Comparing HDPE vs. PVC Conduits: A Comprehensive Guide
1. Introduction
Conduits are vital components in both electrical and communication systems, serving as protective pathways for cables and wires. These conduits safeguard the integrity of the electrical or communication infrastructure by shielding the cables from environmental hazards, physical damage, and interference. Proper conduit selection is crucial for ensuring the durability, safety, and efficiency of these systems.
Two of the commonly used types of conduits are HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) and PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride). Each material has distinct characteristics, advantages, and limitations, making them suitable for different applications and environments. Understanding these differences is essential for engineers, electricians, and anyone involved in planning and installing conduit systems.
The purpose of this article is to compare HDPE conduit and PVC conduit, providing a comprehensive overview to help readers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and project requirements.
2.Know More About HDPE Conduit
2.1 What is HDPE?
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer derived from petroleum. It is one of the most versatile and widely used plastics in the world due to its unique properties. HDPE is produced through a polymerization process that results in long chains of ethylene molecules. The high density of these chains gives HDPE its characteristic strength and rigidity.
2.2 What are the material properties and characteristics of HDPE?
HDPE’s material properties make it highly suitable for a variety of applications, including conduits. Key properties include:
– High Strength-to-Density Ratio: HDPE’s density typically ranges from 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm³, which contributes to its strength while remaining lightweight.
– Flexibility: HDPE can be bent, coiled, and maneuvered around obstacles without breaking or cracking, which is crucial for installations that require curved pathways.
– Chemical Resistance: HDPE is resistant to many chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. This property ensures that HDPE conduits do not degrade or corrode when exposed to harsh substances.
– UV Resistance: HDPE can withstand prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, making it suitable for outdoor applications where other materials might degrade over time.
– Low Moisture Absorption: HDPE absorbs very little water, which helps maintain its structural integrity even in wet conditions.
– Impact Resistance: HDPE is known for its ability to absorb impacts without damage, making it ideal for environments where physical stresses are common.
2.3 What are the applications of HDPE conduit?
HDPE conduits are employed across a wide range of industries due to their durability and adaptability. Here are some notable applications:
– Telecommunications: HDPE conduits are extensively used to protect fiber optic cables and other telecommunications infrastructure. They are particularly useful for underground and direct burial installations where they provide excellent protection against environmental factors and physical damage.
– Power Systems: HDPE conduits are used in power distribution networks to house and protect electrical cables. Their flexibility and resistance to harsh conditions make them ideal for both underground and above-ground installations.
– Gas and Water Distribution: HDPE pipes are frequently used for the distribution of gas and water. Their resistance to corrosion and chemicals ensures a long lifespan and reliable performance in these critical applications.
– Industrial Applications: In industrial settings, HDPE conduits protect electrical and communication cables from chemicals, physical damage, and environmental stresses. This is especially important in chemical plants and manufacturing facilities.
– Agriculture: HDPE conduits are used in agricultural applications to protect irrigation lines and electrical cables, ensuring reliable operation of automated systems.
2.4 In which scenarios is HDPE conduit preferred?
– Rural and Remote Areas: In rural and remote locations, HDPE conduits are preferred due to their flexibility and ease of installation. They can be laid over long distances without the need for numerous joints and fittings, reducing installation time and costs.
– Harsh Environments: In environments with high levels of pollution, chemical exposure, or extreme weather conditions, HDPE conduits offer superior protection. Their resistance to corrosion and chemicals ensures longevity and reliability.
– Outdoor Installations: For outdoor telecommunications or power systems, HDPE conduits provide excellent protection against UV radiation and environmental stress. This makes them a preferred choice for outdoor applications, including those in coastal areas where salt and moisture can cause significant damage to other materials.
2.5 What advantages does HDPE conduit have?
2.5.1 Durability and Flexibility
One of the primary advantages of HDPE conduits is their exceptional durability and flexibility. HDPE can be bent and shaped without cracking, which simplifies the installation process, especially in applications that require curved pathways or where ground movement is a concern. This flexibility also reduces the need for additional fittings and connectors, which can be potential points of failure.
2.5.2 Resistance to Corrosion and Chemicals
HDPE’s resistance to corrosion and chemicals is another significant advantage. This property makes HDPE conduits suitable for a wide range of environments, including those with high levels of chemical exposure or moisture. Unlike metal conduits, which can rust and degrade over time, HDPE remains unaffected by most chemicals and corrosive substances, ensuring a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs.
2.5.3 Lightweight and Ease of Installation
HDPE is lightweight compared to other materials such as metal or concrete, which simplifies transportation and handling. This reduces labor costs and installation time. Additionally, the ease of cutting, bending, and joining HDPE conduits with heat fusion or mechanical fittings further streamlines the installation process. This can be particularly beneficial in large-scale projects where speed and efficiency are critical.
2.5.4 Environmental Friendliness
HDPE is a recyclable material, which contributes to its environmental friendliness. Used HDPE products can be melted down and reformed into new products without significant degradation of material properties. This recyclability makes HDPE a more sustainable choice compared to some other materials, reducing the environmental impact of conduit installations.
