Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction
An electrical conduit pipe is a protective tubing system designed to house and safeguard electrical wiring from mechanical damage, moisture, and environmental hazards. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and longevity of electrical installations by preventing exposure to elements that could lead to short circuits, fires, or other hazards. Electrical conduits come in various materials, including metal (such as steel, aluminum, and stainless steel) and non-metallic options like PVC, ENT, and fiberglass. Each type offers unique benefits suited for different applications, from residential wiring to industrial and underground installations.
In the following sections, this post will provide a detailed exploration of different conduit materials, their characteristics, advantages, and applications. By understanding these options, you can make an informed decision that best suits your project’s needs. We hope this guide helps you choose the right electrical conduit with confidence!
2. Understanding Conduit Standards: Ensuring Compliance and Safety
Before diving into the main discussion, we’d like to clarify an important aspect—conduit standards—to help readers better understand these regulations and make informed decisions when selecting the right conduit for their projects.
Electrical conduit standards are essential for ensuring safety, compatibility, and performance in electrical installations.
Globally, conduit standards vary based on regional requirements. In North America, the UL (Underwriters Laboratories), CSA (Canadian Standards Association), and establishes guidelines for conduit, tubing, and fittings, ensuring compliance with safety and performance regulations. While aligned with national codes, these standards also allow for adaptations based on climatic, infrastructural, and regulatory needs.
In contrast, IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards govern conduit systems in many European and international markets. AS/NZS Standard is comm0nly used in Australian and New Zealand. However, significant differences exist between North American, IEC and AS/NZS standards, particularly in conduit tests and system compatibility.
Understanding these differences is essential for ensuring electrical safety, regulatory compliance, and long-term system reliability. When selecting a conduit system, always verify that it meets the required national or international standards for your specific application.
3. Understanding Electrical Conduit Materials: Guide for Optimal Selection
Electrical conduits are broadly categorized by flexibility (rigid vs. flexible) and material composition (metallic vs. non-metallic), each serving distinct scenarios. And in the following section, we will make the detailed introduce based on the different material of electrical conduits.
3.1 Key Properties of Electrical Conduit Materials
Selecting the right electrical conduit material requires understanding the fundamental properties that influence its performance, installation, and long-term reliability.
Mechanical Strength & Durability: Electrical conduits are often installed in harsh environments where they must withstand physical impact, crushing forces, vibrations, and mechanical stress
Corrosion & Chemical Resistance: Conduits are often exposed to moisture, chemicals, and extreme weather conditions.
Electrical Conductivity & Grounding Benefits: Metallic conduits can serve as a grounding path, reducing the need for additional grounding conductors. Non-metallic conduits (PVC, HDPE) do not conduct electricity, requiring separate grounding systems.
Fire & Heat Resistance: Electrical conduits must comply with fire safety regulations to prevent flame spread and toxic emissions. Some materials, such as low-smoke halogen-free (LSZH) conduits, are specifically designed to reduce smoke and toxic gas release in fire incidents.
Weight & Ease of Installation: Heavy conduits require more labor, specialized tools, and increased support structures. Lightweight conduits are easier to transport, cut, and install, reducing labor costs.
Cost vs. Long-Term Value: While some materials have a lower upfront cost, others provide greater durability and require less maintenance over time. Cost considerations should include installation labor, maintenance, and lifespan.
3.2 Comparison of Common Electrical Conduit Materials and Types
Selecting the right electrical conduit material depends on various factors, including environmental conditions, mechanical requirements, electrical properties, and regulatory compliance.
Conduit materials fall into two main categories:
Metallic Conduits – Typically made from steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and bronze, available in both rigid and flexible types.
Non-Metallic Conduits – Made from PVC, HDPE, and RTRC (Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Conduit), PVC conduit also available in both rigid and flexible types.
