Cómo elegir el conducto eléctrico flexible adecuado para uso en exteriores: una guía completa
1. Introducción
Can flexible conduit be used outdoors? The answer is yes!
🌞But to make sure your outdoor wiring stays safe and lasts long, you need to choose the right type of flexible electrical conduit that suits the outdoor environment.
🔍For example, a contractor once installed a flexible conduit for a garden lighting system without considering outdoor conditions.
🌧️After a rainy season, the metal conduit started to rust, causing damage and requiring costly replacement. Choosing the right rust-resistant outdoor flexible conduit from the start could have saved time and money.
📚 In this guide, we’ll explore the different kinds of flexible conduits made for outdoor use, their materials, and how to pick the best one for your needs.
👷♂️Whether you’re a electrician, engineer, or contractor, this post meybe helpful.

2. What is Electrical Flexible Conduit?
Flexible conduits, as the name suggests, are bendable tubes made from materials like plastic or metal. They’re designed to protect and guide electrical wires.
Some types have a smooth outer surface, while others have a ridged or corrugated design.
They can easily adapt to different layouts and environments, making them especially useful in tight spaces or areas where wires need to bend or move. This flexibility makes them a popular choice in many electrical installations.
These conduits act like a flexible shield, protecting wires from moisture, dust, heat, and physical damage.
3. What’s the Difference Between Flexible and Rigid Conduits?
Flexible wire conduit can be bent by hand without special tools, but rigid conduits are straight and require tools and fittings to cut and change direction.
Rigid conduits also differ from flexible conduits in shape and surface texture. They typically have smooth inner and outer surfaces.
These differences also determine the distinct installation methods, applications, and impact resistance between flexible and rigid conduits.
Rigid conduits provide excellent protection but lack the adaptability needed for intricate routing.
In contrast, flexible conduits allow for seamless transitions and adjustments without the need for additional fittings.
4. Importance of Choosing the Right Flexible Conduit for Outside
As we mentioned earlier, using the correct flexible conduit for outdoor applications is vital; it can save you time and money by preventing damage and costly repairs.
Outdoor environments expose conduits to tough challenges like UV radiation, moisture, and physical wear.
So outdoor use flexible conduit is made from upgraded materials like UV-resistant plastic or corrosion-resistant metal.
These materials offer better protection against sunlight, rain, and harsh weather conditions.
Choosing the right conduit improves safety and extends the wiring system’s lifespan. This reduces the risk of electrical failures and potential hazards.
5. What Are Different Types of Electrical Flexible Conduit?
There are several ways to classify electrical flexible conduits.
One common way to classify them is by whether they have an outer jacket and what materials they’re made of.
📊🧵To make it easier to understand, we’ve grouped them just like in the diagram — into two main types: Jacketed and Unjacketed.
🔍In the following sections, we’ll stick to this classification and explain each category in detail to help you gain a clear and complete understanding of the flexible conduit options available.
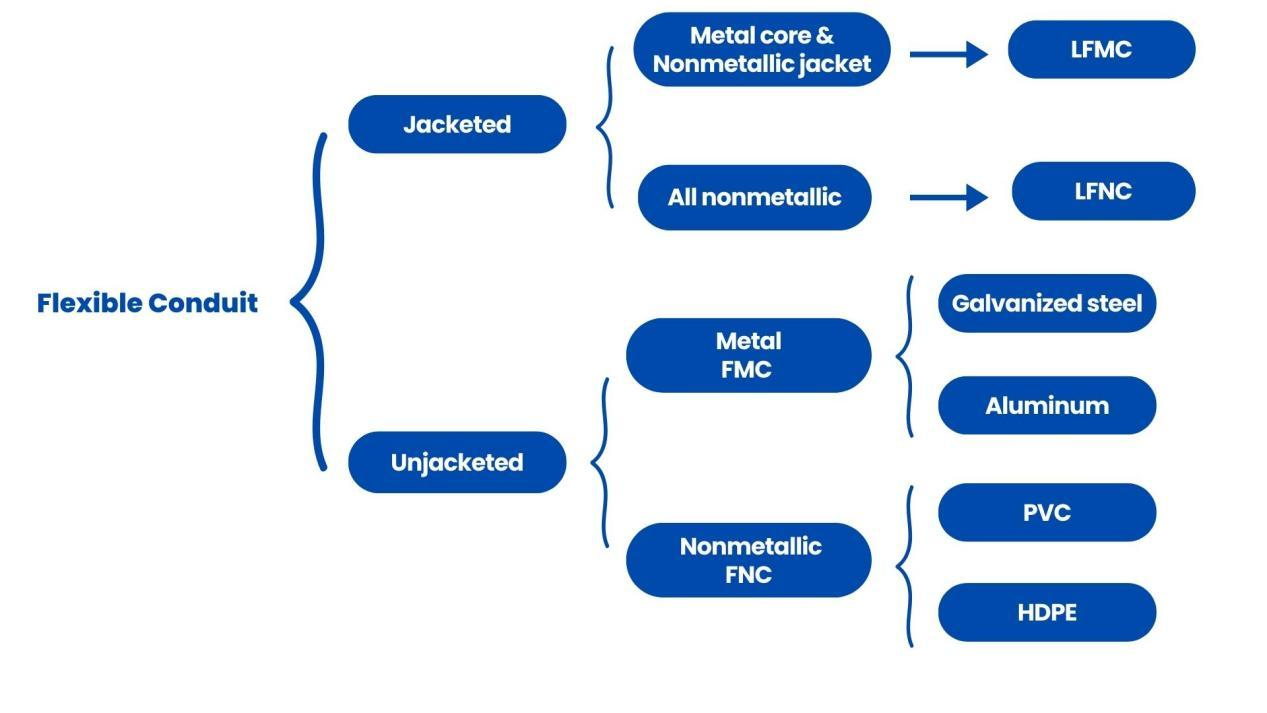
Based on the picture above, Jacketed flexible conduits can be further classified by their material composition.