2.5.5 Cost-Effectiveness in the Long Term
Although the initial cost of HDPE conduits may be higher than some alternatives, their long-term cost-effectiveness should be considered. The durability, low maintenance requirements, and extended lifespan of HDPE conduits can lead to significant savings over time. Additionally, the reduced need for repairs and replacements further enhances their cost-effectiveness.
2.6 What disadvantages does HDPE conduit have?
2.6.1 Cost Considerations
One of the primary disadvantages of HDPE conduits is their higher initial cost compared to other materials like PVC. This can be a significant factor for projects with tight budgets or those that require a large quantity of conduit. However, it is important to weigh this initial expense against the long-term benefits and potential cost savings provided by HDPE’s durability and low maintenance requirements.
2.6.2 Potential Limitations in Specific Environments
Despite its many advantages, HDPE conduits may have limitations in certain environments. For instance:
– Temperature Sensitivity: HDPE can become too flexible at extremely high temperatures, which may compromise the stability of the conduit system. In applications where high temperatures are common, additional measures may be needed to ensure the conduit’s stability.
– Structural Support: In situations where extreme rigidity and structural support are required, HDPE may not be the best choice. For example, in environments with high mechanical loads or where conduits need to support significant weight, more rigid materials like metal or concrete might be preferable.
– Installation Challenges in Cold Weather: While HDPE is flexible, it can become less pliable at very low temperatures, making installation more challenging. Specialized techniques or equipment may be necessary to install HDPE conduits in cold weather conditions.
2.7 Installation Complexity in Some Applications
– Planning and Design: Proper planning involves assessing project requirements, determining conduit size, route, and placement, and considering environmental factors such as soil conditions, temperature variations, and exposure to UV radiation. Detailed design plans help minimize bends, optimize cable protection, and ensure efficient installation.
– Handling and Transportation: HDPE conduits should be handled and transported with care to prevent damage during transit and storage. Protecting conduits from physical impact, bending, and exposure to extreme temperatures ensures they arrive at the installation site in optimal condition.
– Jointing Methods: Depending on project specifications and requirements, HDPE conduits may require heat fusion or mechanical fittings to create secure joints and connections. Heat fusion involves welding the ends of HDPE conduits together using specialized equipment to form strong, leak-proof bonds. Mechanical fittings provide an alternative method for joining HDPE conduits without heat, offering flexibility and ease of installation in various applications.
– Environmental Conditions: Consideration of environmental factors such as temperature variations, soil conditions, and exposure to UV radiation is critical during HDPE conduit installation. Extreme temperatures can affect the flexibility and performance of HDPE conduits, requiring careful monitoring and adjustment during installation to ensure reliable performance and longevity.
– Safety and Compliance: Installation of HDPE conduits must comply with industry standards, regulations, and best practices to ensure safety, functionality, and compliance with project specifications. Adhering to safety guidelines and using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) during installation minimizes risks and enhances workplace safety.
3.Know More About PVC Conduit
3.1 What is PVC?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a synthetic plastic polymer widely utilized for its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. PVC is formed through the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomers, creating a material that can be either rigid or flexible, depending on the additives used. This flexibility allows PVC to be tailored to specific applications, ranging from plumbing to electrical conduits. Here we mainly talk about pvc conduit for electrical installation.
3.2 What are the material properties and characteristics of PVC?
PVC exhibits several key properties that make it suitable for use in conduits:
– Rigidity and Strength: PVC conduits are known for their robust mechanical protection, maintaining their shape under load without deforming.
– Non-Conductive: PVC is an excellent electrical insulator, providing an additional layer of safety by preventing electrical currents from escaping the conduit.
– Fire Resistance: PVC has inherent flame-retardant properties, meaning it is less likely to ignite and will self-extinguish if exposed to fire.
– Chemical Resistance: PVC is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and salts, ensuring its longevity in various environments.
– UV Resistance: When formulated with UV stabilizers, PVC can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight without significant degradation.
– Ease of Processing: PVC can be easily cut, bent, and joined using standard tools and methods, making installation straightforward and cost-effective.
3.3 What are the common uses of PVC conduits in various industries?
PVC conduits are widely used across different industries due to their beneficial properties. Some common applications include:
– Construction: PVC conduits are extensively used in residential, commercial, and industrial construction for routing electrical wiring through walls, ceilings, and floors. They provide reliable protection and organization for electrical systems.
– Electrical Systems: PVC conduits are a standard choice for electrical installations, offering mechanical protection and insulation for wires.
– Telecommunications: PVC conduits protect telecommunication cables, including fiber optics, in both indoor and outdoor installations.
– HVAC Systems: In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, PVC conduits are used to protect control wiring and sensors.
3.4 In which scenarios is PVC conduit preferred?
– Indoor Installations: PVC conduits are ideal for indoor electrical and communication wiring due to their rigidity, ease of installation, and fire-resistant properties.
– Residential Construction: In homes, PVC conduits provide an economical solution for routing electrical wiring through walls and ceilings. Their ease of installation makes them a popular choice among electricians.
– Commercial Buildings: For large commercial buildings with extensive electrical and communication systems, PVC conduits offer a reliable and cost-effective solution for organizing and protecting cables.