In the following table, we provide some common conduit types.
| Category | Material | Common Types |
| Metallic Conduits | Steel | Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC), Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC), Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT),Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC), Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit (LFMC) |
| Aluminum | Rigid Aluminum Conduit (RAC), Flexible Aluminum Conduit,Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) | |
| Stainless Steel | Stainless Steel RMC & FMC,Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT), | |
| Bronze | Specialized applications | |
| Non-Metallic Conduits | PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | Rigid PVC Conduit (Schedule 40, Schedule 80, DB, EB, Type A), Flexible PVC Conduit (ENT) |
| LSZH (Low Smoke Haologen Free) | Rigid ConduitFlexible Corrugated Conduit | |
| HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) | Corrugated HDPE, Smoothwall HDPE | |
| RTRC (Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Conduit) | Rigid Fiberglass Conduit |


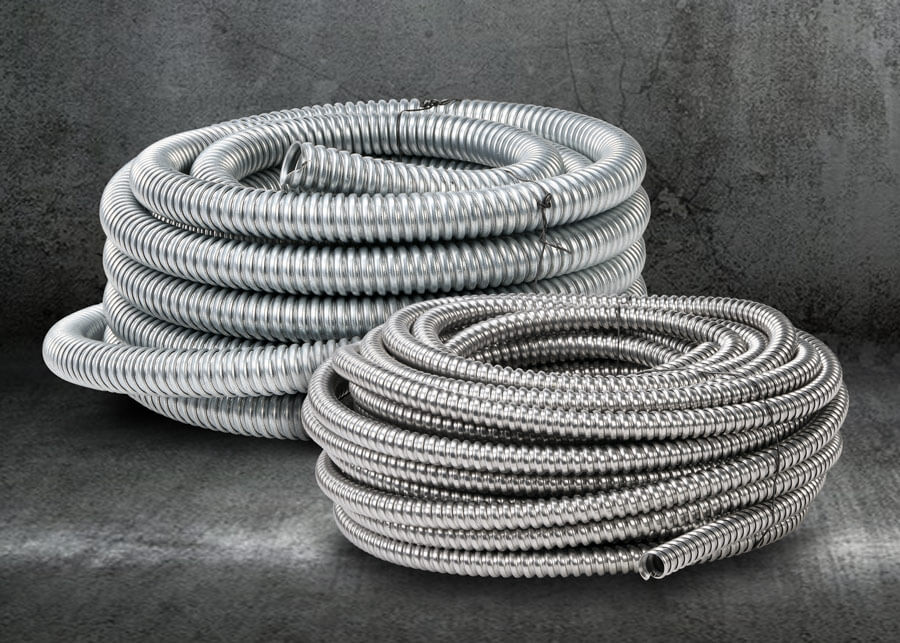
Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC): FMC is made of spiral-wound, interlocked steel or aluminum, providing moderate mechanical protection while allowing flexibility.
Stainless Steel FMC: For applications where standard galvanized steel is insufficient, stainless steel flexible conduit offers superior corrosion resistance in extreme environments.
Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit (LFMC): LFMC is a variant of FMC with an additional liquid-tight, non-metallic jacket, enhancing protection in wet and outdoor locations.
