rays and preserving the wire’s integrity.
🔵 From the Weather (Moisture & Temperature)
Rain, snow, extreme heat, or freezing cold—outdoor wiring faces it all.
→ Conduit acts like a raincoat in winter and a heat shield in summer, keeping your system dry and stable.
🟢 From Physical Threats (Impact & Interference)
Rodents, sharp tools, falling debris, or even careless footsteps can damage exposed wires.
→ A conduit acts like armor, stopping bites, dents, and wear before they become costly problems.
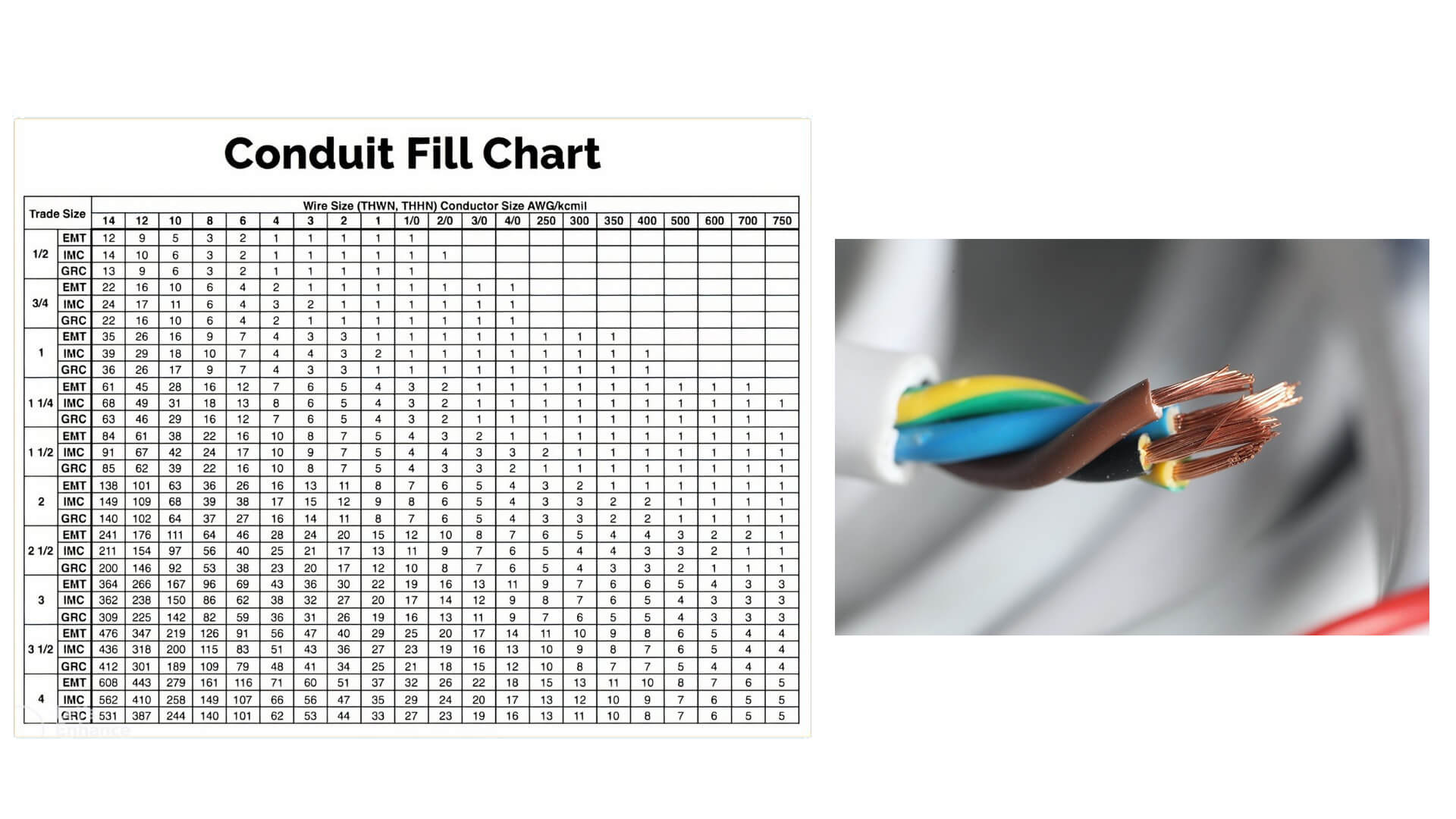
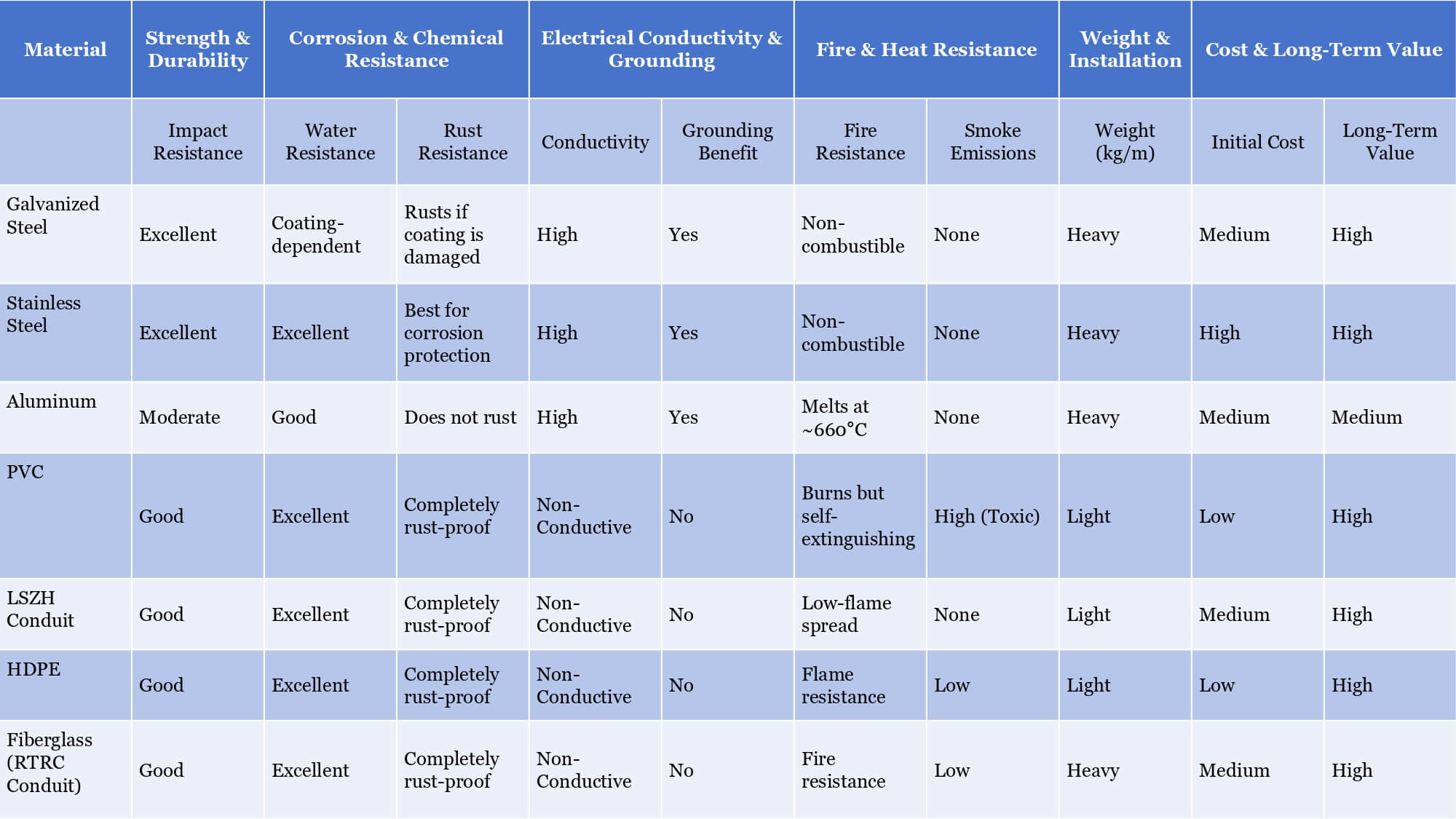
2. Common Materials and Types of Solar Conduit and Their Applications
Now, we can classify solar conduit in a few ways — by material, shape, or flexibility. Beacuese different materials and types have very different performance levels, certifications, and installation uses.