– Outdoor Installations with UV Exposure: When treated with UV stabilizers, PVC conduits are suitable for outdoor installations where they will be exposed to sunlight, ensuring long-term durability without degradation.
3.5 What advantages does PVC conduit have?
3.5.1 Cost-Effectiveness
One of the most significant advantages of PVC conduits is their cost-effectiveness. PVC is generally less expensive than other conduit materials like metal or HDPE, making it an attractive option for a wide range of projects, especially those with tight budgets. The lower material cost, combined with the ease of installation, results in significant overall savings.
3.5.2 Rigidity and Strength
PVC conduits provide excellent rigidity and strength, making them ideal for applications where mechanical protection is crucial. Their rigid nature ensures that the conduits maintain their shape and position, providing consistent protection to the enclosed cables. This rigidity also simplifies the installation process, as the conduits do not sag or deform under their weight or the weight of the cables.
3.5.3 Resistance to Fire and UV Rays
PVC’s inherent fire-resistant properties make it a safer choice for electrical installations. It is less likely to catch fire, and if it does, it will self-extinguish, reducing the risk of fire spreading. Additionally, PVC conduits with UV stabilizers can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight without significant degradation, making them suitable for outdoor applications.
3.5.4 Ease of Installation
PVC conduits are easy to work with, which simplifies the installation process. They can be cut, bent, and joined using standard tools and fittings, reducing labor costs and time. Solvent welding, a common method for joining PVC conduits, creates strong, watertight connections that enhance the system’s durability. The ease of installation makes PVC conduits a popular choice for both small and large projects.
3.5.6 Versatility
PVC conduits are available in a variety of sizes and configurations, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Whether for small residential projects or large commercial installations, there is a PVC conduit solution that fits the requirements. This versatility ensures that PVC conduits can meet the needs of diverse applications and environments.
3.5.7 Corrosion Resistance
PVC conduits are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for use in environments where they may be exposed to moisture or corrosive substances. This property ensures a longer lifespan and reduces maintenance requirements, as the conduits do not rust or degrade over time.
3.5.8 Lightweight Nature
PVC conduits are lightweight compared to metal conduits, which simplifies transportation and handling. This reduces labor costs and installation time, making PVC an efficient choice for large-scale projects. The lightweight nature of PVC also makes it easier to install in difficult-to-reach areas.
3.5.9 Environmental Friendliness
PVC is a recyclable material, which contributes to its environmental friendliness. Used PVC products can be melted down and reformed into new products without significant degradation of material properties. This recyclability makes PVC a more sustainable choice compared to some other materials, reducing the environmental impact of conduit installations.
3.6 What disadvantages does PVC conduit have?
3.6.1 Brittle Nature at Low Temperatures
One of the main disadvantages of PVC conduits is their brittleness at low temperatures. When exposed to very cold conditions, PVC can become brittle and prone to cracking or breaking if subjected to impact or stress. This characteristic limits the use of PVC conduits in environments where low temperatures are common. Special formulations or additional protective measures may be necessary to mitigate this issue.
3.6.2 Environmental Impact
While PVC is recyclable, the production and disposal of PVC can have environmental impacts. The manufacturing process involves the use of chlorine and other chemicals, which can be harmful efforts to recycle PVC and use it responsibly can help mitigate these concerns. It is important for industries and consumers to consider the environmental implications of using PVC and to adopt sustainable practices whenever possible.
3.6.3 Potential for Degradation in Certain Chemicals
While PVC is resistant to many chemicals, it is not impervious to all. Certain organic solvents and concentrated acids can cause PVC to degrade over time. In environments where exposure to such chemicals is likely, alternative materials may be more suitable. It is important to consider the specific chemical environment when selecting PVC conduits to ensure long-term performance and reliability.
3.6.4 Potential Release of Harmful Chemicals
PVC contains chlorine, and when burned or exposed to very high temperatures, it can release harmful chemicals, such as dioxins and hydrogen chloride gas. These substances can pose health risks and environmental hazards. Therefore, careful handling and proper disposal of PVC products are essential to minimize these risks.
3.6.5 Sensitivity to UV Radiation (without Stabilizers)
While PVC conduits can be formulated with UV stabilizers to resist sunlight degradation, untreated PVC is sensitive to UV radiation. Prolonged exposure to sunlight can cause PVC to become brittle and degrade. It is important to use UV-stabilized PVC conduits for outdoor applications to ensure long-term durability.
3.7 Installation Complexity in Some Applications
While PVC conduit is typically straightforward to install, certain applications can pose challenges that require extra attention and expertise. For instance, installations demanding precise alignment or connections to other materials, such as junction boxes or metal conduits, may necessitate specialized tools like conduit cutters. These tools ensure clean, accurate cuts, which are crucial for achieving a snug fit and maintaining the integrity of the electrical pathway.
4. Key Differences Between HDPE Conduit and PVC Conduit
4.1 What are the differences in material composition and properties?
4.1.1 Material Strengths
– HDPE: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) conduits are composed of long chains of ethylene molecules, which contribute to their high strength-to-density ratio. This structure allows HDPE to withstand significant physical stress while remaining lightweight. HDPE’s impact resistance is a crucial attribute, particularly in environments where conduits are subject to mechanical impacts, vibrations, or ground movements.