⚙️ One type has a metal core with a nonmetallic outer jacket, known as LFMC (Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit).
This type offers both flexibility and strong protection against water, oil, and outdoor conditions.
🔧The other type is LFNC (Liquidtight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit), which is made entirely of nonmetallic materials. It’s lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and ideal for damp or harsh environments.
🔹🔹🔹🔹🔹
On the other hand, Unjacketed flexible conduits fall into two categories: FMC and FNC.
🛠️ FMC (Flexible Metal Conduit) is usually made from galvanized steel or aluminum. It’s strong and durable, making it a good choice for tough indoor or industrial environments.
🔩 FNC (Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit) is made from materials like PVC or HDPE. It’s lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easier to handle, often used in lighter-duty applications.
🎯 Next section, let’s take a closer look at Flexible Electrical Conduits with Jackets in detailed.
6. What is Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit?
Según el artículo 350 del NEC, un conducto metálico flexible hermético a líquidos (LFMC) es un conducto de sección transversal circular que tiene una cubierta exterior hermética a líquidos, no metálica y resistente a la luz solar sobre un núcleo metálico flexible interior.
Características:
- Galvanized steel core
- Waterproof plastic outer jacket
Key Benefits:
- Excellent waterproofing for wet environments
- Strong corrosion resistance from both metal and jacket
- High mechanical protection and impact resistance
Mejor para: Heavy-duty outdoor applications like garden wiring, poolside equipment, and exposed installations requiring strong protection.
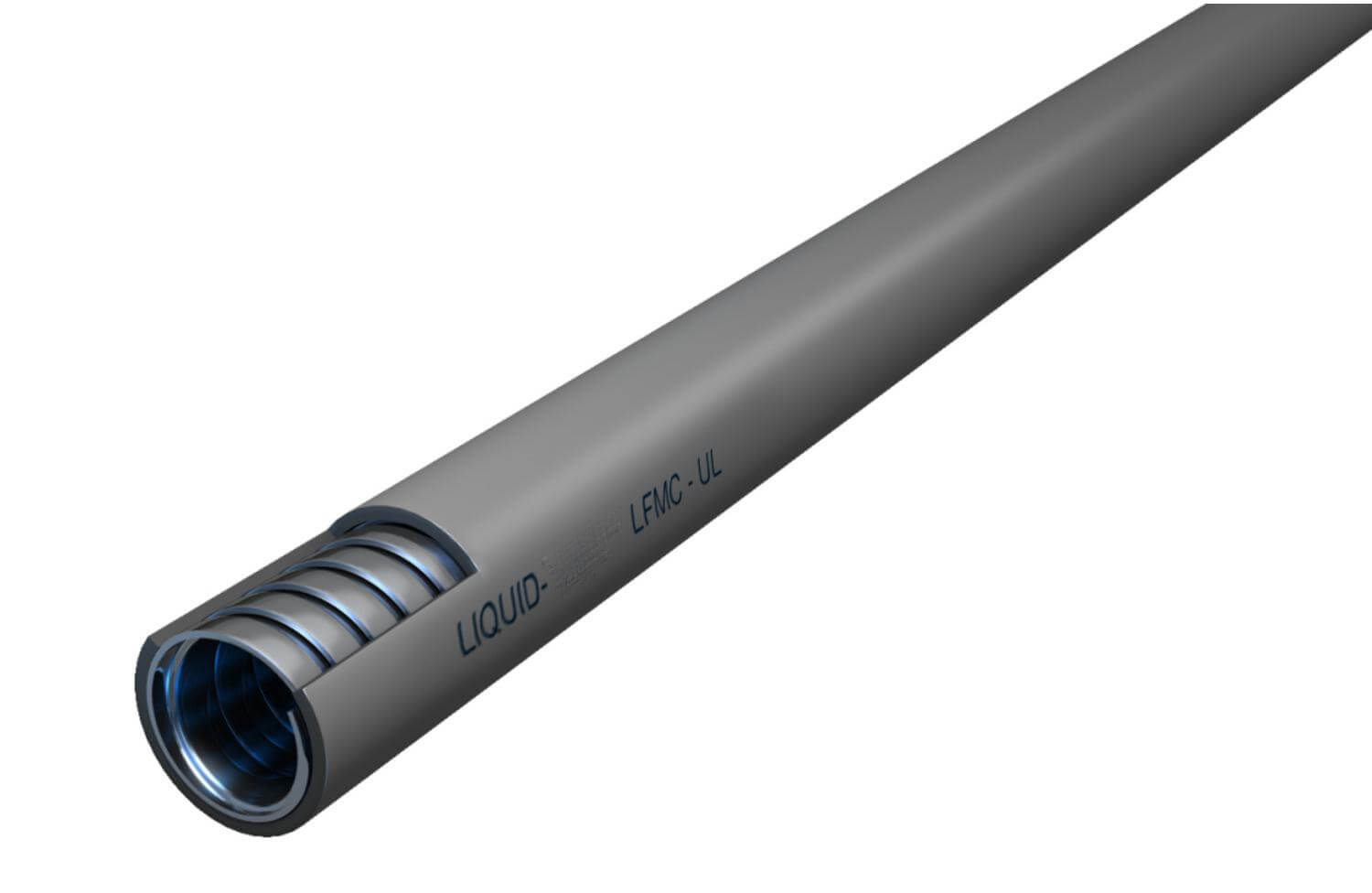

According to UL listings, LFMC conduits are made from materials like aluminum, brass, copper, or stainless steel.
⚡️ The bonding strip must be made and sized to pass electrical resistance tests before high-current testing.
🔄 It should not reduce flexibility or make the conduit harder to bend.
🧵 A metal braiding can be added between the metal core and outer jacket.
The braiding wire must be at least 0.005 inches (0.13 mm) thick.
If the core is aluminum, the braiding must also be aluminum or tinned metal.
Sizes of Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit meet the specified internal and external diameter measurements, as outlined in Table 5.1.