3.2.2 Conduit Types for Non-Metallic Material
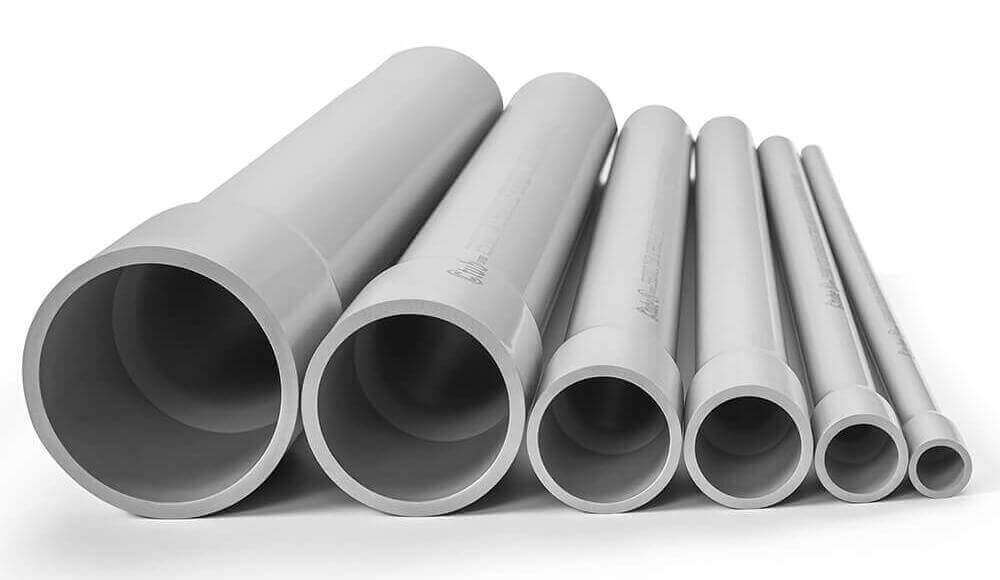
PVC Rigid Conduit: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the most widely used materials for rigid conduits. It is non-conductive, resistant to moisture and chemicals, and does not corrode, making it a preferred choice for both indoor and outdoor applications.
To help you better understand, we introduce some common conduit types used in the American market, all of which are UL-listed for safety and reliability. In this post we have published, we compare the differences between these conduits. Link here and you can learn more if you want.
Schedule 40 & Schedule 80 PVC Conduit: Schedule 40 is commonly used in residential and commercial applications, offering a balance of durability and ease of installation. Schedule 80 has thicker walls, providing extra mechanical protection and making it suitable for exposed installations and high-traffic areas.
DB (Direct Burial) & EB (Encased Burial) PVC Conduit: DB (Direct Burial) Conduit is designed to be buried directly underground without additional protective encasement. EB (Encased Burial) Conduit must be embedded in concrete.
Type A PVC Conduit: A lighter-weight option for specific building code requirements, often used where weight and flexibility are priorities.
Low Smoke Halogen-Free (LSZH) Conduits: LSZH Rigid and Coorugated conduits are specially designed for high-density environments where fire safety is a concern. Emit minimal smoke and no toxic halogen gases when exposed to fire, improving evacuation safety.
RTRC (Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Conduit): Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Conduit (RTRC), commonly referred to as fiberglass conduit, is designed for high-performance applications that require superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and extreme environments.
Flexible Non-Metallic Conduits: Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT) is a corrugated PVC conduit, designed for quick and easy installation in residential and light commercial buildings.
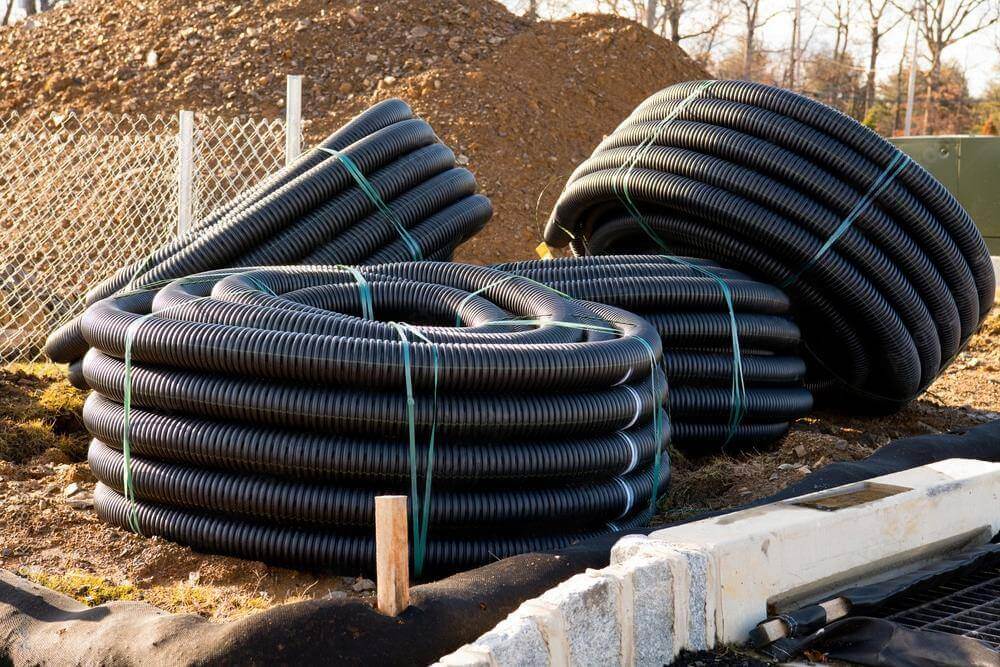
HDPE Conduit: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) corrugated and smoothwallconduit is engineered for underground duct banks, fiber optic networks, and telecommunication lines.