– PVC: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) conduits are composed of vinyl chloride polymerized into a rigid plastic. This rigidity, combined with a higher density (1.3 to 1.45 g/cm³), gives PVC its robust mechanical strength. PVC’s rigidity makes it suitable for applications where the conduit needs to provide strong support and maintain its shape under load.
4.1.2 Flexibility
– HDPE: The flexibility of HDPE conduits is a key advantage in many installations. HDPE can be coiled and bent without cracking, making it ideal for routing around obstacles and through curved pathways. This flexibility also allows HDPE conduits to absorb and distribute stress, reducing the risk of damage from ground movements or thermal expansion and contraction.
– PVC: PVC conduits are much more rigid and less flexible than HDPE. While this rigidity provides excellent structural support and protects cables from physical damage, it limits the ability to bend and maneuver the conduit without additional fittings. For installations requiring frequent changes in direction or navigating tight spaces, this can add complexity and cost.
4.1.3 Durability
– HDPE: HDPE conduits offer exceptional durability due to their resistance to environmental factors. They are impervious to many chemicals, including acids, bases, and organic solvents, which helps them maintain integrity in corrosive environments. HDPE’s UV resistance ensures that it does not degrade under prolonged exposure to sunlight, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
– PVC: PVC conduits are also durable, with good chemical resistance and the ability to withstand exposure to many environmental factors. However, PVC can become brittle at low temperatures, which can lead to cracking and breakage. This brittleness limits PVC’s use in extremely cold environments or applications with frequent temperature fluctuations.
4.2 What are the differences in installation and handling?
4.2.1 Installation Processes and Handling
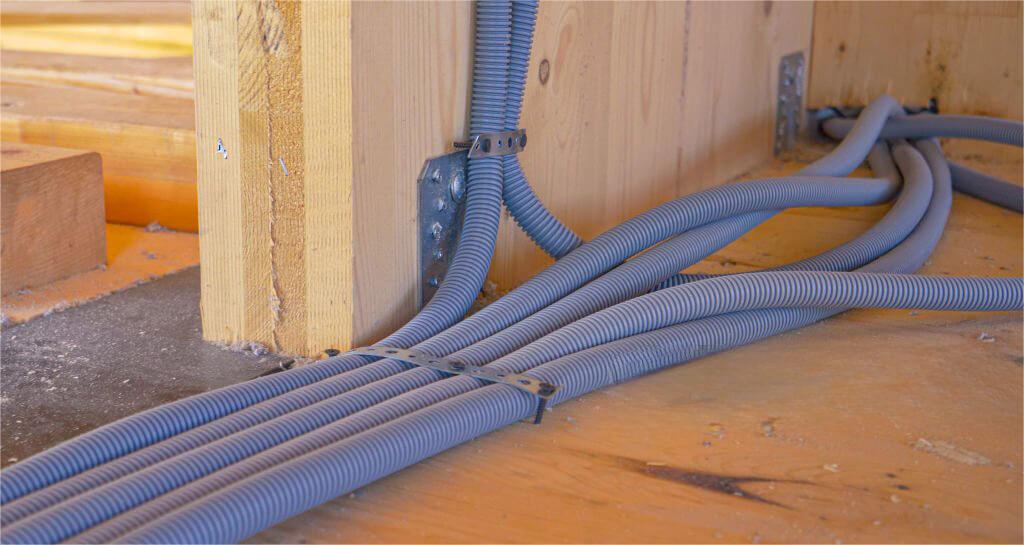
– HDPE Conduits: HDPE conduits are known for their flexibility and lightweight nature, which simplifies handling and installation. Installers typically cut HDPE conduits to length using standard tools and join sections either through heat fusion or mechanical fittings. Heat fusion creates seamless, leak-proof joints that are durable and resistant to environmental stresses. This method allows for the installation of long continuous lengths of conduit, minimizing potential failure points and optimizing installation efficiency.
– PVC Conduits: Installing PVC conduits requires more precise handling due to their rigidity compared to HDPE. The process involves cutting the conduits accurately and joining them using solvent welding or mechanical fittings. Solvent welding involves applying a solvent-based adhesive to the conduit ends and joining them, ensuring a strong, watertight bond. This method demands careful alignment and handling to achieve secure connections. The rigidity of PVC conduits necessitates the use of more fittings and connectors to navigate bends and turns, which adds complexity and time to the installation process.
4.2.2 Ease of Handling
– HDPE Conduits: Because of their lightweight and flexibility, HDPE conduits are easy to transport and maneuver around obstacles and through tight spaces. This attribute significantly reduces labor costs and speeds up installation times, making them particularly suitable for large-scale projects where efficiency is critical.
– PVC Conduits: Although more rigid than HDPE, PVC conduits are still manageable with proper handling techniques. However, their rigidity requires careful handling to prevent damage during installation. While they provide robust mechanical protection, maneuvering around obstacles can be more challenging compared to HDPE conduits.