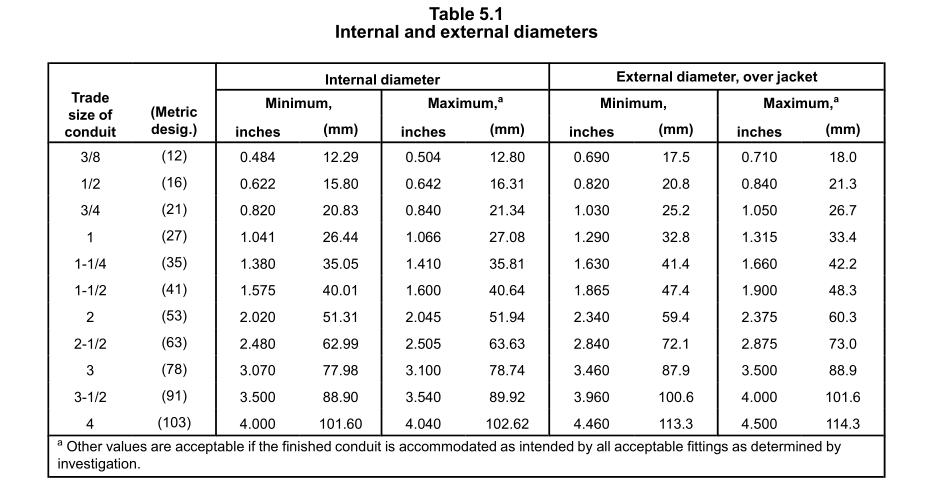
Sizes are for reference only. Please check with your supplier for exact specifications. Same as the following conduit sizes.
7. What is Liquidtight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit?
LFNC is usually a round tube that can have a smooth or ribbed surface depending on the type. It is made from non-metallic plastic and has a protective outer jacket to resist corrosion and damage. Sometimes people call it FNMC.
Features:
- Made of flexible non-metallic PVC or similar materials
- UV-resistant and waterproof
Key Benefits:
- Lightweight and easy to install
- Cost-effective and naturally rust-proof
- Excellent in humid or coastal areas
Best for: Residential outdoor lighting, patio wiring, or areas where flexibility and moisture resistance are needed without heavy-duty protection.

According to UL listed, LFNC is intended for use in wet, dry, or oily locations at a maximum of 60°C(140°F),unless otherwise marked.
🔍There are three main types of LFNC based on their construction and surface design.
🔵Let’s take a closer look at each type.
And for reference, we provide an overview of the key size requirements and testing methods for each LFNC type.
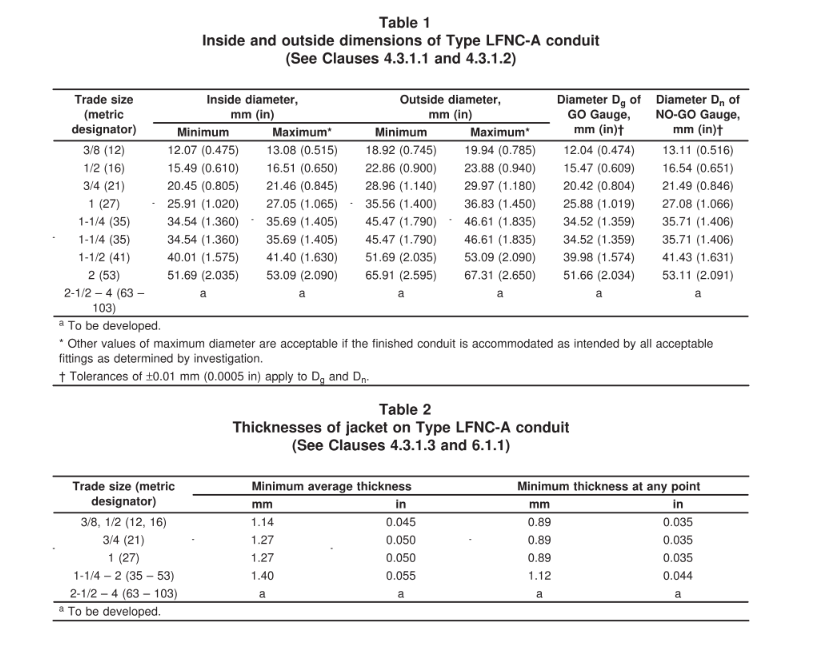
🔴Type LFNC-A: Features a smooth, seamless inner core and cover bonded together, with one or more reinforcement layers between the core and the cover.
📏 Must meet exact inside and outside diameter standards (see Table 1).
✅ Tested with go/no-go gauges.
📐 Jacket thickness is measured from 5 spots; smallest value is minimum allowed.
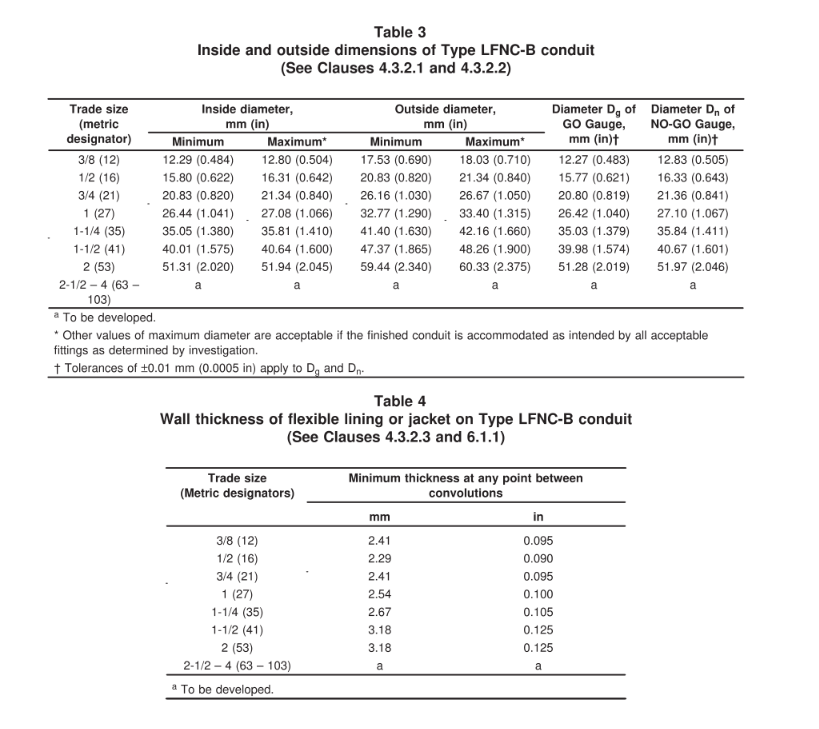
🟢 Type LFNC-B: Has a smooth inner surface with integral reinforcement within the raceway wall.