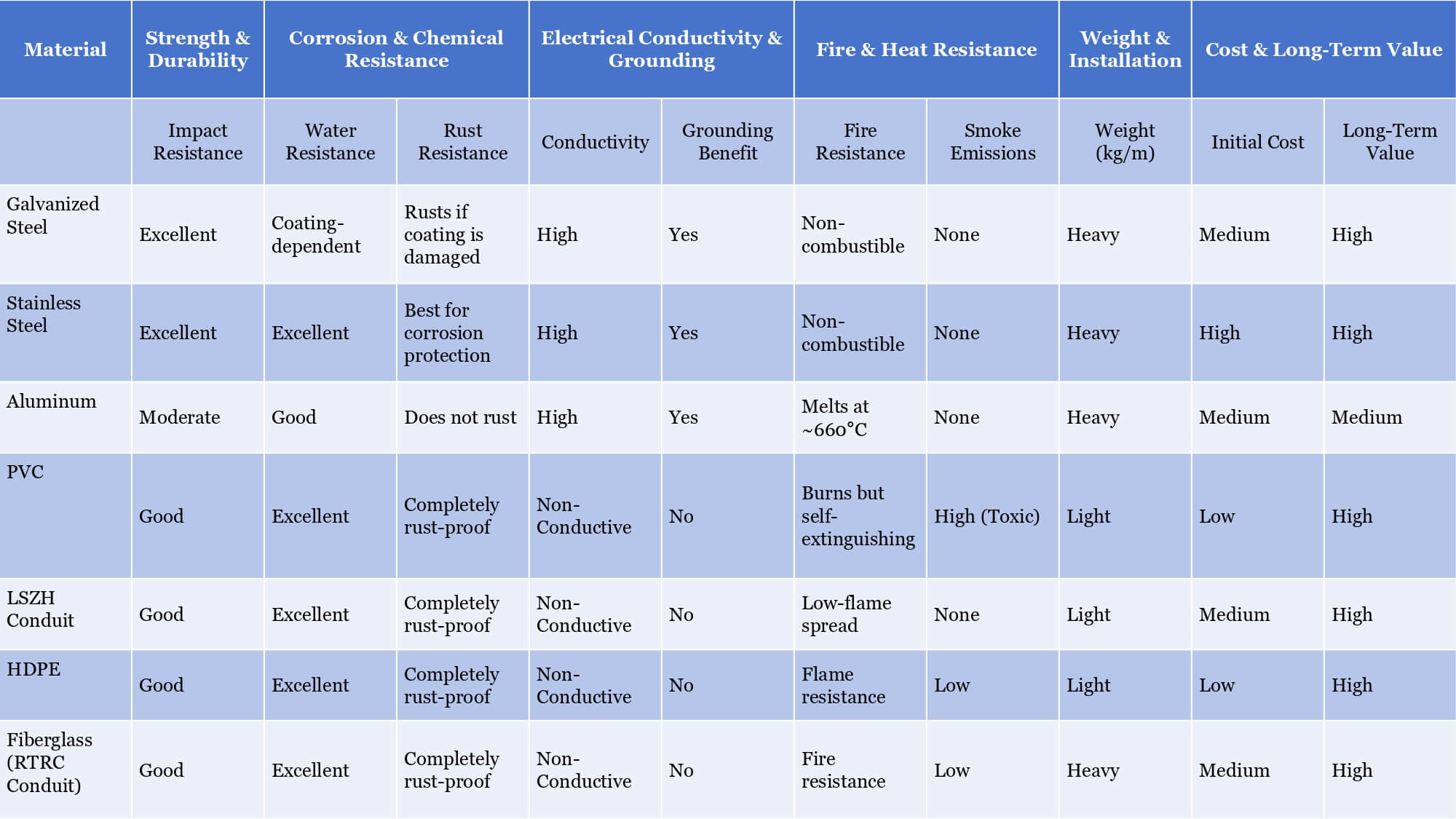
3.3 Detailed Comparison of Electrical Conduit Materials
To help readers make an informed decision, we will now combine the key properties of conduit in chapter 3.1 and conduit types in chapter 3.2 to make the comparison.
This comparison serves as a general reference to help readers understand the differences between various conduit materials and types. However, when purchasing conduit, it is essential to confirm specific technical specifications with the supplier.
Different manufacturers may produce products with slightly varying parameters due to material formulations, manufacturing processes, and industry standards.
As long as these variations fall within the acceptable tolerance range specified by the relevant standards, they are considered compliant.
Always verify the exact properties, such as wall thickness, impact resistance, temperature tolerance, and fire ratings, to ensure the conduit meets the specific needs of your project.
4. Applications of Different Electrical Conduit Materials
When selecting the right electrical conduit, various factors must be considered based on the installation environment, project type, and specific functional requirements. To make it easier for readers to understand, we categorize conduit materials using the following key criteria:
Installation Environment: Whether the conduit will be installed indoors or outdoors, above ground or underground, determines the need for durability, corrosion resistance, and weatherproofing.
Project Type: Different sectors—residential, commercial, industrial, and public infrastructure—have unique demands based on safety standards, load requirements, and environmental exposure.