2.1 Solar UPVC Conduit Comparison: Benefits and Best Uses
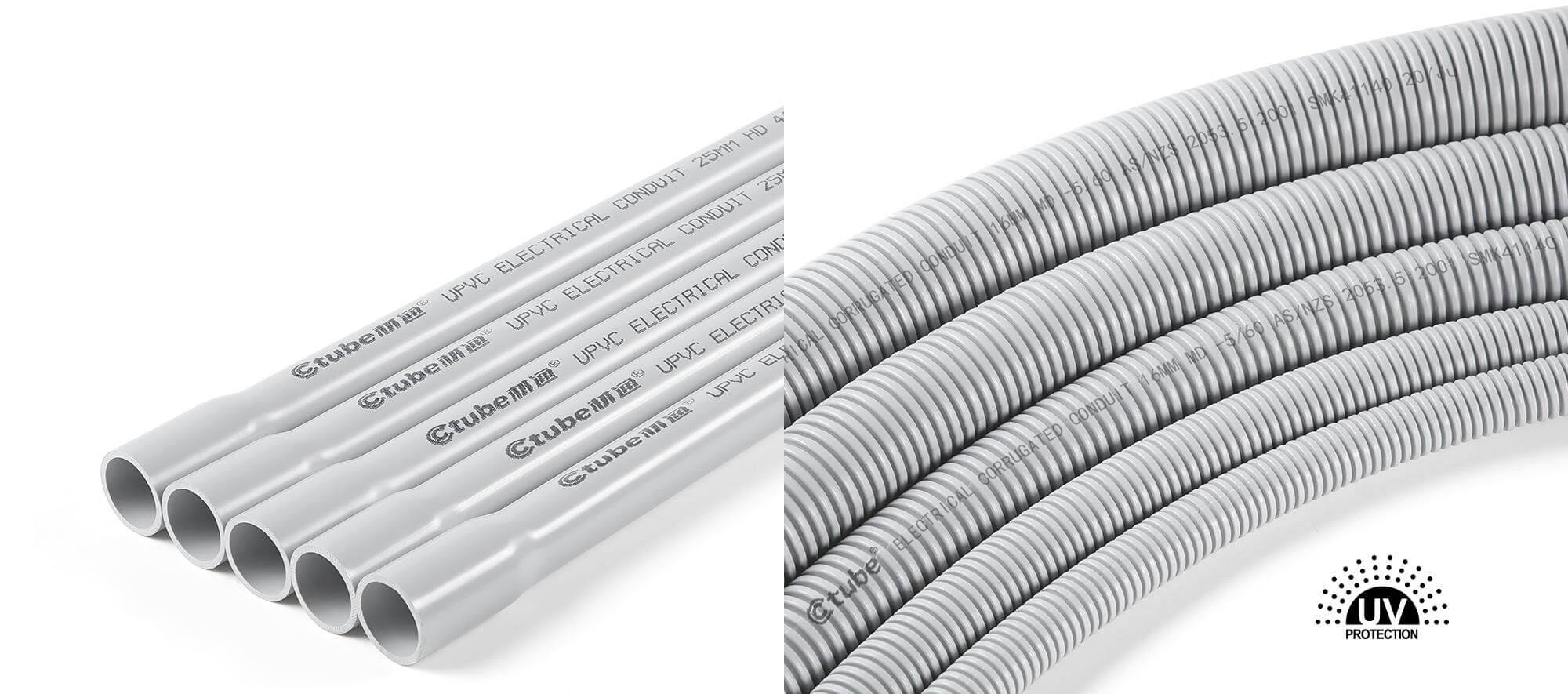
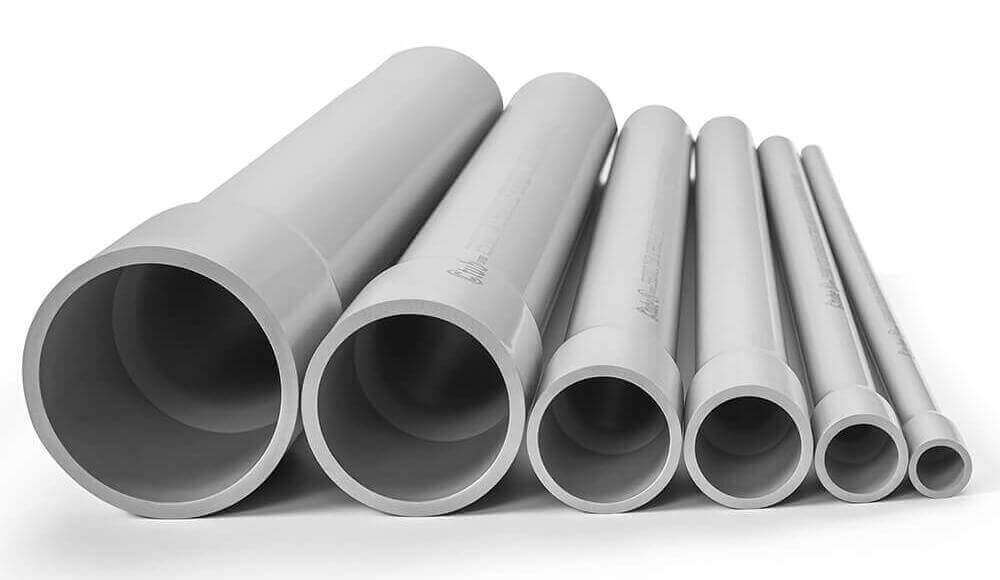
When it comes to cost-effective, durable, and reliable solutions for solar wiring, PVC is often the first material that comes to mind. It’s one of the most widely used conduit types for solar installations — and for good reason.