📏 Has specific diameter requirements (Tabla 3), tested like LFNC-A.
💪 Reinforced jacket thickness measured at 3+ points between folds (Tabla 4).
🟠 Type LFNC-C: Characterized by a corrugated internal and external surface without integral reinforcement in the raceway wall.
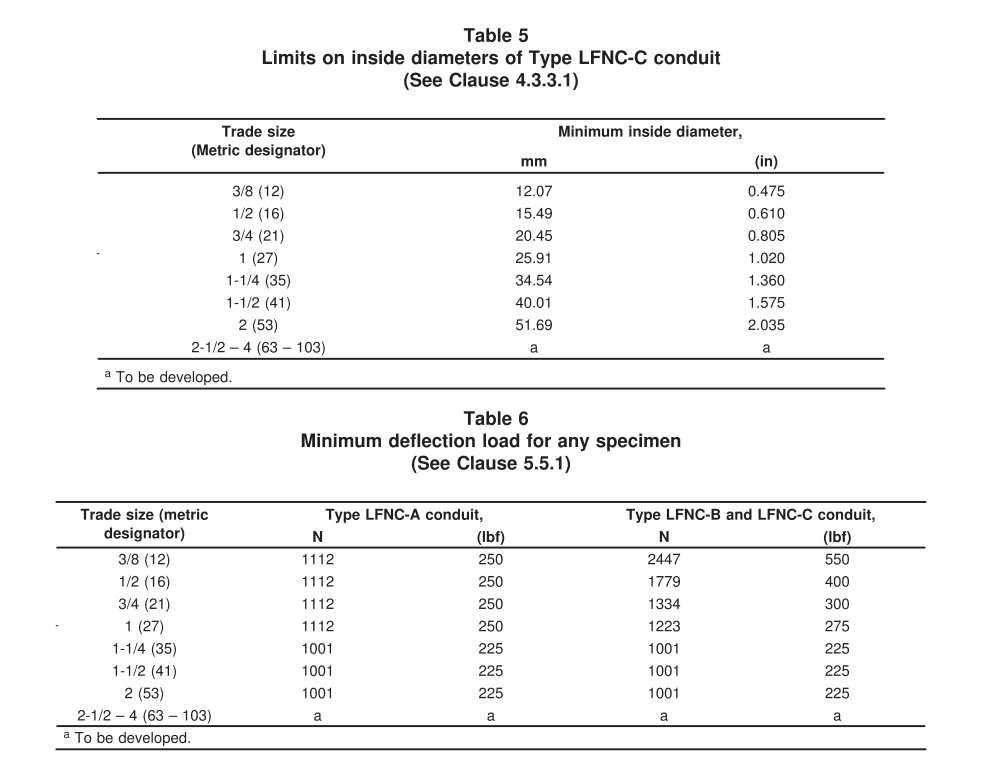
📏 Only minimum inside diameter is required (Tabla 5).
❌ No thickness standard for the jacket.
8. What is Flexible Metal Conduit?
El conducto metálico flexible (FMC) es un conducto de sección transversal circular hecho de tiras metálicas entrelazadas, formadas y enrolladas helicoidalmente.
Features:
- Interlocked metal strip construction (steel or aluminum)
- No plastic sheath
Key Benefits:
- Superior mechanical protection
- Excellent heat resistance
Mejor para: Outdoor environments that demand strong physical protection, but are not heavily exposed to water or humidity.
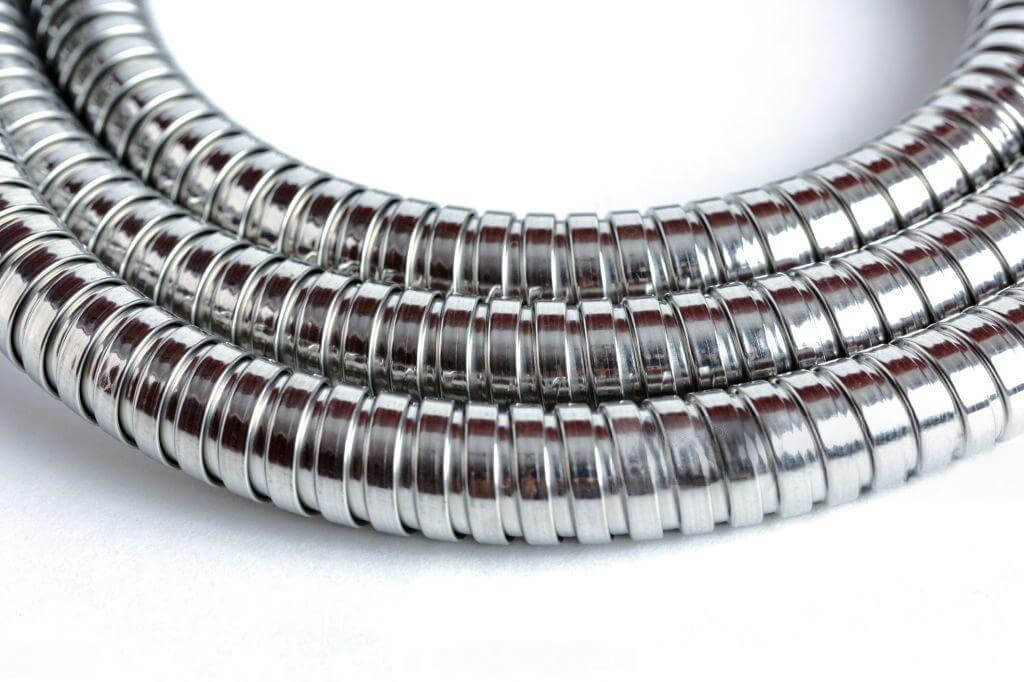

Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC) can be made from different metals.