Material Properties: Strength, corrosion resistance, flexibility, fire resistance, and conductivity play crucial roles in determining the suitability of a conduit material.
With these factors in mind, let’s explore how different electrical conduit materials are applied in real-world scenarios.
4.1 Indoor vs. Outdoor Applications
Electrical conduit selection depends on environmental exposure. Indoor conduits are typically installed within walls, ceilings, or floors, where they are shielded from harsh environmental conditions. And therefore, indoor environments prioritize ease of installation, fire safety, and flexibility.
Outdoor installations face greater exposure to environmental stressors, requiring conduits that can withstand UV radiation, moisture, temperature variations, and physical impact.
4.4.1 Indoor Applications: Prioritizing Safety & Ease of Installation
Fire Safety Compliance: Conduits must meet fire resistance standards to prevent smoke and toxic emissions in enclosed spaces. LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) conduits are essential for high-density areas like offices, hospitals, and transit hubs.
Installation Flexibility: In complex wiring layouts, lightweight and easily bendable materials like ENT (Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing) or FMC (Flexible Metal Conduit) simplify routing.
Minimal Mechanical Stress Requirements: Indoor conduits generally do not face extreme impact or crushing forces, allowing for thinner-walled options like EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) in commercial spaces.
4.4.2 Outdoor Applications: Durability Against Weather & Impact
UV & Weather Resistance: Sunlight can degrade plastic-based conduits, necessitating UV-stabilized PVC (Schedule 40/80) or corrosion-resistant metals like aluminum for exposed areas.