PVC solar conduit is highly valued for its resistance to UV rays, moisture, and extreme temperatures, which is crucial for keeping solar wiring safe in exposed environments like rooftops. It’s also lightweight, easy to handle, and easy to install, making it a good choice for both residential and commercial solar projects.
2.1.1 PVC-U VS PVC-P
There are two main types of PVC based on the amount of plasticizer used:
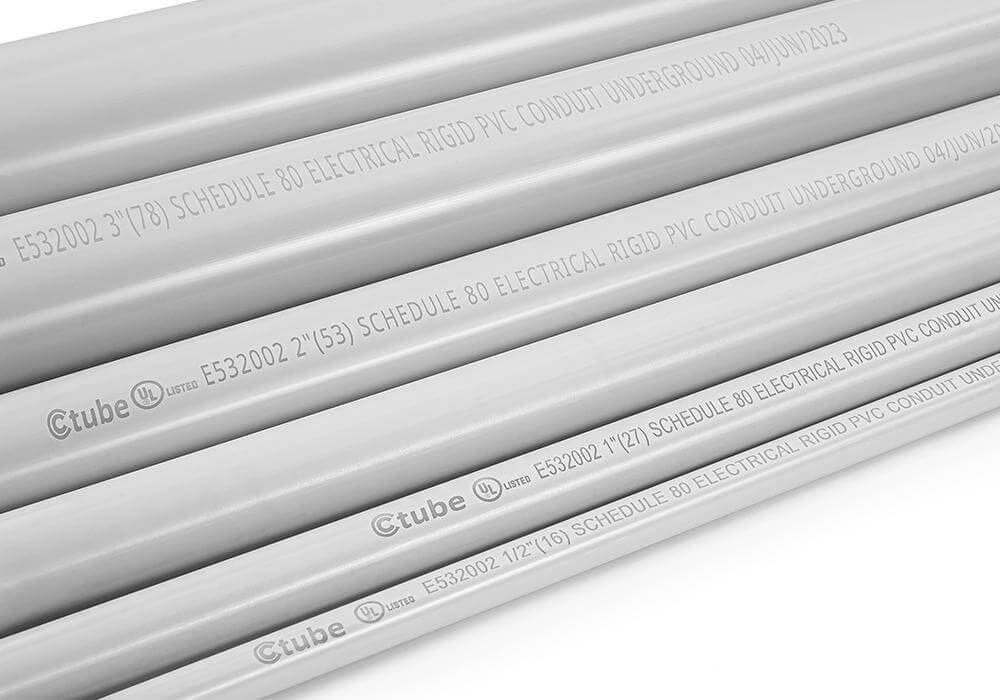
Rigid PVC (PVC-U): Known as unplasticized PVC or non-plasticized PVC, this variant contains minimal or no plasticizer (less than 10%). The content may vary depending on the manufacturer, which could be related to their specific production process. Rigid PVC is widely used in applications requiring mechanical strength and temperature resistance. It is often used for solar electrical conduit because of its ability to withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress.
Flexible PVC (PVC-P): This type contains between 30-70% plasticizer, which makes it flexible and much easier to be bent with some tools. However, because of this, its strength and resistance to UV rays aren’t as high as those of the unplasticized version.
2.1.2 Special Measures or formulation about Solar Conduit
After discussing the basic characteristics of UPVC and PVC, it’s important to address how these materials perform when exposed to solar radiation, which is a key factor in their outdoor durability.
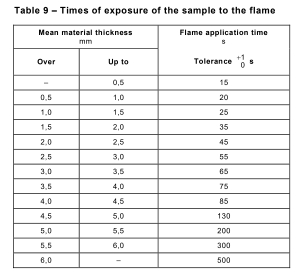
Although there are no standard practical tests for measuring a material’s resistance to solar radiation, experience has shown that the durability of UPVC and PVC against UV rays can be significantly enhanced by adding certain chemical agents.
Acoording to AS/NZS 2053 Standard, part 1, adding 1.5% titanium dioxide (TiO₂) to UPVC resin can provide sufficient protection against solar radiation. For plasticized PVC and polyethylene (PE), adding 2% carbon black can offer similar protection. These additives help prevent degradation, discoloration, and brittleness caused by prolonged UV exposure. Isn’t it amazing? Truly a testament to human ingenuity!
2.1.3 UPVC Rigid Conduit and Flexible Conduit
Of course, it’s important to point out that this difference refers to the material composition—whether it’s soft or hard—not the shape. In fact, PVC/ UPVC conduits come in both flexible and rigid forms in terms of shape, too!
So let’s break down the two UPVC conduit forms so it’s easier to see which one might be best for your solar project.
Rigid UPVC Conduit, also known as straight conduit, this is the good option built for durability and protection.
Smooth Inside and Out: The interior surface is smooth, which helps wires glide through with less friction. The outer surface is also clean and sleek.
Bell End Design: Most rigid UPVC conduits come with a bell end, allowing one conduit to easily slide into the next. This helps with quick, secure connections.
Bending: This conduit doesn’t bend easily. If you need to change direction, you’ll need heat bending tools or pre-bent accessories like elbows or sweeps.
And for flexible UPVC conduit (Corrugated) , although made from the same base material (UPVC), this version is shaped into a corrugated, bendable form. In the North American market, PVC flexible conduit is commonly known as Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing, or ENT for short.
Special Design: A pliable corrugated raceway of circular cross-section.
Bendable by Hand: The corrugated design makes it flexible without needing tools. You can easily navigate around corners, curves, or equipment.
No Bell End: Typically, corrugated conduits come with plain cut ends, and connections are often made using threaded fittings or snap-lock connectors.