4.3 How do HDPE and PVC conduits compare in cost?
4.3.1 Initial Costs
– HDPE: The initial cost of HDPE conduits is typically higher than that of PVC. This is due to the cost of raw materials and the specialized equipment required for heat fusion installations. However, the flexibility and lightweight nature of HDPE can offset some of these costs by reducing labor and installation time.
– PVC: PVC conduits are generally less expensive initially, making them a more budget-friendly option for projects with limited financial resources. The lower material cost and simpler installation process contribute to PVC’s cost advantage.
4.3.2 Long-Term Value
– HDPE: Despite the higher upfront cost, HDPE conduits often prove to be more cost-effective in the long run. Their durability, minimal maintenance needs, and extended lifespan contribute to significant savings over time. The reduced need for repairs and replacements, combined with the ease of installation, can result in lower overall costs.
– PVC: While PVC conduits offer good value initially, their long-term cost-effectiveness can be affected by environmental factors. In less demanding environments, PVC conduits perform well and require minimal maintenance. However, in harsher conditions, the potential for brittleness and damage can lead to higher maintenance and replacement costs over time.
4.3.3 Maintenance and Replacement Costs
– HDPE: HDPE conduits require minimal maintenance due to their resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and physical damage. Their durability ensures they remain functional for extended periods, minimizing the need for repairs or replacements. This contributes to lower long-term costs and greater overall value.
– PVC: PVC conduits may require more frequent maintenance in environments with low temperatures or significant chemical exposure. While they are generally durable, their rigidity and potential for brittleness can lead to increased repair and replacement needs, impacting long-term costs. Proper maintenance and careful handling are essential to ensure the longevity of PVC conduits.
4.4 What are the environmental impacts of HDPE and PVC conduits?
4.4.1 Sustainability and Recyclability
– HDPE: HDPE is highly recyclable, contributing to its environmental friendliness. Used HDPE products can be reprocessed into new items without significant loss of material properties. This recyclability promotes sustainability and reduces environmental impact by minimizing waste.