🟣 For flexible steel conduit, the strip material must be made of carbon steel with a minimum tensile strength of 34,000 lbf/in² (234.5 MPa).
🧽 The strip should have a consistent width and thickness throughout for reliable quality. Also, before applying a protective zinc coating, all surfaces must be clean and free of rust or scale.
🟡 In the case of flexible aluminum conduit, the strip material must meet similar tensile strength requirements, with a minimum tensile strength of 34,000 lbf/in² (234.5 MPa).
⚙️ Additionally, the copper content must be no more than 0.40%.
The aluminum strip should maintain consistent width and thickness along its entire length for reliable performance.
⚠️When it comes to size, the thickness of the metal strip used in FMC must meet minimum values defined for standard wall conduits (see Table 5.1).
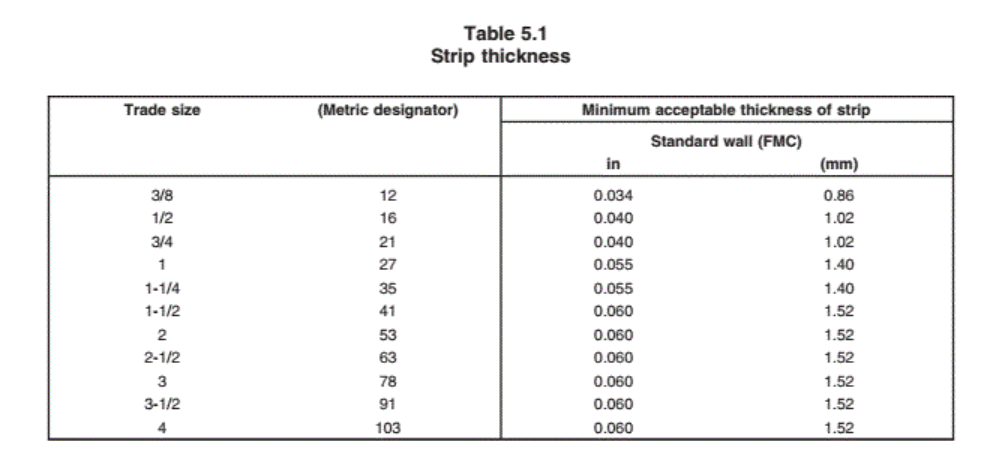
However, reduced-wall FMC can have thinner metal strips if they meet specific reduced-wall standards.
📏External diameter for flexible steel and aluminum conduits (sizes 3/8” to 4”) must be within specified minimum and maximum limits (see Tables 9.1 & 9.2). This ensures the conduit fits properly with connectors and other electrical parts.
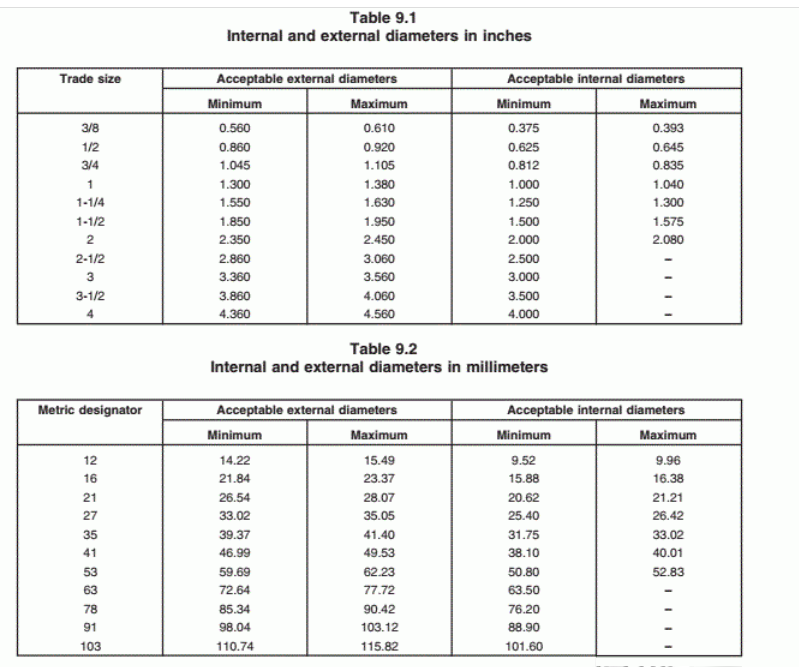
🛢️ Internal diameter also has minimum standards, and for conduits sized 3/8” to 2”, it must not exceed a maximum size to provide enough room for wiring and avoid compression damage.
9. What is Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing?
Los tubos eléctricos no metálicos (ENT) son conductos corrugados, flexibles y no metálicos de sección transversal circular. Los ENT están compuestos de un material resistente a la humedad y a los ambientes químicos y son retardantes de llama.
Features:
- Made from PVC or polyethylene
- Flexible and waterproof
Key Benefits:
- UV- and corrosion-resistant
- Easy to bend around corners
- Suitable for outdoor wet locations
Mejor para: Garden lighting systems, temporary outdoor setups, and coastal areas where corrosion resistance is key.

📌 According to the UL 1653 standard, Otorrinolaringología must be made from rigid (non-plasticized) PVC to provide long-lasting strength and durability.
🔗 Additionally, the fittings used with ENT should be made from materials that meet a minimum Relative Thermal Index (RTI) of 90°C (194°F)—both for electrical properties and mechanical (non-impact) performance, in accordance with UL 746B and CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 0.17.