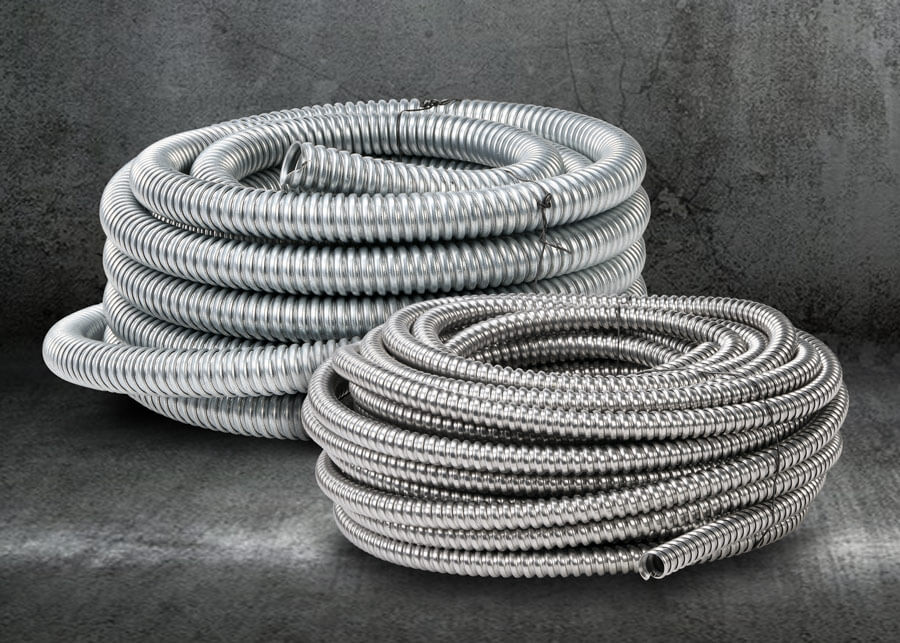
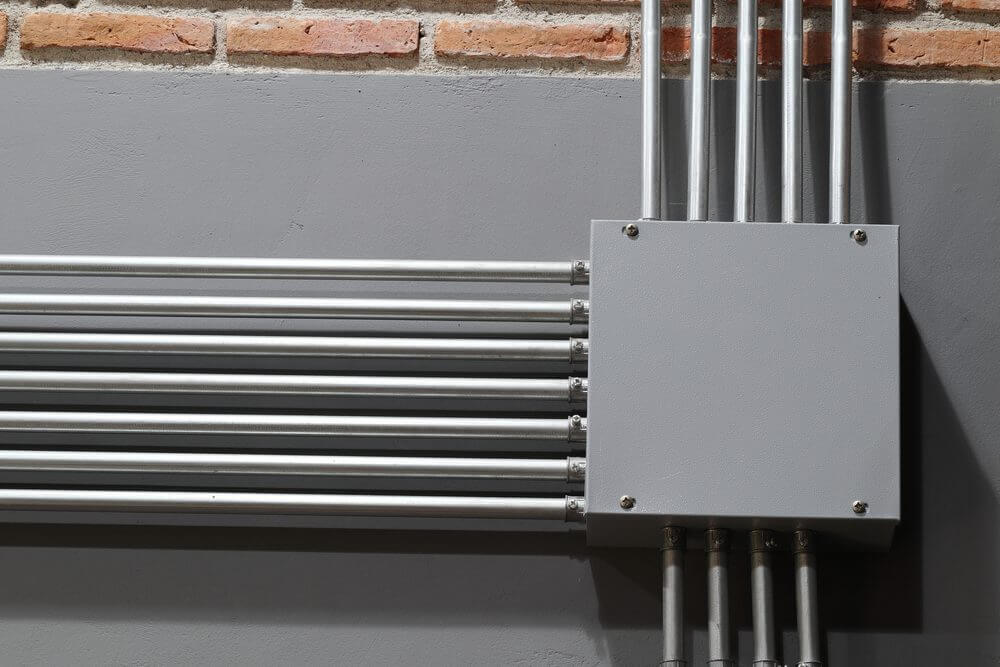
2.2 Exploring Metal Conduit Options for Solar Projects: Types, Pros, and Best Use Cases
Known for their strength, security, and reliability, metal conduits offer superior protection for electrical systems, especially in environments where durability is critical.
Metal conduits come in a variety of materials, each providing different levels of protection, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. The most commonly used metals for conduit systems are steel, stainless steel and aluminum. Let’s take a quick look at what makes each one special.
2.2.1 Differerent Materials of Metal Conduit for Solar
Steel (usually galvanized): Think of this as the heavyweight champion. It’s super strong and great at standing up to bumps, knocks, and rough environments—perfect for areas where wires need extra protection. It also has a zinc coating that helps fight rust, but it’s still better suited for dry or indoor locations unless extra treated.
Stainless Steel: Now, this is the all-weather defender. It doesn’t rust easily, even in coastal areas with salty air or near chemicals. It’s more expensive, yes, but it’s also the best choice if you’re installing solar conduits somewhere harsh and want them to last a long time without a lot of maintenance.
Aluminum: Lightweight and easy to work with—great when you don’t want to wrestle with heavy pipe. It naturally resists corrosion and works well outdoors. The trade-off? It’s softer than steel, so it can get dented more easily if something hits it hard.
So, which one should you use? That depends on where you’re installing your solar panels, how exposed the site is to the elements, and how much protection your wiring needs.
2.2.2 Metal Rigid and Flexible Conduit
Now, let’s take a closer look at how metal conduits are categorized—because just like PVC, metal conduits also come in both rigid and flexible types. But since metals come in more varieties and combinations, the types of metal conduits are even more detailed and specific.
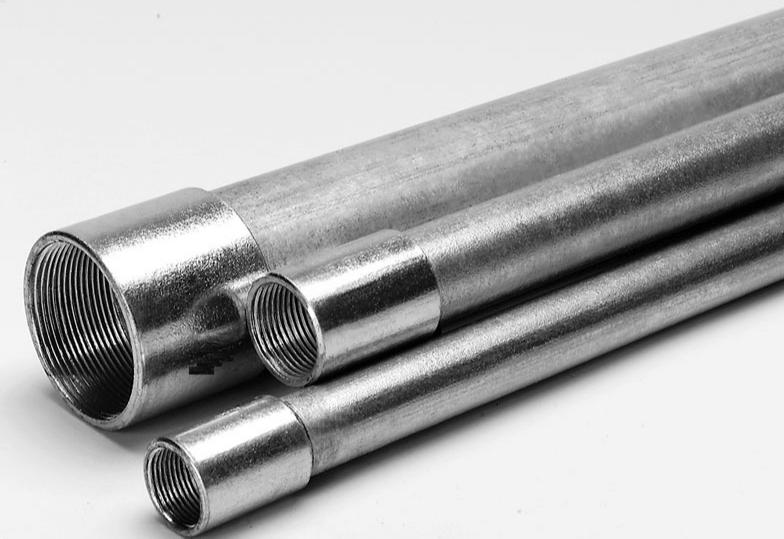
About the shape, just like PVC conduits, rigid metal conduits also come in straight lengths—typically 10 feet (around 3 meters) per piece.
These conduits have smooth inner and outer walls, making it easier to pull wires through without damaging the insulation. Many of them come with a bell-shaped end, also known as a “belled end” or “enlarged end.”
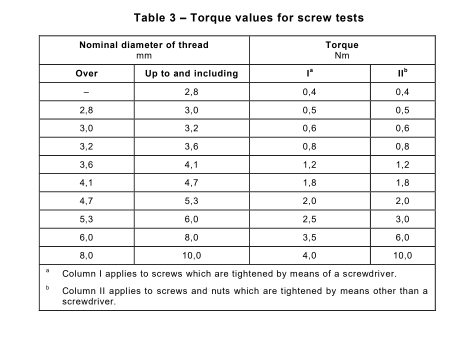
But here’s something unique about metal conduits: These belled ends often include factory-formed threads, especially for RMC and IMC. That means they’re ready to be screwed directly into couplings or threaded fittings, saving time and effort on the job site.