Moisture & Corrosion Protection: LFMC (Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit) and stainless steel conduits provide superior moisture resistance for wet environments.
Impact Resistance: RMC (Rigid Metal Conduit) and IMC (Intermediate Metal Conduit) offer high-strength protection for exposed wiring near roads, industrial sites, or outdoor structures.
Temperature Stability: Extreme climates require materials that resist expansion/contraction, such as RTRC (Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Conduit), which maintains performance in freezing or high-heat conditions.
4.2 Above-Ground vs. Underground Applications
Electrical conduits must be selected based on their placement, as above-ground and underground installations face different environmental conditions and physical stress factors.
4.2.1 Above-Ground Applications: Exposure to External Elements
Conduits installed above ground are often mounted on walls, ceilings, utility poles, or exposed structural frameworks.
UV Radiation & Weathering: Sunlight exposure can degrade plastic conduits over time, requiring UV-resistant PVC (Schedule 40/80) or corrosion-resistant metals like aluminum and stainless steel for longevity.
Mechanical Protection: In public areas, conduits may face accidental impact, requiring rigid metal options like RMC (Rigid Metal Conduit) or IMC (Intermediate Metal Conduit) to prevent damage.
Thermal Expansion & Contraction: Outdoor temperature fluctuations can cause expansion/contraction in plastic conduits. RTRC (Fiberglass Conduit) resists deformation in extreme climates.
4.2.2 Underground Applications: Protection Against Moisture, Pressure & Corrosion
Conduits buried underground must endure soil pressure, moisture exposure, and potential chemical degradation. Depending on installation depth and load conditions, the following factors are critical.
Crush Resistance: Underground conduits must resist soil and traffic loads, with RMC, DB PVC, and RTRC offering the highest compression strength.
Water & Corrosion Resistance: PVC (DB & EB series), HDPE, and fiberglass conduits are preferred for their resistance to underground moisture and chemicals. Stainless steel is sometimes used for extreme conditions.
Ease of Installation: Long, flexible conduits like HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) allow for trenchless installations, reducing labor costs in large projects.
Direct Burial vs. Encased Installation: Some conduits (e.g., DB PVC, HDPE) are designed for direct burial, while others (e.g., EB-PVC) require encasement in concrete for added protection.
4.3 Residential vs. Commercial vs. Industrial Applications
Electrical conduit selection varies significantly depending on the scale of the project, environmental conditions, and regulatory requirements.
4.3.1 Residential Applications: Prioritizing Cost, Flexibility & Safety
In residential buildings, conduit installations are generally indoor, concealed within walls, ceilings, or underground. The requirements are similar with indoor applications, what we have mentioned above.
4.3.2 Commercial Applications: Balancing Safety, Compliance & Durability
Commercial buildings have more extensive electrical systems than residences, requiring conduits that comply with strict codes, offer high durability, and support large-scale electrical networks.
Fire Safety Compliance: In office buildings, malls, and hotels, fire-resistant conduits like LSZH, EMT, and RMC are preferred.
Ease of Maintenance & Modifications: Large commercial spaces may need frequent electrical upgrades, making EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) a common choice due to its ease of bending and installation.
Mechanical Protection: Public spaces require durable conduits like IMC and RMC to protect electrical wiring from physical damage.
4.3.3 Industrial Applications: Heavy-Duty Protection & Extreme Conditions
Industrial settings involve high power loads, extreme temperatures, heavy machinery, and exposure to corrosive substances
Maximum Mechanical Strength: Factories and plants require RMC, IMC, or stainless steel conduits to withstand mechanical impacts.
Corrosion & Chemical Resistance: Facilities like oil refineries and chemical plants use stainless steel, aluminum, and RTRC fiberglass conduits for longevity.
Moisture & Temperature Resistance: Industries with extreme heat or moisture, such as marine applications, benefit from LFMC (Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit) and RTRC.