– PVC: PVC can also be recycled, but the process is more complex due to the presence of chlorine and other additives. Effective recycling of PVC requires specialized facilities to handle the material safely and minimize environmental harm. While PVC is recyclable, the process is less straightforward than that of HDPE.
4.4.2 Environmental Considerations in Production and Disposal
– HDPE: The production of HDPE involves fewer hazardous chemicals compared to PVC, resulting in a lower environmental impact. HDPE’s long lifespan and recyclability further enhance its environmental credentials. However, like all plastics, HDPE must be managed properly to prevent environmental pollution.
– PVC: The production of PVC uses chlorine and other chemicals, which can pose significant environmental risks if not properly controlled. Improper disposal or incineration of PVC can release harmful substances such as dioxins, making safe disposal and recycling practices essential to mitigate its environmental impact.
4.5 What factors should you consider when choosing between HDPE and PVC conduits?
When selecting the appropriate conduit, the specific application plays a pivotal role. Here are key considerations:
4.5.1 Type of Infrastructure
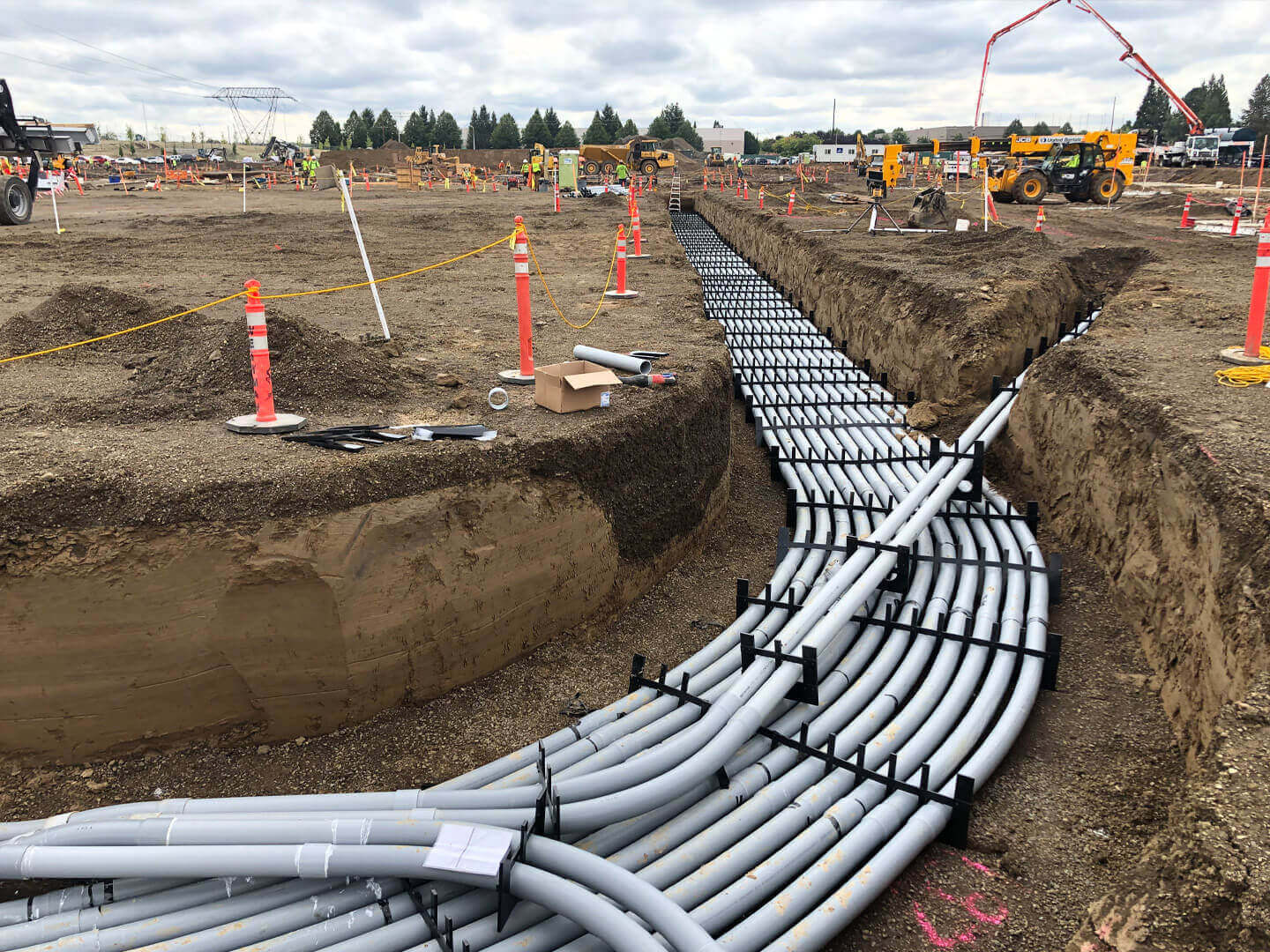
– Telecommunications: For protecting fiber optic cables, HDPE is often the conduit of choice due to its flexibility, allowing for smooth transitions and minimal signal interference. It can accommodate the installation of multiple cables in a single conduit without compromising performance.
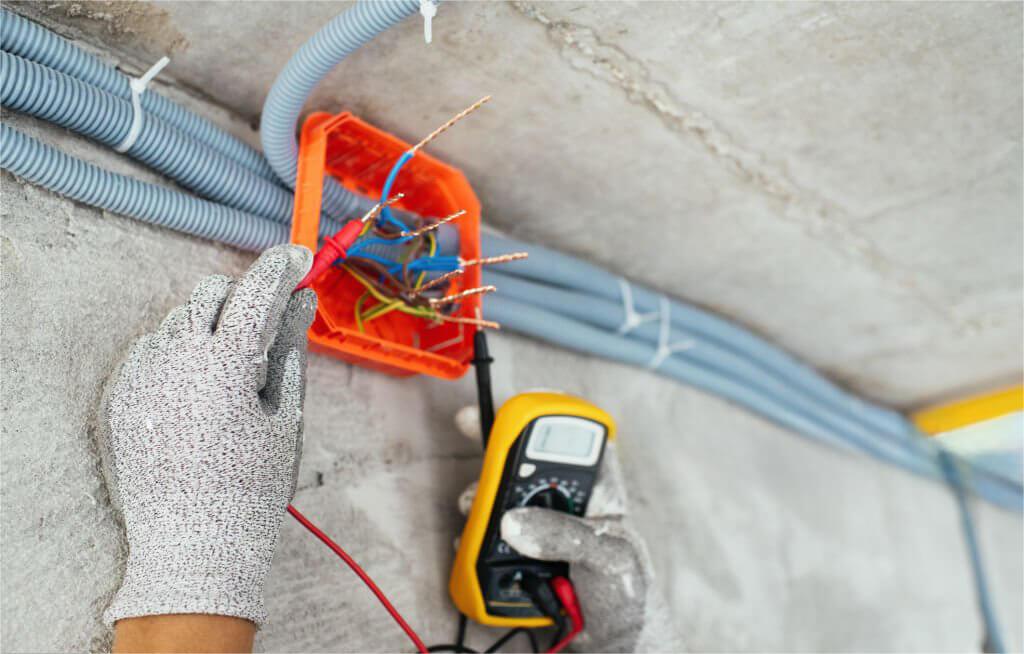
– Electrical Systems: PVC is commonly used in electrical systems, especially for indoor applications, due to its rigid structure that supports the weight of cables and prevents sagging over time. It’s essential for installations requiring strict adherence to fire safety codes.
4.5.2 Installation Environment
– Underground vs. Above Ground: HDPE is ideal for underground installations, where flexibility and resistance to ground movement are crucial. It can withstand soil pressure and shifting landscapes without compromising structural integrity. In contrast, PVC is often used above ground, where rigidity and structural support are paramount.
4.5.3 Environmental Conditions and Durability Needs
Understanding the environmental context is vital for ensuring the conduit’s long-term performance:
– Temperature Extremes:
– HDPE: This material maintains its integrity in a wide temperature range, from -40°F to 140°F (-40°C to 60°C). However, extreme heat can lead to softening, necessitating careful consideration for high-temperature applications.