For EMT (which is typically unthreaded, but some also threaded), fittings are usually secured using set-screw or compression connectors, depending on the environment and code requirements.
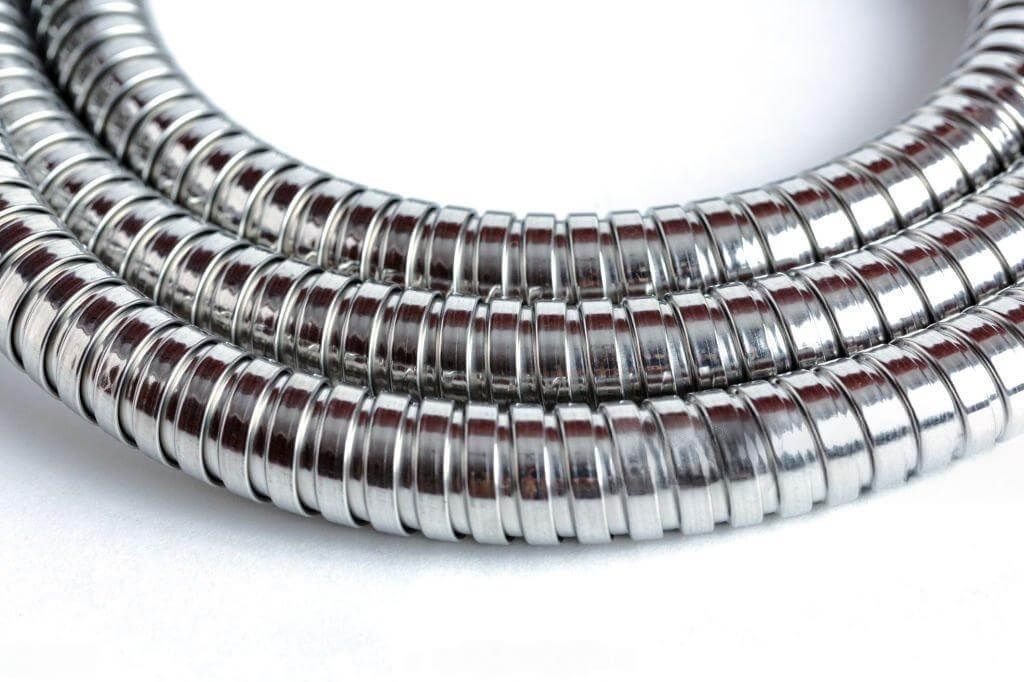
Not all metal conduits are straight and stiff—some are bendy and flexible, kind of like a metal version of a “snake tube.” This type is called Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC), also known as corrugated metal conduit, because of its spiral, wavy shape that looks a lot like a spring.
As PVC flexible conduit we have mentioned, the surface of FMC is not smooth—it has a bumpy, spiral-shaped outer layer that gives it great flexibility. You can also easily bend it by hand, which makes it super helpful when you need to route around tight corners or work inside walls or equipment.
If the environment is humid or outdoors, there’s also a version called Liquid-Tight Flexible Metal Conduit (LFMC). It has a waterproof plastic jacket over the metal core—perfect for solar installations exposed to rain or high humidity.
2.2.3 Different Types of Metal Conduit: EMT, IMC, RMC, FMC
It can feel a little overwhelming at first—with names like EMT, IMC, and FMC flying around—but don’t worry. We’ll give you a simple overview here to help you get your bearings. And if you’re curious to dive deeper, we’ve created a separate guide that explains each type of rigid conduit and flexible conduit in more detail—just click through and explore at your own pace.
RMC – Rigid Metal Conduit: The heavyweight champion of metal conduit. Usually made of galvanized steel or stainless steel.
It’s like the bodyguard of conduit—bulky but dependable. Best for industrial solar fields or rooftops where strength and weather resistance are key.
IMC – Intermediate Metal Conduit: The middleweight. Strong, but not quite as bulky as RMC.
Thinner walls than RMC, but still rigid and tough. Lighter and easier to handle than RMC. IMC is like RMC’s leaner sibling—still strong, but a bit more.
EMT – Electrical Metallic Tubing: The lightweight champ. Usually steel or sometimes aluminum. Not recommended for severe outdoor use unless corrosion protection is added. Of course, not suggested for outdoor solar application, here we just talking about this.
FMC (Flexible Metal Conduit): Usually made from galvanized steel or aluminum. It’s got those signature corrugated, spiral-wound grooves.
Areas where you need to bend the conduit to go around corners or tight spaces—think of places where you don’t have room for rigid pipes.
It’s not the toughest option out there, so if you need something super strong for really harsh conditions, it might not be your best bet.
LFMC (Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit): Like FMC, but with a liquid-tight plastic coating over the metal. Still that same flexible, spiral-wound shape, but now it’s protected against water, oils, and other liquids.
It’s way better at keeping moisture out, so it’s great for outdoor solar setups that will face rain or other wet conditions.
We hope this guideline helps you navigate the world of PVC and metal conduits for solar application. Whether you’re working on a large-scale solar energy project or a smaller rooftop installation, there’s a conduit type that suits your needs.
Now that we’ve covered the metal conduit options, let’s move on to another popular choice for solar projects: RTRC (Rigid Thermoset Resin Conduit).
2.3 Understanding RTRC Solar Conduit for Outdoor Environments
RTRC, short for Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Conduit, might sound like a mouthful—but don’t worry, it’s easier to remember its more common name: fiberglass conduit.
This type of conduit is made from thermosetting resin (like epoxy or polyester) that’s reinforced with glass fibers, giving it an impressive combo of lightweight structure and high strength.
You’ll only find RTRC in rigid forms, not flexible ones. But what it lacks in bendability, it more than makes up for in durability. Unlike some older or heavier metal options, RTRC is corrosion-resistant, non-conductive, and doesn’t react to moisture, chemicals, or UV exposure—a perfect fit for harsh outdoor solar environments.
And here’s another bonus: it’s incredibly lightweight, often about one-fifth the weight of steel conduit. That makes it easier to transport, lift, and install, especially in large-scale solar farms where every pound counts. It’s a favorite in projects where environmental exposure is a concern—think deserts, coastal zones, or chemical plants.
However, RTRC does come with a higher price tag than traditional materials like PVC or even some metal conduits. But for long-term performance and reduced maintenance, many project planners consider it worth the investment—especially when reliability and longevity are key.
