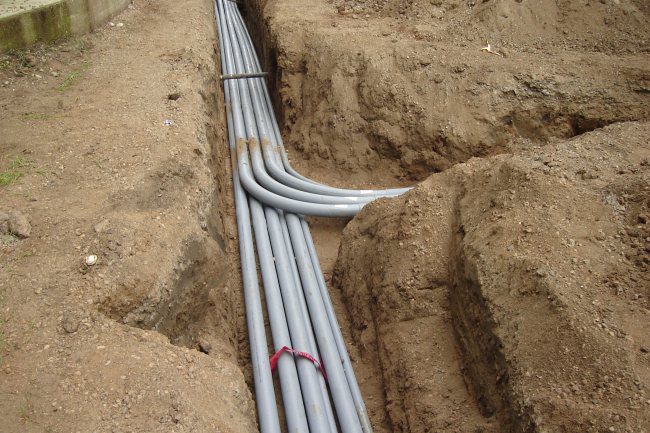
O National Electrical Code (NEC) fornece diretrizes para enterrar cabos e fiação elétrica, comumente chamados de instalações de enterramento direto. Esses requisitos de profundidade são descritos na tabela 300.5 do NEC. A profundidade de enterramento varia entre 4 polegadas e 24 polegadas, dependendo do método de fiação específico empregado.
| Artigo 300 – Requisitos gerais para métodos e materiais de fiação | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tabela 300.5 Requisitos mínimos de cobertura, 0 a 1000 volts, nominal, enterramento em milímetros (polegadas) | ||||||||||
| Tipo de método de fiação ou circuito | ||||||||||
| Localização do método de fiação ou circuito | Coluna 1 Enterro direto Cabos ou Condutores |
Coluna 2 Metal rígido Conduíte ou Intermediário Conduíte de metal |
Coluna 3 Não metálico Pistas de corrida listadas para sepultamento direto Sem Concreto Encapsulamento ou Outros aprovados Pistas de corrida |
Coluna 4 Filial Residencial Circuitos Classificados 120 Volts ou Menos com GCFI Proteção e Proteção máxima de sobrecorrente de 20 Amperes |
Coluna 5 Circuitos para Controle de Irrigação e Iluminação de paisagens Limitado a não mais Mais de 30 Volts e Instalado com Tipo UF ou em Outro Cabo identificado ou Pista de corrida |
|||||
| milímetros | em. | milímetros | em. | milímetros | em. | milímetros | em. | milímetros | em. | |
| Todos os locais não especificados abaixo | 600 | 24 | 150 | 6 | 450 | 18 | 300 | 12 | 150 a,b | 6 a,b |
| Em vala abaixo de 50 mm (2 pol.) | 450 | 18 | 150 | 6 | 300 | 12 | 150 | 6 | 150 | 6 |
| Debaixo de um prédio | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| (em canaleta ou cabo Tipo MC ou Tipo MI identificado para enterramento direto) | (em canaleta ou cabo Tipo MC ou Tipo MI identificado para enterramento direto) | (em canaleta ou cabo Tipo MC ou Tipo MI identificado para enterramento direto) | ||||||||
| Sob uma laje externa de concreto com espessura mínima de 102 mm (4 pol.) sem tráfego de veículos e a laje se estendendo não menos que 152 mm (6 pol.) além da instalação subterrânea | 450 | 18 | 100 | 4 | 100 | 4 | 150 | 6 | 150 | 6 |
| (enterro direto) | (enterro direto) | |||||||||
| 100 | 4 | 100 | 4 | |||||||
| (na pista de corrida) | (na pista de corrida) | |||||||||
Opções de conduíte subterrâneo:
Eletroduto de PVC – Um dos tipos de eletroduto mais utilizados para instalações subterrâneas.
Feito de tubulação rígida de cloreto de polivinila (PVC). Durável, resistente à corrosão e relativamente acessível. Disponível em vários tamanhos.
Conduíte de HDPE – Feito de polietileno de alta densidade (HDPE), é flexível e mais fácil de instalar do que conduíte de PVC rígido. Frequentemente usado para aplicações de enterramento direto. Resistente à corrosão e muito durável.
Conduíte de aço – O conduíte de aço rígido galvanizado fornece máxima durabilidade subterrânea, mas é mais pesado e mais caro para instalar do que PVC ou HDPE. Altamente resistente à corrosão.
Conduíte de fibra de vidro – Não metálico e resistente à corrosão. Boa alternativa onde propriedades não condutivas e não magnéticas são necessárias. Mais caro que PVC.
ENT (tubulação elétrica não metálica) – Tubulação de PVC flexível usada como uma alternativa de baixo custo ao conduíte rígido, tipicamente para percursos subterrâneos curtos. Mais fácil de instalar do que o conduíte rígido, mas fornece menos proteção física.
Conduíte pré-dobrado – Disponível para PVC e HDPE. O design pré-dobrado facilita a instalação ao longo de alinhamentos curvos sem precisar formar curvas no campo.