– PVC: While suitable for moderate temperatures, PVC can become brittle in freezing conditions, risking cracks during installation or under stress. This sensitivity may limit its use in colder climates or unprotected outdoor settings.
– Chemical Exposure:
– HDPE: Known for its exceptional chemical resistance, HDPE is often used in environments with aggressive chemicals, such as chemical manufacturing plants or laboratories. Its non-corrosive nature ensures longevity and reliability in these demanding applications.
– PVC: Although PVC is resistant to many chemicals, it is not universally suitable for all chemical exposures. In environments with corrosive substances, such as certain industrial applications, HDPE is typically favored to prevent degradation and ensure system integrity.
– UV Exposure:
– HDPE: With inherent UV resistance, HDPE can withstand prolonged outdoor exposure without significant degradation. This property makes it ideal for applications in solar energy, telecommunications, and other outdoor infrastructure projects.
– PVC: While standard PVC can degrade under UV exposure, UV-resistant formulations are available. However, these options may come at a higher cost and still may not offer the same durability as HDPE in harsh outdoor environments.
4.5.4 Budget Constraints and Long-Term Investment
Budget considerations are essential in making conduit choices, impacting both initial and ongoing costs:
– Initial Costs:
– PVC: Generally, PVC conduits come with a lower initial purchase price, making them attractive for budget-conscious projects. This can be a significant advantage for large-scale installations where volume purchases can lead to substantial savings.
– HDPE: While HDPE conduits typically incur a higher initial cost, it’s essential to consider the potential for lower installation costs due to reduced labor time and fewer joints required in flexible installations.
– Long-Term Costs:
– HDPE: The upfront investment in HDPE conduits often pays off in the long run due to their durability, resulting in lower maintenance and replacement costs. This can lead to significant savings over the lifespan of the installation.
– PVC: PVC may require more frequent repairs or replacements, especially in challenging environments, which can escalate long-term expenses. It is crucial to factor in potential maintenance needs when making budgetary decisions.
– Maintenance Requirements:
– HDPE: With its low maintenance needs and high durability, HDPE conduits are often preferred for long-term projects, reducing lifecycle costs significantly. This reliability minimizes downtime and enhances system performance over time.
– PVC: While PVC conduits are generally low-maintenance, they may require more attention in environments prone to brittleness or chemical exposure. Planning for potential maintenance costs is critical when opting for PVC.
4.6 What do experts recommend for choosing HDPE or PVC conduits?
4.6.1 Insights from Industry Experts
Industry experts often provide invaluable insights when it comes to conduit selection based on specific application requirements:
4.6.2 Telecommunications and Data Networks
– Experts commonly advocate for HDPE due to its flexibility and durability in fiber optic installations. The ability of HDPE to protect delicate cables while accommodating ground movement makes it indispensable in these projects.
4.6.3 Electrical Systems in Buildings
– For indoor electrical systems, PVC is the favored option among experts due to its rigidity and structural support. PVC’s resistance to fire also aligns with safety regulations, making it a preferred choice for building applications.
4.6.4 Outdoor and Harsh Environments
– In settings where exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme weather is a concern, experts typically recommend HDPE. Its resistance to corrosion and UV degradation ensures reliable performance over time in challenging environments.
4.7 Certifications for HDPE and PVC Conduits
4.7.1 National Electrical Code (NEC)
– NEC Requirements: Both HDPE and PVC conduits comply with NEC standards, which are essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical installations. These standards cover aspects such as installation methods, maximum fill capacities, burial depths, and protection against physical damage.
4.7.2 ASTM Standards (American Society for Testing and Materials)
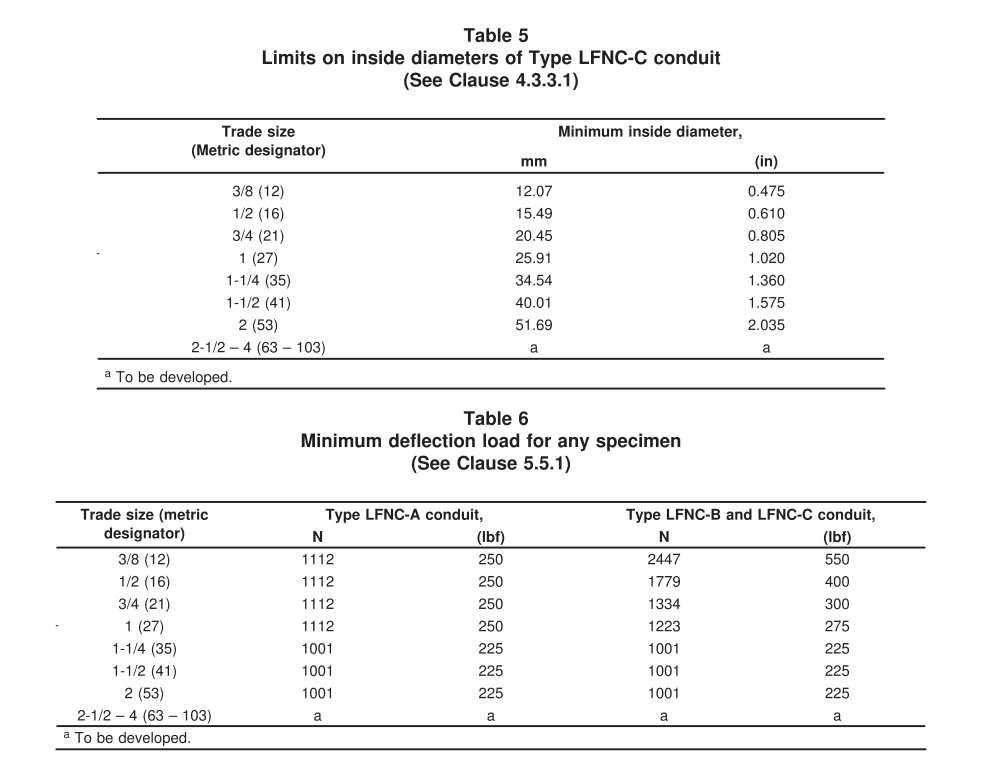
– ASTM F2160: This standard specifies requirements for solid-wall high-density polyethylene (HDPE) conduit based on controlled outside diameter. It covers material properties, dimensions, and performance criteria to ensure reliability and durability in underground and above-ground applications.