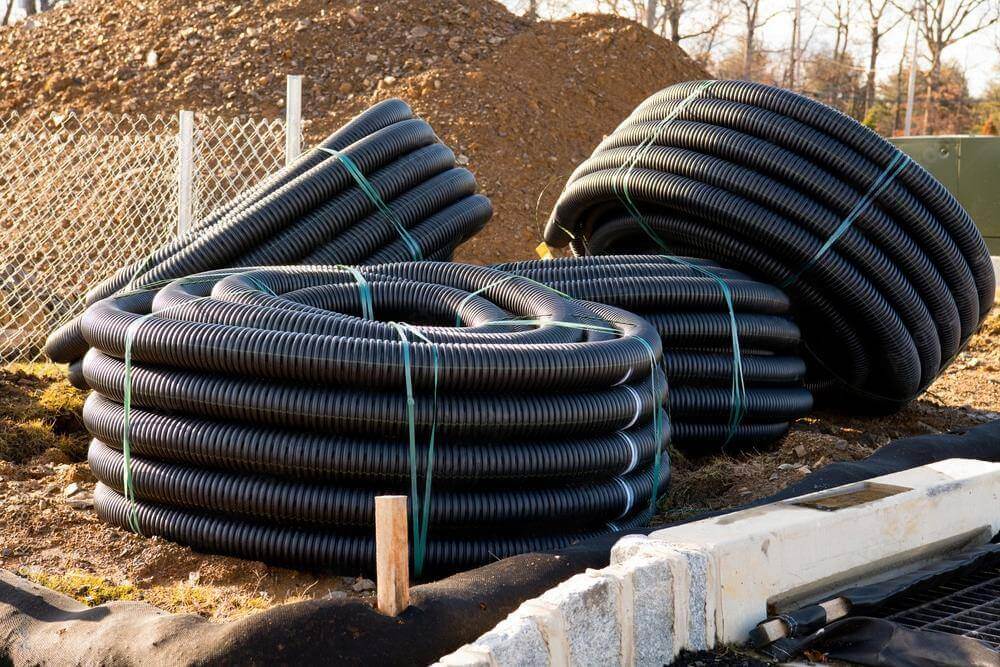
2.4 Getting to Know HDPE Solar Conduit with Flexible and Tough
Alright, now let’s talk about something totally different from the stiff and solid RTRC we just covered. Say hello to HDPE conduit, short for High-Density Polyethylene.
And here’s the fun part—it’s completely flexible! Yep, unlike RTRC that only comes in rigid form, HDPE is always bendy. Kind of like the yoga master of conduit options.
HDPE is a type of thermoplastic, which means it can soften when heated and harden again when it cools—pretty handy during manufacturing. It’s also crazy tough, lightweight, and doesn’t rust or corrode, making it a popular pick for underground or solar conduit systems or installations in tricky environments like wetlands, rough terrain, or places with harsh soil chemicals.
2.4.1 Smoothwall HDPE vs Corrugated HDPE
Now, here’s where it gets even more interesting—HDPE conduit isn’t just one type. It actually comes in two flexible styles, each with its own personality:
Smoothwall HDPE Conduit: This one’s like the smooth talker of the group. It has a clean, slick surface inside and out, making it super easy to pull cables through, especially over long distances.
Ideal for trenching, plowing, and horizontal directional drilling. The low friction saves time and energy during installation—literally.
Corrugated HDPE Conduit: This one looks like a slinky or those bendy straws. It has a rippled, bumpy outer wall, which makes it even easier to twist, bend, and fit around tight spaces or uneven terrain. Some types even have a smooth inner lining to help with cable pulling. Super flexible, super handy.
Both types usually come in long coils, sometimes hundreds of meters, which means fewer joints and fittings to worry about. That’s a big plus when you’re running cable over long solar fields or winding through challenging layouts.
Pretty amazing, right? It’s like the complete opposite of RTRC: where RTRC is only stiff, HDPE is only flexible. But both have their special role in solar projects.
2.5 PVC-Coated Metal Conduit:A Powerful Hybrid for Tough Solar Power
Ever heard the phrase “the best of both worlds”? Well, PVC-coated metal conduit is exactly that. When people realized that no single conduit material is perfect, why not combine the strengths of different materials and cancel out the weaknesses?
That’s how we ended up with this clever hybrid: a tough metal core wrapped in a protective layer of PVC plastic. Sounds simple, but the result is one of the most durable and weather-resistant conduits out there—perfect for some of the toughest solar project environments.
🧱 Metal Core for Strength
Inside, you’ve got either galvanized steel or aluminum. This gives the conduit excellent mechanical strength, meaning it can handle physical impacts, pressure, and heavy loads—perfect for industrial or outdoor solar installations where protection really matters.
🛡️ PVC Jacket for Protection
On the outside, there’s a thick coating of polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This coating protects the metal from corrosion, chemicals, UV rays, and even saltwater spray in coastal environments. It also adds an extra layer of electrical insulation, reducing the risk of shorts or damage to cables inside.
🌦️ Built for the Worst Weather
PVC-coated conduits shine in extreme outdoor conditions. Whether you’re dealing with scorching sun, pouring rain, snow, or salty air, this conduit type can take it. That’s why it’s often used in offshore solar farms, chemical plants, or heavy-duty rooftops.
Pretty cool, right? It’s like a superhero version of conduit—strong on the inside, smartly protected on the outside. If you’re looking for a solution that blends power, protection, and durability, PVC-coated metal conduit might just be your best friend on solar jobs that push the limits.
But superpowers don’t come for free, right? Of course, that also means it’s not cheap.
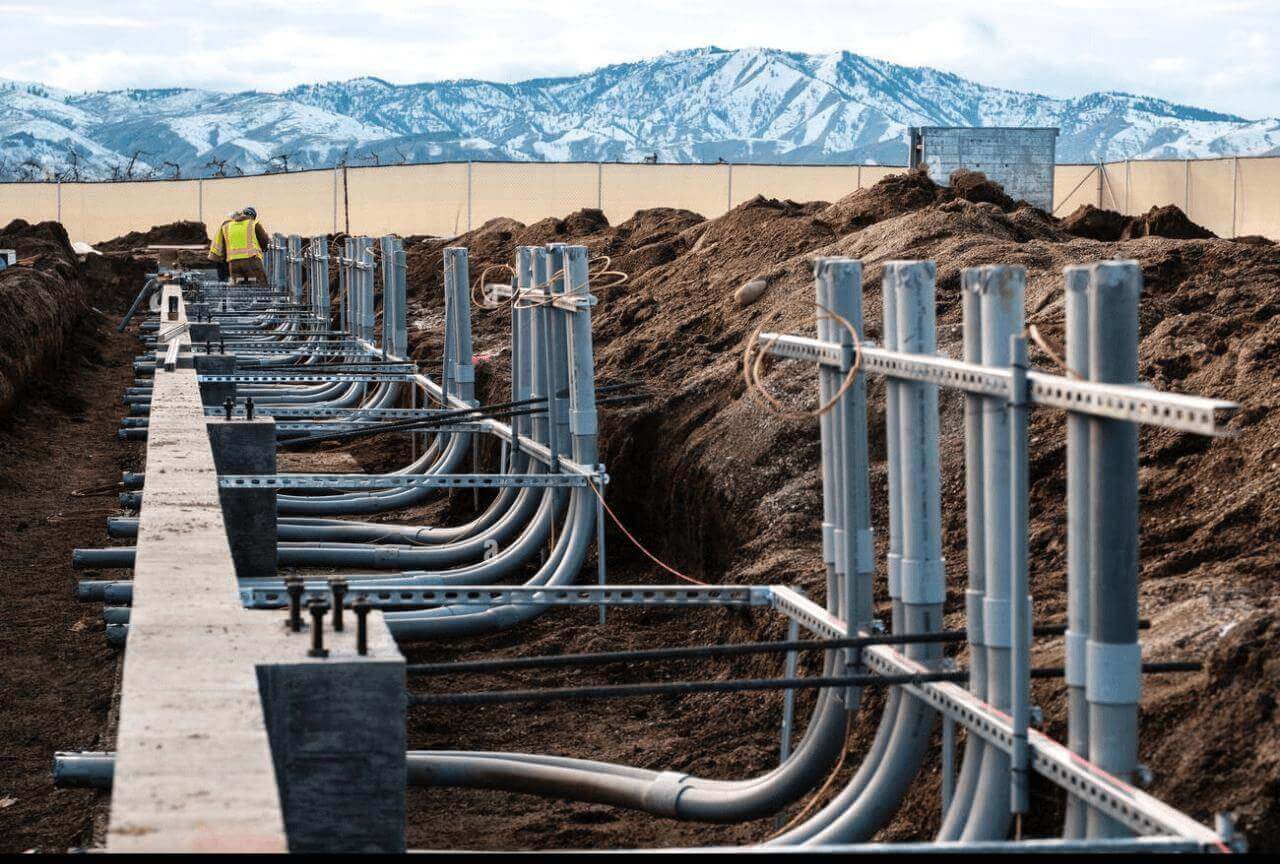
3. Solar Conduit Applications in Real-World Solar Installations
We’ve just taken a tour through a whole toolbox of solar conduit types—rigid, flexible, metal, plastic, even fiberglass and coated combos!