💡 According to UL 1653, ENT is designed for use in specific temperature and installation conditions:
📈 Continuous operating temperature: up to 75°C (167°F)
🌡️ Maximum ambient temperature: up to 50°C (122°F)
In attic installations, ENT must:
- Be installed no more than 900 mm (3 feet) above the ceiling joist bottom
- Be rated for at least 60°C (140°F) to perform safely in warmer spaces
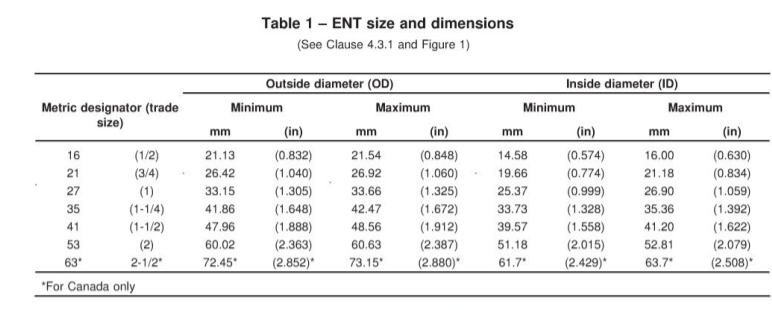
ENT is available in different trade sizes, all defined by standard dimensions listed in Table 1.
Want to dive deeper into this conduit type?
👉 Check out our detailed guide:
The Ultimate Guide to Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT): Everything You Need to Know
🎥 Video about ENT for you if you are interested in.
9. What is High Density Polyethylene Conduit?
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) conduit is a nonmetallic raceway with a circular shape, known for its flexibility and moisture resistance.
Features:
- Constructed from polyethylene
- Designed for underground or outdoor use
Key Benefits:
- Outstanding waterproofing and corrosion resistance
- High impact strength and flexibility
- Withstands extreme cold and heat
Mejor para: Long-term underground installations in harsh environments such as solar energy systems, utility wiring, and telecom cabling.
It comes in several common types such as Schedule 40, Schedule 80, EPEC-A, and EPEC-B, based on classifications defined under UL 651B, the standard for continuous-length HDPE conduit.
🔍 Note: The “Schedule 40” and “Schedule 80” mentioned here refer to types of HDPE conduit and should not be confused with rigid PVC Schedule 40 or Schedule 80 conduit, which are defined under different standards (such as UL 651 for rigid PVC). While the naming is similar, the materials, physical characteristics, and installation methods are different.
When choosing the right HDPE conduit, it’s also important to consider the sizes and types available.
These size limits are outlined in standardized tables like Table 5.1 for outer diameters, and Tables 5.2 and 5.3 for wall thicknesses.
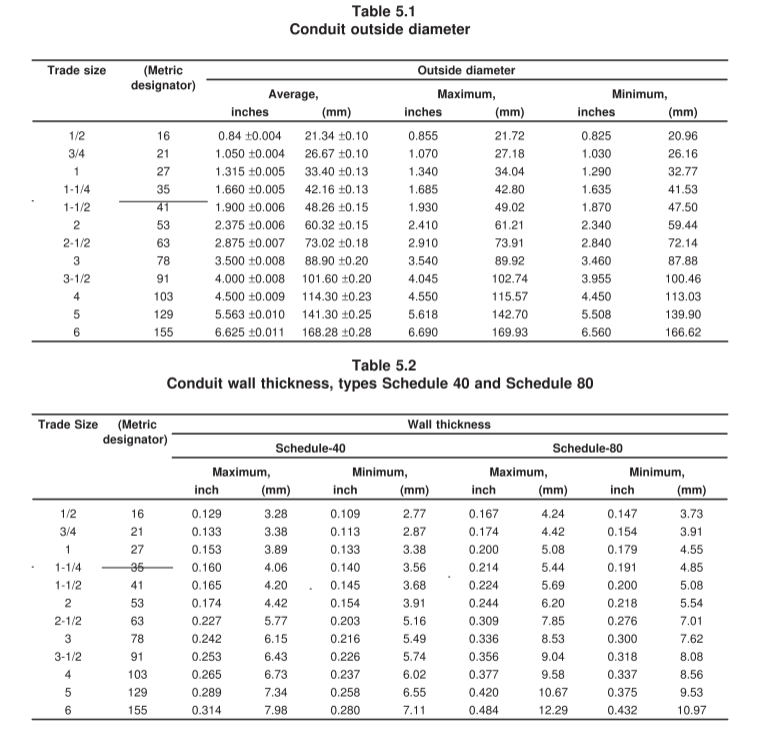
Limits on the wall thicknesses
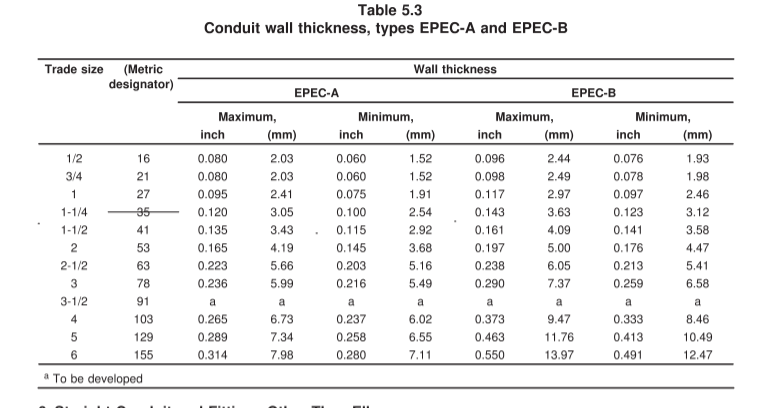
To meet performance requirements, HDPE conduit must also withstand tests of mechanical strength and temperature performance.
10. Key Environmental Requirements for Outdoor Flexible Conduit
Outdoor environments can be harsh, so the conduit must be designed to withstand a range of challenging conditions.

- Resistente al agua y a la humedad:El conducto debe evitar la entrada de agua para proteger el cableado eléctrico de daños y cortocircuitos, especialmente en ambientes lluviosos o húmedos.