Explosion-Proof & Hazardous Location Compliance: Class 1, Division 1 hazardous locations (e.g., petrochemical plants) require explosion-proof conduit systems.
5. How to Select a Reliable Electrical Conduit and Material Supplier
As a professional supplier specializing in non-metallic PVC and LSZH conduit, we understand the importance of choosing a qualified and reliable supplier to ensure safety, compliance, and long-term performance. In the next section, we will provide key insights into selecting the right supplier, including essential certifications, quality assurance practices, and supplier evaluation criteria.
5.1 Verifying Supplier Certifications & Documentation
To ensure product reliability, it is essential to request official documentation and verify the supplier’s claims.
Check Certification Numbers – UL, CSA, and IEC certifications can be verified on the issuing organization’s official website.
Request Factory Test Reports – Reliable suppliers provide batch test results confirming product compliance with industry standards.
Look for Third-Party Audits – Regular independent inspections by SGS or TÜV indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality.
Compare Certifications Across Suppliers – Some manufacturers self-certify their products, but third-party verification is more reliable.
Request Product Samples – Testing a sample before bulk purchasing ensures the conduit meets performance expectations.
5.2 Factory Inspection & Quality Control Measures
Before selecting a supplier, factory inspections and audits are essential. A well-managed factory with strict quality control procedures ensures that the conduit products are consistently manufactured to specification. Key factors to assess include:
5.2.1 Raw Material Sourcing & Testing
PVC Conduits: Must be made from virgin PVC resin to ensure high impact strength and fire resistance.
Metal Conduits: Should use galvanized steel, stainless steel, or aluminum for corrosion protection.
Verification: Ask for raw material test reports confirming compliance with ASTM or IEC standards.
5.2.2 Manufacturing Process & Dimensional Accuracy
Conduit Wall Thickness: Check if the conduit meets UL or ASTM thickness standards.
Bending & Impact Resistance: Evaluate if the material withstands mechanical stress without cracking.
5.2.3 Fire Testing & Thermal Stability
LSZH Conduits: Must pass low smoke emission and halogen-free toxicity tests.
Flame Retardancy: PVC conduits should be self-extinguishing (V0 fire rating).
5.2.4 Electrical Performance Testing
Dielectric Strength: Ensures non-metallic conduits insulate electrical wiring properly.
Grounding & Conductivity Tests: Essential for metal conduits used in grounding applications.
5.2.5 Long-Term Performance & UV Stability
UV Resistance: Outdoor conduits should pass ISO 4892 or other UV exposure tests.
Corrosion Resistance: Metal conduits should have a protective zinc coating or anodized finish.
5.2 Essential Product Certifications for Electrical Conduits
UL (Underwriters Laboratories) develops safety standards for electrical products, including conduits, fittings, and support hardware. These standards help ensure compliance with fire, mechanical, and environmental requirements. Below is an overview of key UL standards categorized by material for your reference.
| Metal Conduit Standards | UL 1 – Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC) UL 6 – Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC) – Steel UL 6A – Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC) – Aluminum and Stainless Steel UL 1242 – Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC) – Steel UL 360 – Liquid-Tight Flexible Metal Conduit (LFMC) |
| Nonmetallic Conduit Standards | UL 651 – Schedule 40 and 80 Rigid PVC Conduit and Fittings UL 651A – High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Conduit UL 1660 – Liquid-Tight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit (LFNC) UL 1990 – Nonmetallic Underground HDPE Conduit with Conductors |
| Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Conduit (RTRC) Standards | UL 2515 – Aboveground RTRC Conduit and Fittings UL 2420 – Belowground RTRC Conduit and Fittings UL 2515A – Extra Heavy Wall RTRC and Fittings |
| Fittings, Supports, and Accessories | UL 514B – Conduit, Tubing, and Cable Fittings UL 2239 – Hardware for the Support of Conduit, Tubing, and Cable |
6. Conclusion