Now you might be wondering: Where do all these conduits actually go?
Well, let’s zoom out a bit and see how they fit into the real world. From sunny rooftops to dusty deserts, every conduit has its moment to shine (literally).
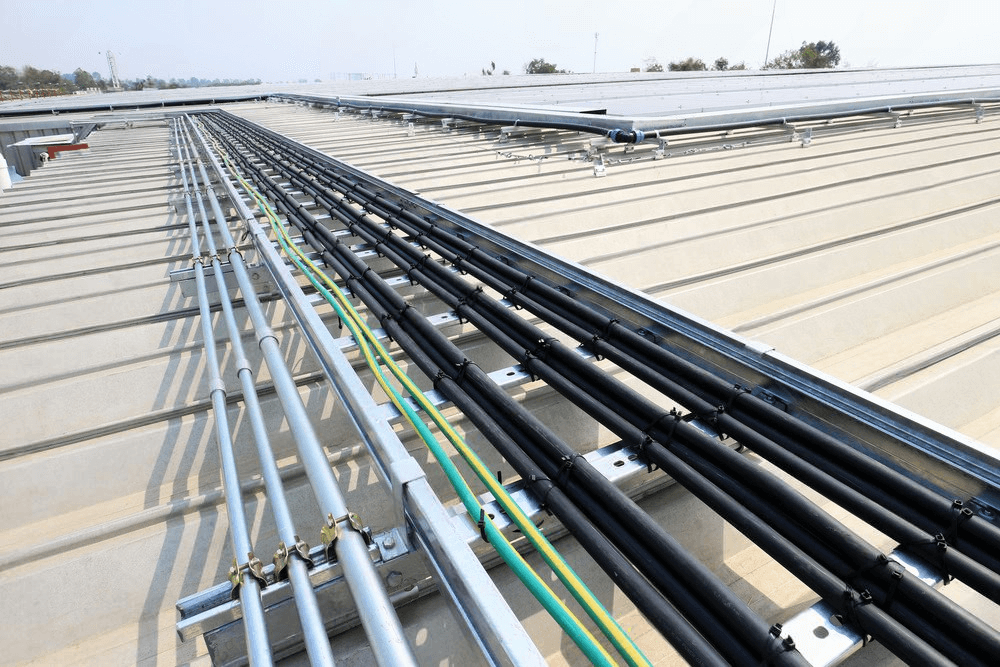
3.1 Utility-Scale Solar Farms
Utility-scale solar farms—those massive solar fields you see stretching across the horizon. These farms are often located in areas with intense sunlight, high temperatures, and dust—so using the right conduit ensures long-term reliability and safety.
They shoule be durable, UV-resistant conduits that can handle long cable runs, exposure to weather, and sometimes even underground installation.
PVC, RTRC, and HDPE are popular here due to their non-corrosive properties and flexibility in layout.
Metal conduits like RMC or IMC may also be used for exposed sections where extra mechanical protection is needed.
3.2 Rooftop Solar Installations
For residential or commercial rooftops, installers usually prefer lighter, easier-to-handle conduits.
FMC (Flexible Metal Conduit) might be used when weaving through tight roof spaces.
PVC and HDPE corrugated conduits are excellent for outdoor runs due to their UV resistance and ease of bending around obstacles.
3.3 Harsh Outdoor Environments
Think deserts, coastal areas, or snowy regions—these places demand special attention to environmental resistance.
RTRC conduits made from fiberglass stand out in corrosive or high-temperature zones, such as solar farms near chemical plants or industrial areas.
PVC with UV stabilizers or plasticized PVC with carbon black are used to prevent cracking and fading over time.
Alright, everything we’ve covered so far is just the tip of the iceberg. Picking the right conduit isn’t as simple as it sounds—it’s a balancing act between convenience, durability, and, let’s be real, your budget.
Sometimes you want easy installation, sometimes you need something tough enough for the elements, and sometimes, your wallet or budget call the shots.
So, take these tips, but remember, it’s all about choosing what works best for YOUR project.
4. Regulatory and Environmental Considerations for Solar Conduit Selection
4.1 Regulatory Requirements for Solar Conduit in PV Systems
Now that we’ve explored the different types of solar conduits and how they’re used, let’s take a moment to talk about something that’s crucial for any solar installation: regulations.
Regulations can vary from country to country, so always check the local rules where you’re installing.
Here we make the example in Australia and New Zealand, the AS/NZS 5033 standard governs solar system installations. Here’s a quick look at what it says:
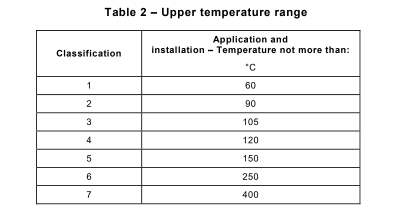
Conduit Requirements: Cables exposed outdoors must either be UV-resistant or protected by UV-resistant conduit. This ensures they won’t degrade under harsh weather conditions.
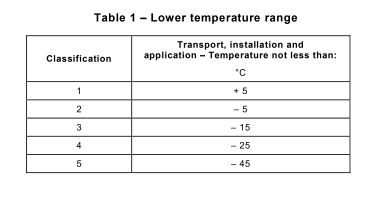
Cable Ratings: Cables must be rated for the temperatures they’ll face during their life—no cutting corners here!