- Resistencia a la corrosión:Las instalaciones en exteriores suelen estar expuestas a elementos que pueden provocar corrosión, sobre todo en zonas costeras o industriales. El material debe ser resistente a la corrosión para garantizar un rendimiento duradero.
- Resistencia a los rayos UV:La exposición al sol puede degradar los materiales con el tiempo. Un conducto resistente a los rayos UV es esencial para evitar la fragilidad o el agrietamiento debido a la exposición prolongada a la luz solar.
- Tolerancia de temperatura:Los conductos exteriores deben poder soportar fluctuaciones extremas de temperatura, tanto altas como bajas, para evitar la expansión, contracción o degradación del material.
- Resistencia a la presión y al impacto:En áreas donde el conducto puede estar sujeto a estrés físico, como estar enterrado bajo tierra o montado en lugares expuestos, debe poder soportar la presión y los posibles impactos sin sufrir daños.
11. Comparing Different Flexible Conduit Types
A continuación, comparamos diferentes conductos flexibles en función de estos estándares de prueba esenciales para ayudarlo a tomar la decisión correcta al seleccionar el conducto eléctrico.
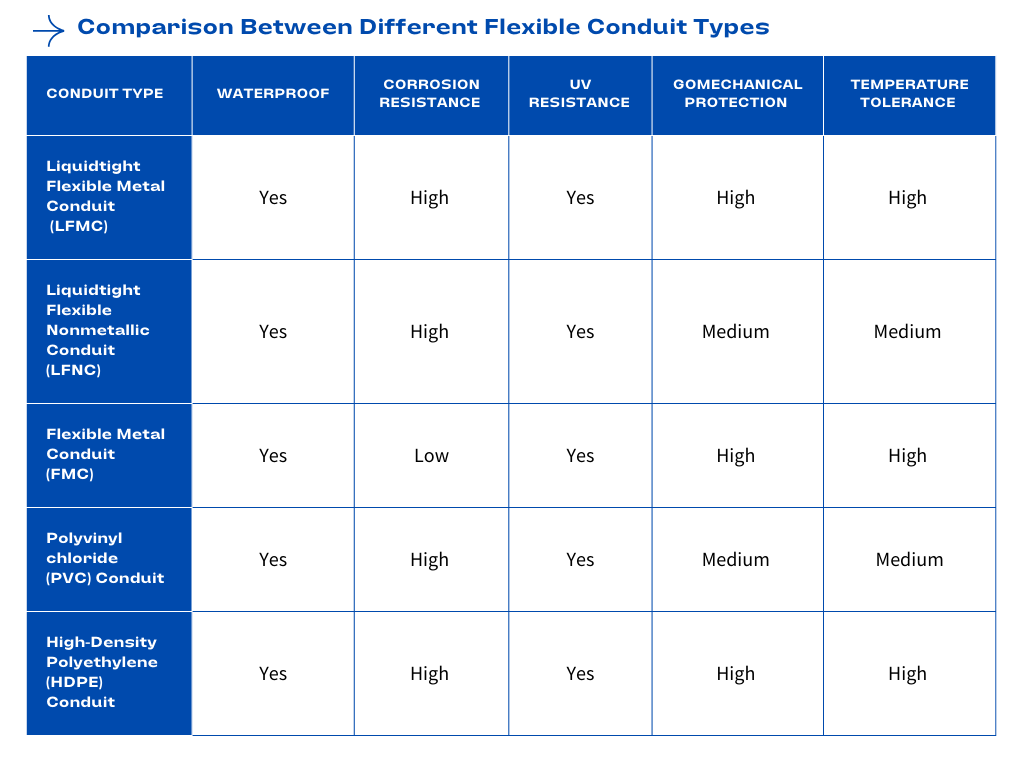
And we Uprovide a Use Case Comparison Table to help you better choose the conduit of your outdoor projects.
| Solicitud | Recommended Type | Por qué |
|---|---|---|
| Garden or wet area | LFMC / LFNC | Waterproof, flexible |
| High stress / heavy load | LFMC / FMC | Fuerte protección mecánica |
| Humid / coastal area | LFNC / Nonmetallic | Corrosion and UV resistant |
| Underground / solar | HDPE | Extreme durability and flexibility |
| Outdoor lighting | LFNC | Easy to install, affordable |
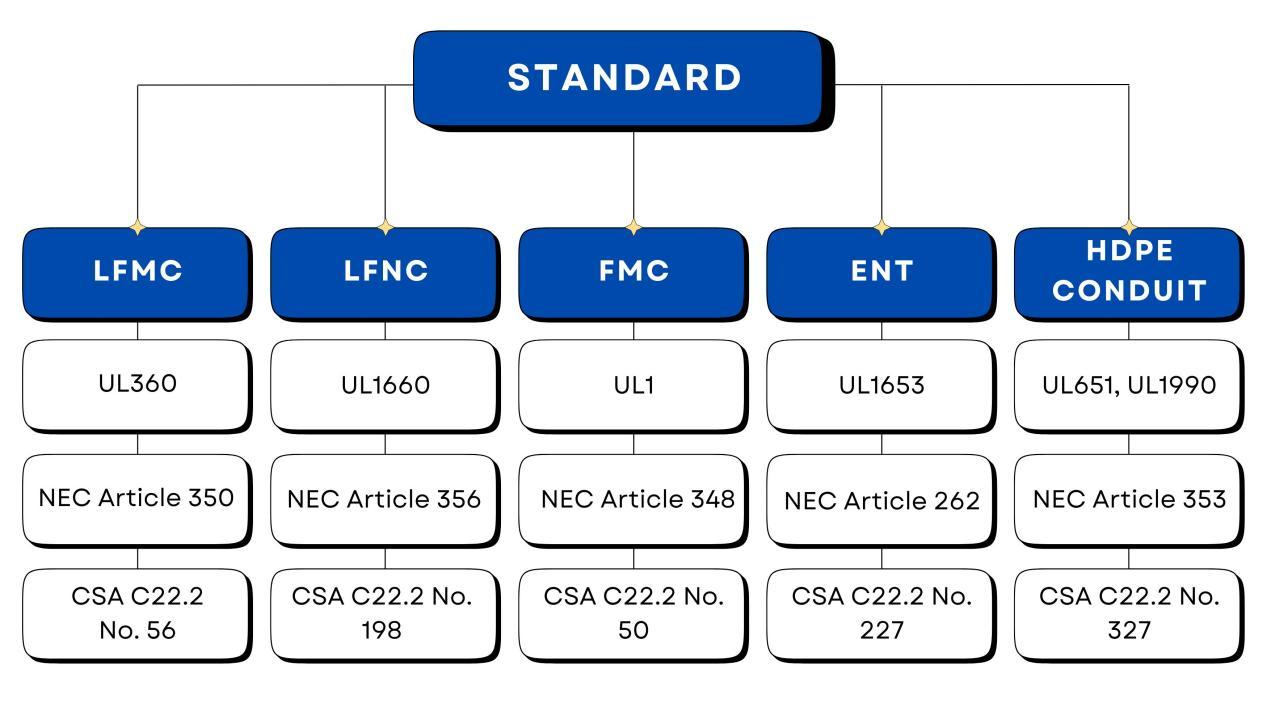
12. Flexible Electrical Conduit Codes, Standards And Certifications
Para mejorar su comprensión, proporcionamos algunas referencias a las normas pertinentes sobre catéteres flexibles. Las distintas normas pueden adaptarse a distintos usos y aplicaciones finales, por lo que es importante revisar el alcance de cada norma para comprender su finalidad.