– ASTM F512: This standard covers rigid PVC conduit and fittings used for electrical installations. It defines material properties, dimensions, and performance criteria to ensure compliance with safety and performance requirements.
4.7.3 UL 651 (Underwriters Laboratories Standard 651)
– UL Listing: UL 651 covers PVC conduit, including Schedule 40, Schedule 80, Type EB. UL Listing ensures that these conduits meet specific safety and performance criteria such as fire resistance, impact resistance, and suitability for above-ground applications. HDPE conduit strictly adhere to industry standards such as UL 651A.
4.7.4 NEMA Standards (National Electrical Manufacturers Association)
– NEMA TC 7: This standard covers nonmetallic underground conduit with conductors, applicable to both HDPE and PVC conduits. It sets requirements for material specifications, dimensions, and installation practices to ensure safe and effective use in underground applications, including trenching and direct burial.
These certifications and standards collectively ensure that HDPE and PVC conduits are manufactured and installed to meet rigorous safety, performance, and durability requirements. Compliance with these standards is crucial for ensuring the integrity of electrical and communication systems in various applications, from residential to industrial settings.
5. Conclusion:Choosing the Right Conduit for Your Needs
In this article, we’ve explored the key differences between HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) and PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) conduits. HDPE conduits are highly flexible, impact-resistant, and well-suited for harsh environments and long-distance installations. In contrast, PVC conduits offer rigidity, durability, and ease of installation, making them ideal for above-ground and direct burial applications. Cost, longevity, and environmental impact are also important considerations when choosing the right conduit for your specific needs.
Selecting the appropriate conduit is crucial for the efficiency, safety, and longevity of your electrical installations. Assessing your project’s requirements and consulting with professionals can help you make an informed decision.
At Ctube, we are the leading and professional PVC conduit and fittings manufacturer in China. We specialize in the development and production of innovative PVC conduits and fittings for cable management and protection. Our main products include UL-listed PVC conduit pipes, solar conduit & fittings, halogen-free conduit & fittings, AS/NZS 2053, and British standard PVC conduit & fittings. We have passed certifications including UL, AS/NZS 2053, CSA, CE, ROHS, and IEC. We strive to deliver our products and services promptly and efficiently, ensuring top quality and reliability in all our offerings. Choose Ctube for your conduit needs and experience excellence in PVC conduit solutions.
To round out the shortcomings of pvc conduit that we mentioned above, Ctube’s photovoltaic solar series conduit is specially designed for outdoor UV environments. Enhanced with stabilizers, our conduit maintains durability and resists becoming brittle under prolonged exposure to UV rays. And Ctube’s low smoke halogen free products significantly improve fire safety by reducing smoke density and toxic emissions, ensuring better visibility and safer evacuation during a fire.
If you need personalized advice or a quote for your project, please contact us. We’re here to help you find the perfect solution for your conduit needs.
FAQ
1. Are HDPE conduits suitable for underground applications?
Yes, HDPE conduits are highly suitable for underground applications. They resist corrosion and can handle the physical stresses of being buried under soil or rock.
2. Are HDPE conduits more expensive than other types of conduits?
The cost of HDPE conduits can be higher than some alternatives like PVC, but they often provide better value over the long term due to their durability and reduced maintenance needs.
3. Can PVC conduit be used in underground applications?
Yes, certain types of PVC conduit, such as DB (Direct Burial), EB (Encased Burial) series, and Schedule 40 and 80, are designed specifically for underground use. However, ENT (Electrical Non-metallic Tubing) is not suitable for underground applications.
4. Is PVC conduit compatible with all types of electrical wiring?
PVC conduit is compatible with most types of electrical wiring, including THHN and THWN wires. It is essential to choose the appropriate size and type of conduit to match the specific wiring and application requirements.
Comparing HDPE vs. PVC Conduits: A Comprehensive Guide Read More »