Safety Considerations: Inside buildings, cables need to be safely enclosed, either in metal conduit or heavy-duty insulating enclosures to reduce short-circuit risks. And any internal cable runs in residential or commercial installations should use medium-duty conduit to meet AS/NZS 3000 standards.
To ensure the best performance and durability of your solar conduit system, we recommend using matching fittings made from the same material as your solar conduits.
For example, UPVC fittings with UPVC conduit. This helps maintain consistent UV resistance, thermal expansion behavior, and mechanical strength.
That said, in some cases, mixed-material setups may be acceptable, as long as the combination complies with local regulations and safety standards, you’re good to go.
4.2 Solar Radiation and Location-Based Conduit Selection
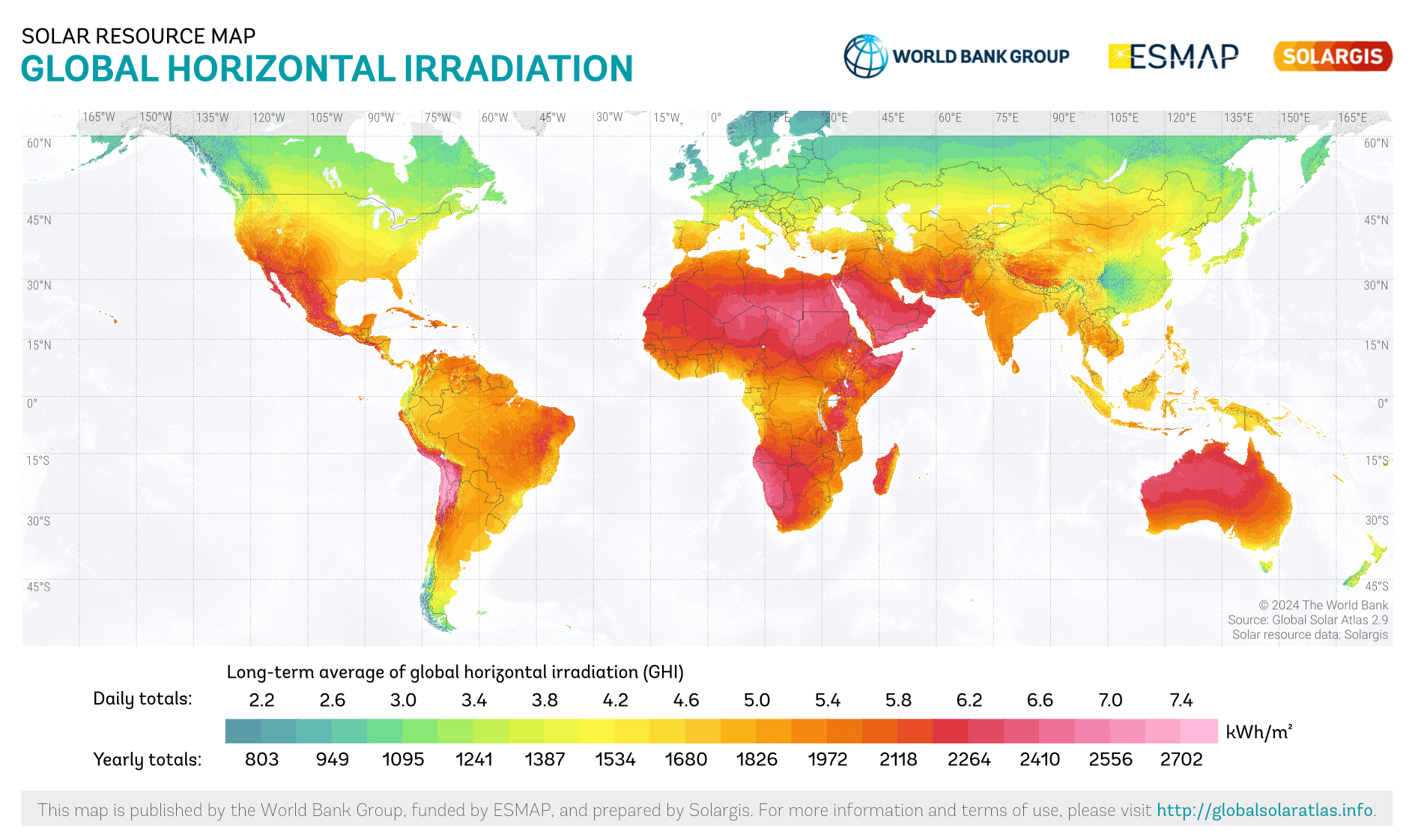
Here’s an interesting thing you may not have thought about when choosing the right solar conduit for your system: solar radiation.
Yes, the intensity of sunlight varies globally! And as much as we love sunshine, its impact on your solar installation—and the materials you choose—depends a lot on where you are.
Solar radiation refers to the amount of sunlight energy hitting a given surface area in a specific location. It varies based on factors like geographic location, time of year, and altitude.
The higher the solar radiation, the more stress your materials (such as cables and conduits) will face. More sunlight means more UV exposure, and UV exposure can degrade your materials faster. So, choosing a conduit that can withstand those conditions becomes crucial.
In places with blazing sun, like tropical or desert areas, you need tough materials. Go for UV-resistant conduits like PVC coated conduit, solar UPVC conduit or RTRC conduit.
In places with more moderate sun, like temperate climates, standard PVC or metal conduits with UV protection should do the trick.
More solar radiation means more energy for your system—great news, right? But too much UV can damage your conduit, making it a bit of a “blessing and a curse.”
Don’t worry though! By picking the right conduit for the job, you can enjoy the sunshine without stressing about your system’s durability. With the right protection, your solar system will be ready to soak up all that good energy safely and efficiently!
5. Conclusion
As we’ve seen throughout this guide, choosing the right solar conduit is about more than just picking a material—it’s about matching your system’s needs with durability, flexibility, compliance, and performance.
From rigid to flexible conduit, and from harsh desert sunlight to temperate rooftops, every solar project brings its own unique set of challenges—and solutions.
At Ctube, we’re proud to be part of that solution. As a trusted supplier of electrical conduits, we offer a wide range of high-quality products including PVC conduit, UPVC solar conduit, and LSZH conduit, all designed to meet international standards like IEC, AS/NZS 2053, UL, and CSA certifications.
Here the video for you:
Whether you’re working on a rooftop installation or a full-scale solar farm, we’ve got you covered with products that are reliable, safe, and built to last.
Thanks for your reading! We’ll continue to share helpful insights, practical tips, and the latest updates in conduit technology—so stay tuned.
And of course, if you have a project in the pipeline and need expert support or custom conduit solutions, we’d love to hear from you. Good luck with your projects!
Website: https://www.ctube-gr.com
Email: [email protected]
Phone/WhatsApp: +86 13925733207
Published by Ctube Official
Edited on April 12, 2025
Everything You Need to Know About Solar Conduit (2025 Updated) Read More »