13. Conclusion
This post provides a detailed overview of the different types of flexible electrical conduits, highlighting the unique benefits and features of each material.
In summary, selecting and choosing the right flexible conduit for outdoor use means carefully assessing your project’s environment, application needs, budget, and regulatory requirements to achieve the best performance and safety.
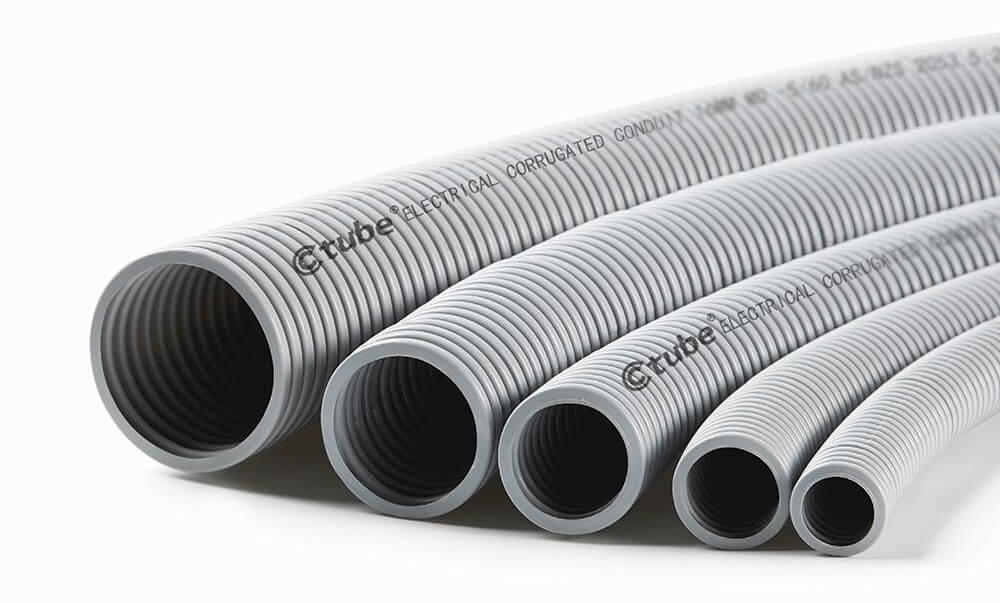

Ctube es un fabricante profesional de conductos, dedicado a proporcionar productos confiables y duraderos para instalaciones eléctricas versátiles.
Nuestro Conductos flexibles de PVC Cumplir con certificaciones internacionales como UL 651, AS/NZS 2053 y CSA, garantizando una flexibilidad, durabilidad y seguridad excepcionales en diferentes entornos.
Ctube also provides special flexible conduit series : the Conducto solar Series and the Low Smoke Halogen-Free (LSZH) Conduit Series.
If you are searching for outdoor conduit for your projects and interested in our products, feel free to contact us for more information.
Thank you for reading. Hope your project goes well.

Preguntas frecuentes
1. ¿Cómo sé qué material de conducto flexible es mejor para mi proyecto?
Para elegir el conducto adecuado, tenga en cuenta factores como las condiciones ambientales (por ejemplo, humedad, exposición a rayos UV), las necesidades de protección mecánica, los requisitos de seguridad, el presupuesto del proyecto y las normativas locales. Por ejemplo, los conductos de PVC son rentables y resistentes a la corrosión, mientras que los conductos de metal ofrecen mayor durabilidad y protección contra impactos.
2. ¿Cuánto duran los conductos flexibles en instalaciones exteriores?
La longevidad de los conductos flexibles en instalaciones al aire libre depende del material y de las condiciones ambientales. Los conductos de PVC son muy resistentes a la corrosión y a los daños causados por los rayos UV, mientras que los conductos de metal ofrecen una durabilidad duradera frente al estrés físico. El mantenimiento y la inspección regulares pueden prolongar aún más la vida útil de los conductos.
3. ¿Cómo se comparan los conductos flexibles con los conductos rígidos para uso en exteriores?
Los conductos flexibles son más fáciles de instalar en diseños complejos y áreas con espacios reducidos o movimiento. Son ideales para aplicaciones donde se requiere adaptabilidad. Sin embargo, los conductos rígidos ofrecen mayor protección mecánica y generalmente se utilizan en áreas donde el conducto no necesita doblarse ni torcerse. Ambos tipos tienen sus ventajas según la aplicación y el entorno.


